Unveiling the Tapestry of the United States: A Comprehensive Look at the Physical Map
Related Articles: Unveiling the Tapestry of the United States: A Comprehensive Look at the Physical Map
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Tapestry of the United States: A Comprehensive Look at the Physical Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Tapestry of the United States: A Comprehensive Look at the Physical Map
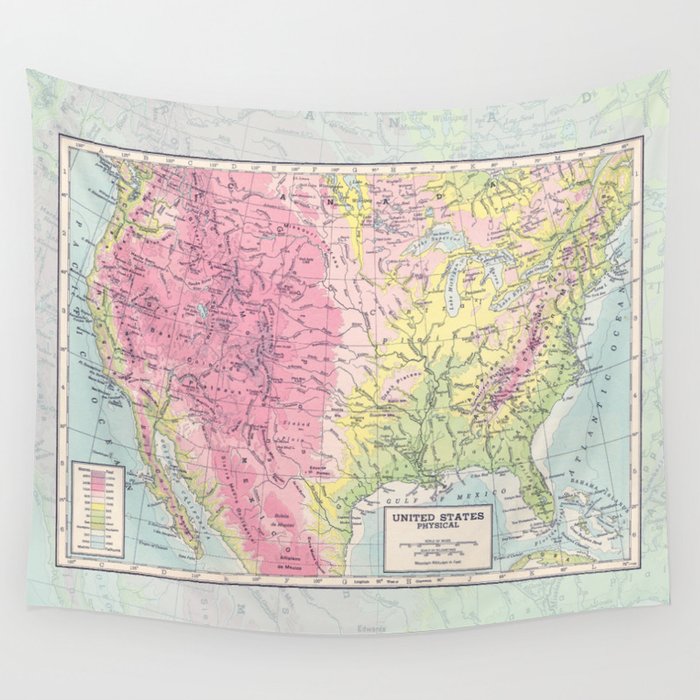
The United States, a vast and diverse nation, possesses a landscape as intricate and captivating as its history. Its physical geography, a mosaic of mountains, valleys, rivers, and coastlines, has profoundly shaped its development, culture, and identity. Understanding the physical map of the United States is essential for appreciating the interconnectedness of its natural features, the challenges they present, and the opportunities they provide.
A Land of Contrasts: Geographic Regions and Their Defining Features
The United States is broadly divided into ten distinct geographic regions, each with its own unique set of physical characteristics:
-
The Appalachian Mountains: This ancient mountain range, stretching from Alabama to Maine, is characterized by rolling hills, deep valleys, and fertile plateaus. The Appalachian Mountains are rich in natural resources, including coal, timber, and natural gas, and have played a significant role in the nation’s economic development.
-
The Atlantic Coastal Plain: This flat, low-lying region extends from the Appalachian Mountains to the Atlantic Ocean. Its fertile soil and proximity to the sea have made it a center of agriculture, fishing, and maritime trade. The region is also home to numerous coastal cities, including Boston, New York City, and Washington, D.C.
-
The Interior Lowlands: This vast, flat region, encompassing the Great Plains and the Midwest, is known for its fertile soil, abundant rainfall, and extensive agricultural production. The Interior Lowlands are also home to major rivers, including the Mississippi, Missouri, and Ohio, which have facilitated transportation and trade throughout the nation’s history.
-
The Great Plains: This semi-arid region, stretching from the Mississippi River to the Rocky Mountains, is characterized by vast grasslands and a dry, continental climate. The Great Plains are a major agricultural region, known for wheat, cattle ranching, and wind energy production.
-
The Rocky Mountains: This majestic mountain range, running from Canada to Mexico, is a spine of towering peaks, deep canyons, and rugged terrain. The Rocky Mountains are a popular destination for outdoor recreation, including skiing, hiking, and camping, and are rich in mineral resources.
-
The Intermountain West: This arid region, located between the Rocky Mountains and the Sierra Nevada, is a mosaic of deserts, plateaus, and mountain ranges. The Intermountain West is home to the Great Basin, a unique ecosystem characterized by its internal drainage, and is a major source of geothermal energy.
-
The Pacific Coast Ranges: This series of mountain ranges, extending from California to Alaska, is characterized by steep slopes, deep canyons, and lush forests. The Pacific Coast Ranges are home to some of the most spectacular scenery in the United States, including the Redwood National Park and the Olympic Mountains.
-
The Pacific Coastal Plain: This narrow coastal region, extending from the Pacific Coast Ranges to the Pacific Ocean, is known for its mild climate, fertile soil, and abundant rainfall. The Pacific Coastal Plain is a major agricultural region, known for fruits, vegetables, and wine production.
