Unveiling the Foundation of Geographic Information: Understanding Map Units
Related Articles: Unveiling the Foundation of Geographic Information: Understanding Map Units
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Foundation of Geographic Information: Understanding Map Units. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Foundation of Geographic Information: Understanding Map Units

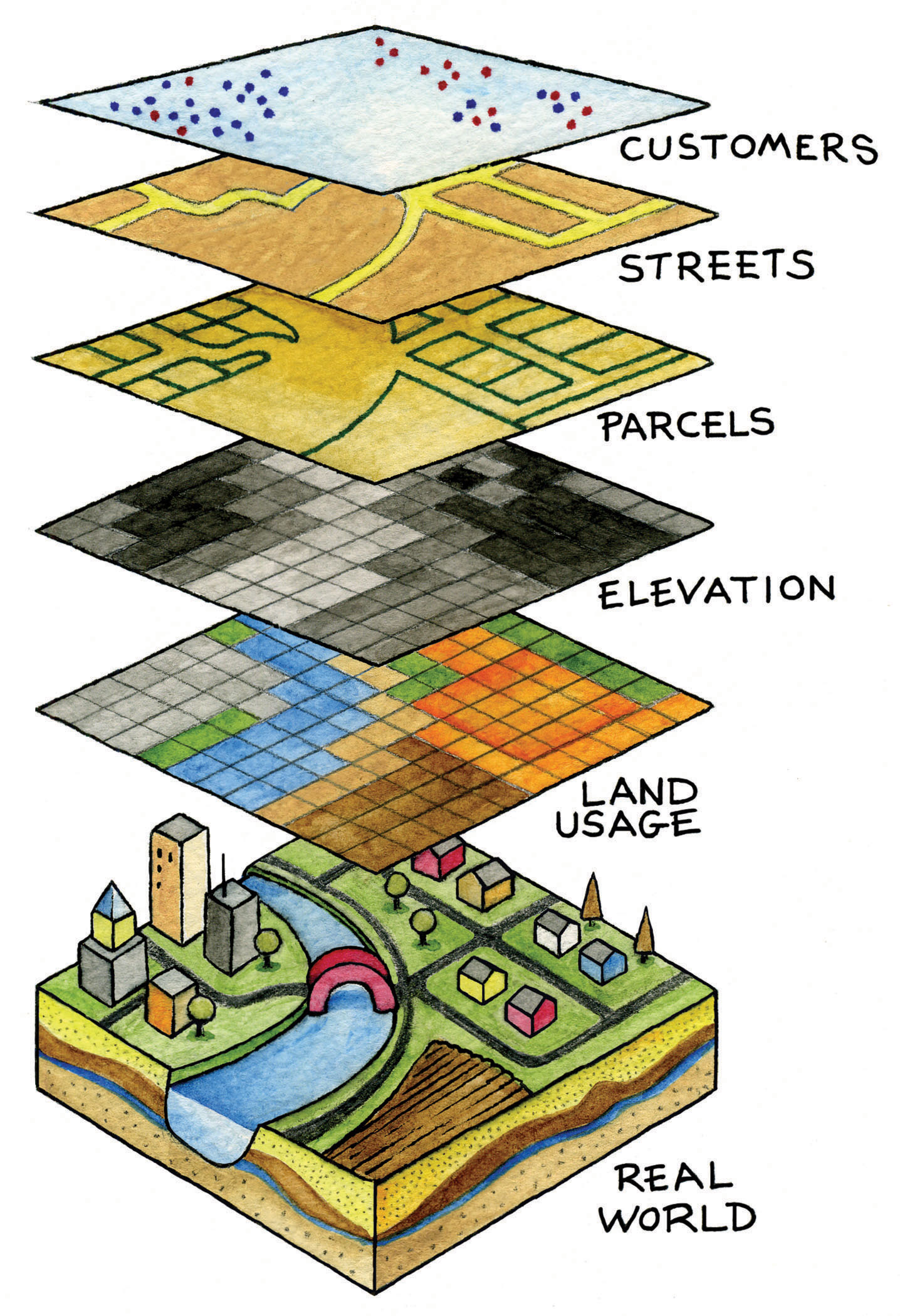
In the realm of geographic information systems (GIS) and cartography, the concept of map units serves as the cornerstone for accurate spatial representation and analysis. These units, often overlooked, play a crucial role in defining the scale, measurement, and interpretation of data displayed on maps. Understanding map units is essential for ensuring consistency, facilitating meaningful comparisons, and ultimately, drawing accurate conclusions from geographic information.
