Unveiling the Power of Visual Data Analysis: A Comprehensive Guide to Heat Map Tools
Related Articles: Unveiling the Power of Visual Data Analysis: A Comprehensive Guide to Heat Map Tools
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Power of Visual Data Analysis: A Comprehensive Guide to Heat Map Tools. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Power of Visual Data Analysis: A Comprehensive Guide to Heat Map Tools
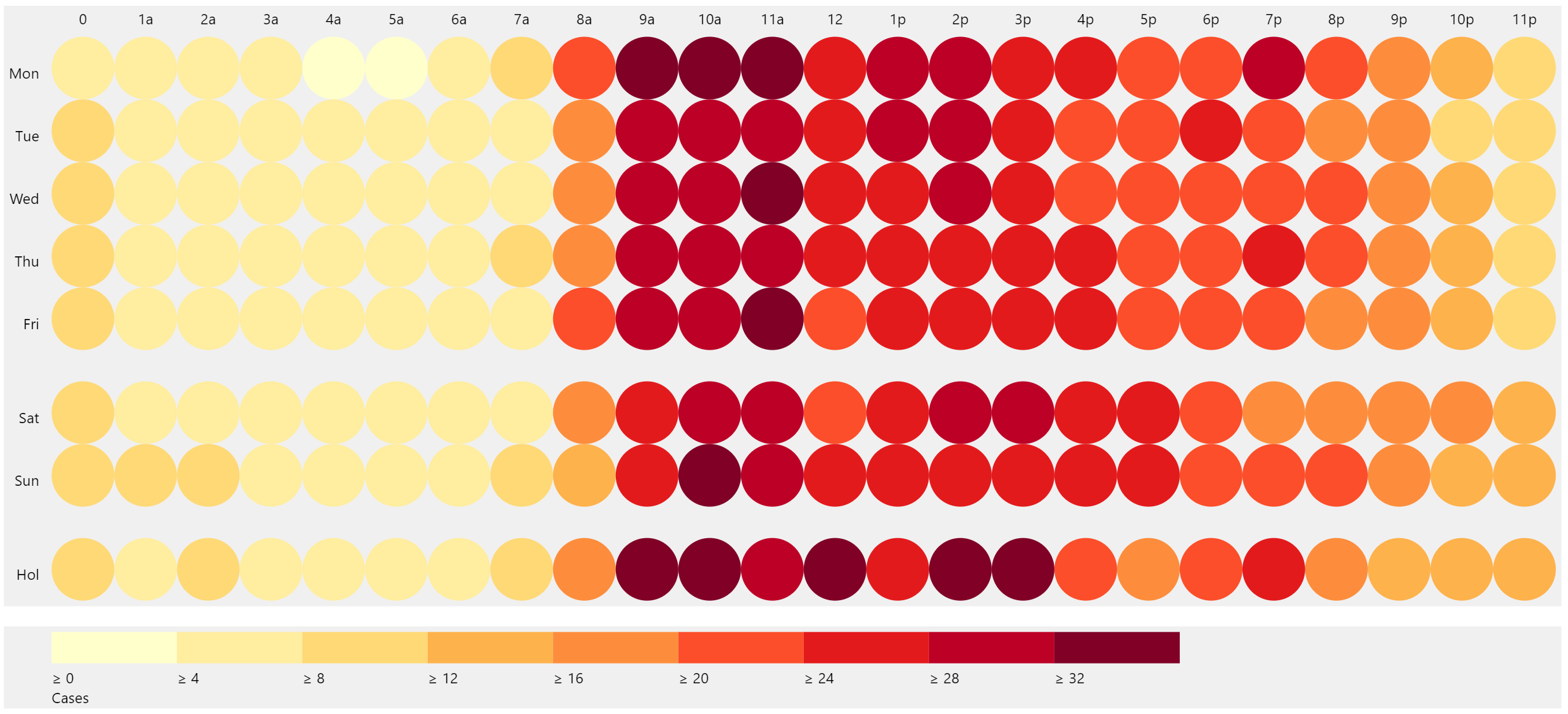
Heat maps are powerful visual representations of data, using color gradients to depict the intensity or density of a particular variable across a defined space. This technique transforms complex datasets into easily digestible, insightful visuals, facilitating quicker understanding and more effective decision-making across diverse fields. This exploration delves into the functionality, applications, and benefits of these tools, offering a comprehensive understanding of their capabilities.