-
The Alaska Range: This massive mountain range, located in south-central Alaska, is home to Denali, the highest peak in North America. The Alaska Range is a rugged and remote region, known for its glaciers, wildlife, and breathtaking scenery.
-
The Hawaiian Islands: This volcanic archipelago, located in the central Pacific Ocean, is a unique and diverse ecosystem, characterized by its tropical climate, volcanic landscapes, and diverse flora and fauna. The Hawaiian Islands are a popular tourist destination, known for their beaches, surfing, and volcanic scenery.
The Significance of the Physical Map: Understanding the Interplay of Nature and Human Activity
The physical map of the United States is not just a collection of geographic features; it is a living tapestry that reveals the intricate interplay between nature and human activity. The map helps us understand:
-
The distribution of natural resources: The map highlights the location of key resources, such as coal, oil, natural gas, timber, and minerals. This information is crucial for economic development, energy production, and environmental management.
-
The patterns of climate and weather: The map reveals the diverse climate zones of the United States, from the arid deserts of the Southwest to the humid forests of the Southeast. Understanding these patterns is essential for agriculture, transportation, and disaster preparedness.
-
The importance of water resources: The map shows the major rivers, lakes, and aquifers of the United States. These water resources are essential for drinking water, irrigation, and transportation, and their management is crucial for sustainable development.
-
The challenges of natural hazards: The map identifies areas prone to natural disasters, such as earthquakes, hurricanes, floods, and wildfires. This information is vital for disaster preparedness, mitigation, and response.
-
The opportunities for recreation and tourism: The map showcases the nation’s natural beauty, from its majestic mountains to its pristine beaches. These natural attractions are a source of economic activity and a source of inspiration for millions of Americans.
FAQs about the Physical Map of the United States
Q: What are the major mountain ranges in the United States?
A: The major mountain ranges in the United States include the Appalachian Mountains, the Rocky Mountains, the Sierra Nevada, the Cascade Range, and the Alaska Range.
Q: What are the major rivers in the United States?
A: The major rivers in the United States include the Mississippi River, the Missouri River, the Ohio River, the Colorado River, the Rio Grande, and the Columbia River.
Q: What are the major climate zones in the United States?
A: The major climate zones in the United States include the humid subtropical climate, the humid continental climate, the semi-arid climate, the arid climate, and the tundra climate.
Q: What are some of the major natural hazards in the United States?
A: The major natural hazards in the United States include earthquakes, hurricanes, tornadoes, floods, wildfires, and volcanic eruptions.
Q: How does the physical map of the United States influence its culture and identity?
A: The physical map of the United States has profoundly shaped its culture and identity. The nation’s diverse landscapes have inspired its literature, art, music, and folklore. The challenges presented by its physical geography have fostered resilience, ingenuity, and a spirit of adventure.
Tips for Understanding the Physical Map of the United States
- Use a variety of resources: Explore physical maps, atlases, online tools, and educational videos to gain a comprehensive understanding of the nation’s geography.
- Focus on the key features: Identify the major mountain ranges, rivers, lakes, and climate zones.
- Connect the physical features to human activities: Consider how the geography influences agriculture, transportation, energy production, and recreation.
- Explore specific regions: Delve into the unique physical characteristics and cultural aspects of each geographic region.
- Engage with the map actively: Trace the major rivers, locate key cities, and identify areas prone to natural hazards.
Conclusion
The physical map of the United States is a powerful tool for understanding the nation’s natural heritage, its economic development, and its cultural identity. By examining the intricate tapestry of its mountains, valleys, rivers, and coastlines, we gain a deeper appreciation for the forces that have shaped this vast and diverse nation. The map serves as a reminder of the interconnectedness of nature and human activity, and underscores the importance of responsible stewardship of our planet’s resources.



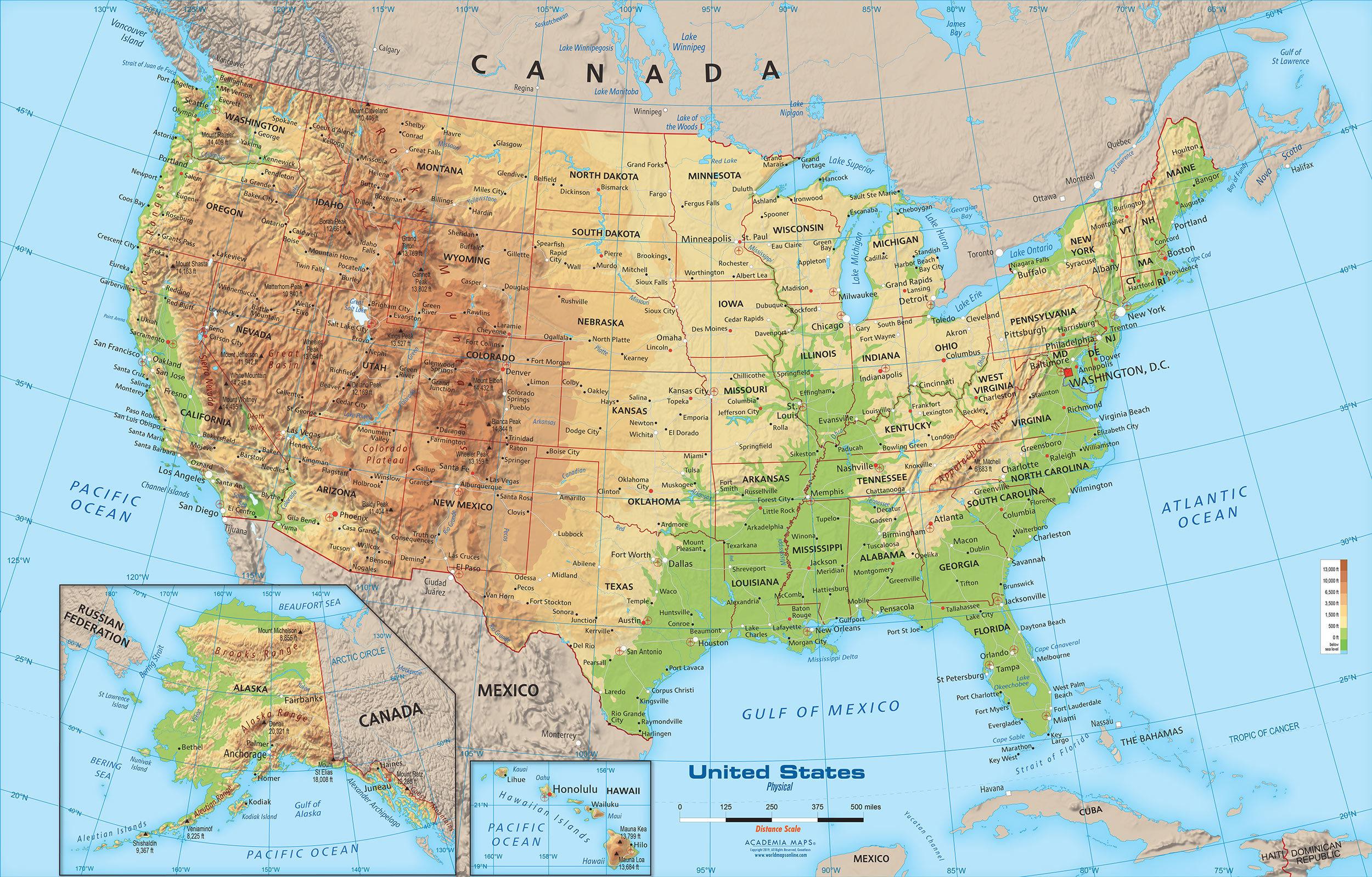
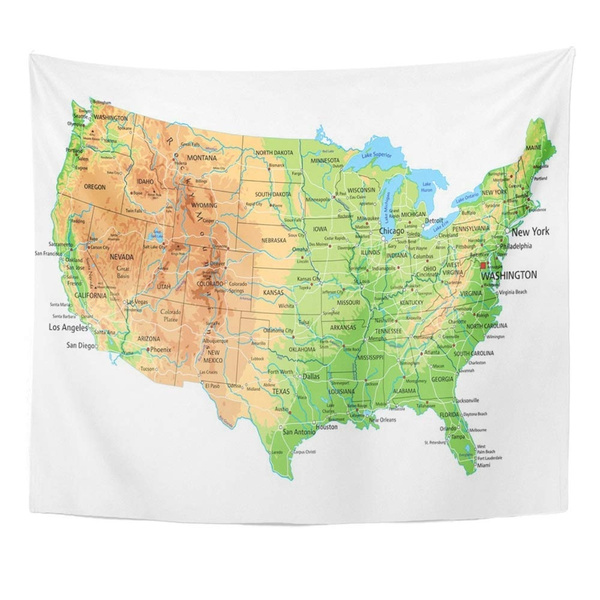


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Tapestry of the United States: A Comprehensive Look at the Physical Map. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!