Understanding the Mechanics of Heat Map Generation
The foundation of any heat map lies in the data it visualizes. This data typically represents a measurement or count associated with specific locations or points within a defined area. The area itself can take many forms, from a geographical region to a website layout, a product image, or even a complex network diagram. The tool then processes this data, assigning a color to each data point based on its value. Higher values are typically represented by warmer colors (reds, oranges), while lower values are shown using cooler colors (blues, greens). The resulting visual gradient allows for immediate identification of areas of high and low concentration, revealing patterns and trends that might otherwise remain hidden within raw numerical data.
Diverse Applications Across Industries
The versatility of these tools extends across numerous sectors. In website analytics, they pinpoint areas of high user engagement or frustration on web pages, informing design improvements and user experience optimization. Marketing departments leverage them to analyze campaign performance, identifying geographic regions with high conversion rates or specific demographics showing strong interest in particular products or services. In the realm of business intelligence, these visualizations can illuminate sales trends, identifying high-performing products or geographic areas requiring additional attention.
Within the manufacturing sector, these tools are used to analyze production processes, identifying bottlenecks or areas prone to defects. Supply chain management benefits from the ability to visualize delivery times and logistical efficiency, highlighting areas needing optimization. Even in healthcare, these visual representations can assist in analyzing patient data, revealing geographical clusters of disease outbreaks or identifying areas with high concentrations of specific medical conditions.
Key Features and Capabilities of Modern Heat Map Tools
Sophisticated software packages offer a range of features that enhance the utility of these visualizations. Many tools allow for the customization of color palettes, ensuring optimal clarity and readability for specific datasets. Interactive capabilities allow users to drill down into specific data points, obtaining detailed information about individual locations or values. Data filtering and sorting options enable users to focus on specific subsets of the data, facilitating a more focused analysis. The ability to overlay multiple datasets onto a single map allows for the simultaneous visualization of different variables, revealing complex relationships and correlations. Furthermore, many tools offer export options, allowing users to share their findings in various formats, such as images, reports, or presentations.
Benefits of Utilizing Heat Map Tools for Data Analysis
The advantages of using these tools are multifaceted. Their intuitive visual nature makes complex data easily understandable, even for individuals without extensive statistical expertise. This improved accessibility facilitates quicker identification of trends and patterns, accelerating the decision-making process. The ability to quickly identify areas of high and low concentration allows for the prioritization of resources and efforts, leading to improved efficiency and cost savings. By highlighting areas requiring attention, these tools can proactively identify potential problems or opportunities, enabling timely intervention and strategic planning. Moreover, the visual nature of the output makes it easier to communicate complex findings to stakeholders, fostering better collaboration and understanding.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What types of data can be visualized using heat maps? A wide range of quantitative data can be represented, including counts, frequencies, averages, percentages, and other numerical measurements.
-
What software packages are available for creating heat maps? Numerous software packages exist, ranging from standalone applications to plugins for spreadsheet software and data visualization platforms. Many offer free versions with limited functionality, while more advanced features are typically available in paid versions.
-
How can the accuracy of a heat map be ensured? Accuracy relies on the quality and completeness of the underlying data. Careful data cleaning and validation are essential to minimize errors and ensure the reliability of the resulting visualization.
-
What are the limitations of heat maps? While powerful, they may not be suitable for all types of data analysis. They are most effective when visualizing data with a spatial or geographical component. Overly complex datasets with numerous variables might require more sophisticated analytical techniques.
-
Can heat maps be used for predictive analysis? While not directly predictive, they can reveal patterns and trends that can inform predictive models. By identifying areas of high concentration or activity, they can help to pinpoint areas requiring further investigation or targeted interventions.
Tips for Effective Heat Map Creation and Interpretation
-
Clearly define the objective: Establish the specific question or problem that the heat map aims to address.
-
Select appropriate data: Ensure the data is relevant, accurate, and representative of the population or area of interest.
-
Choose a suitable color palette: Select a color scheme that is both visually appealing and effectively conveys the data’s range.
-
Consider the scale and resolution: The scale and resolution should be appropriate for the data and the intended audience.
-
Annotate the map: Include labels, legends, and other annotations to enhance clarity and understanding.
-
Interpret cautiously: Avoid over-interpreting the results. Consider potential confounding factors and limitations of the data.
Conclusion
Heat maps provide a powerful and versatile method for visualizing and interpreting complex datasets. Their ability to transform numerical data into readily understandable visual representations makes them an invaluable tool across a wide spectrum of disciplines. By carefully considering the data, selecting appropriate software, and interpreting the results thoughtfully, these tools can unlock significant insights, driving more informed decision-making and ultimately, improved outcomes. The continued development of these tools and their increasing accessibility promise to further enhance their role in data analysis and visualization in the years to come.


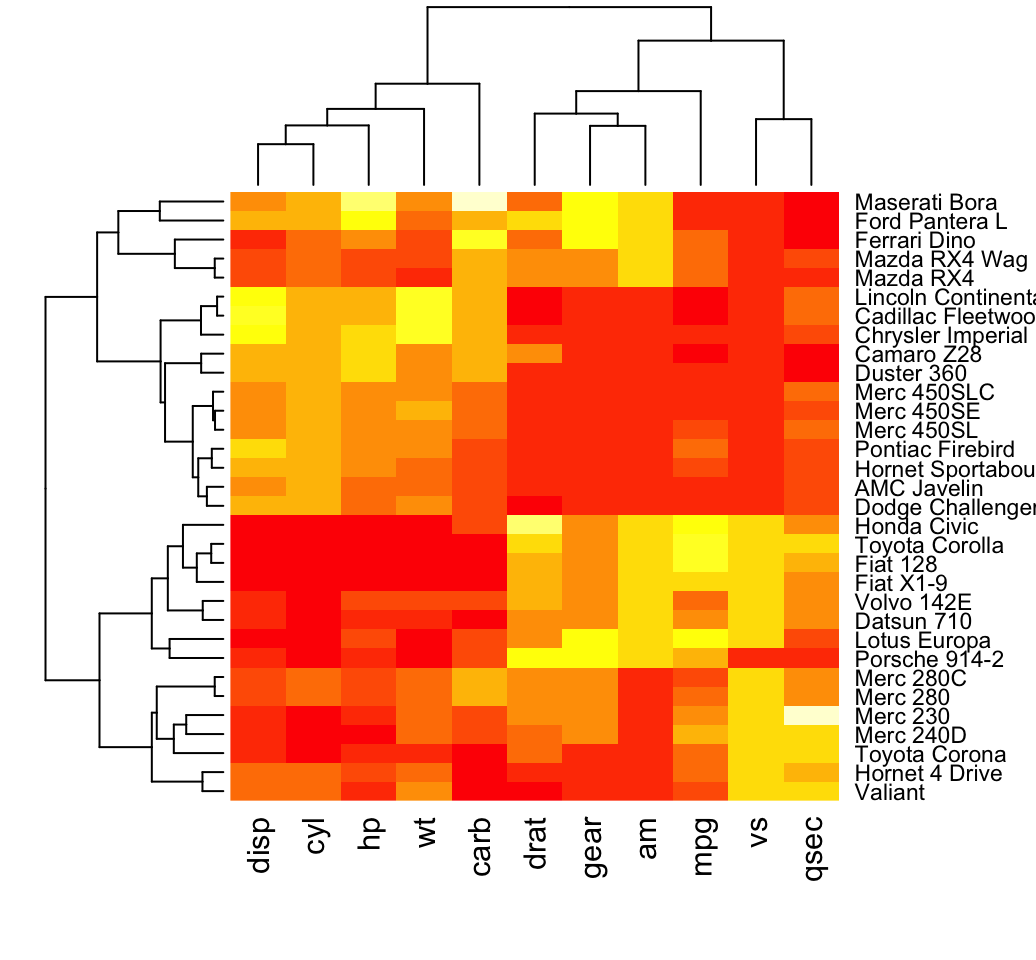





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Power of Visual Data Analysis: A Comprehensive Guide to Heat Map Tools. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!