Defining the Essence of Map Units
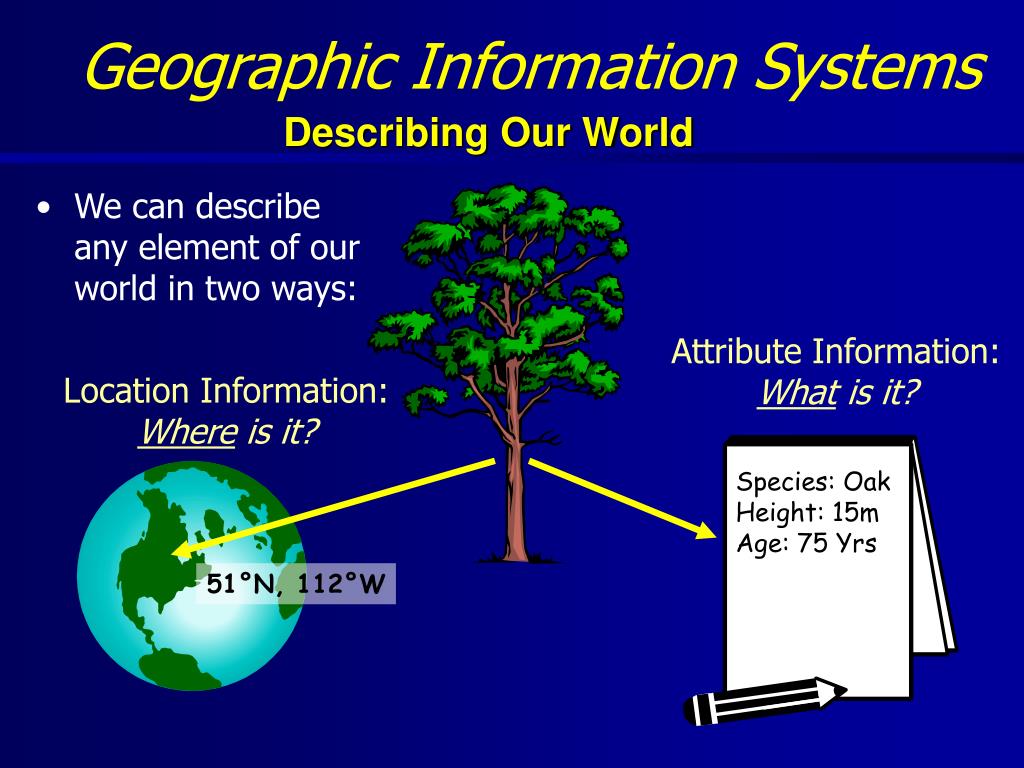
Map units represent the fundamental unit of measurement employed to depict distances, areas, and other spatial properties on a map. They serve as a bridge between the real world and its cartographic representation, providing a standardized language for communicating spatial information.
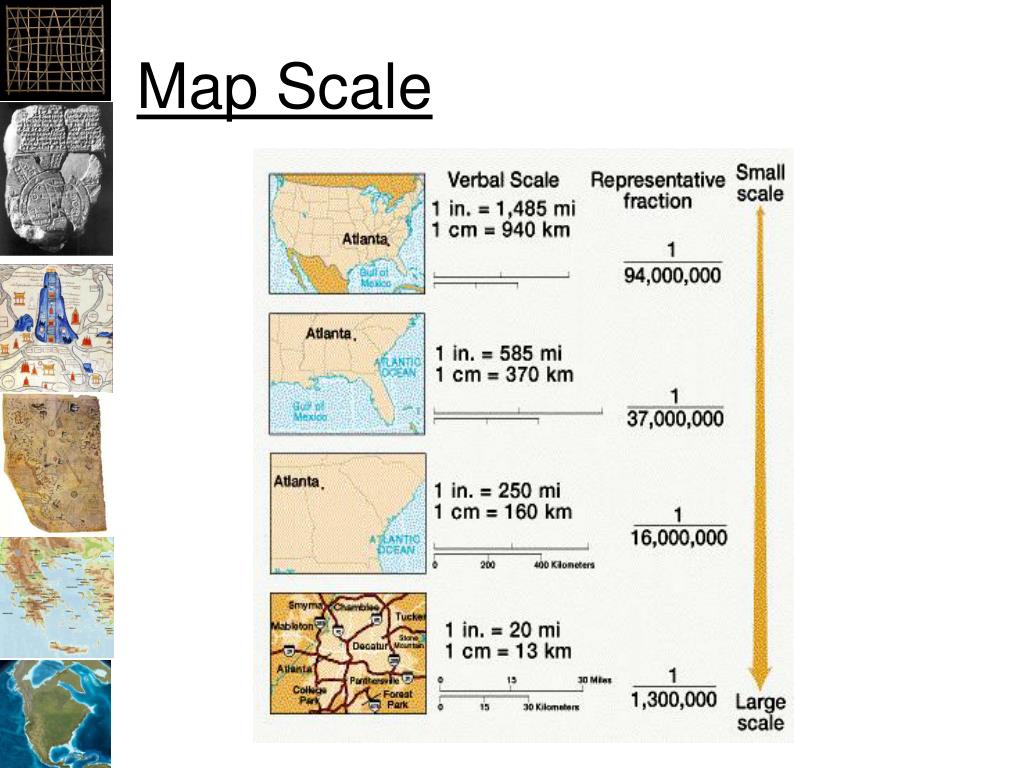
A Comprehensive Spectrum of Map Units
The choice of map units depends on the specific application and the nature of the geographic data being analyzed. Common map units include:
- Metric Units:
- Meters (m): The standard unit of length in the International System of Units (SI), widely used in scientific and engineering contexts.
- Kilometers (km): A larger metric unit, often used for representing distances between cities or countries.
- Centimeters (cm): A smaller metric unit, frequently employed in detailed maps and drawings.
- Millimeters (mm): An even smaller metric unit, useful for representing fine details and precise measurements.
- Imperial Units:
- Feet (ft): A common unit of length in the United States and other countries, used for measuring distances, elevations, and building dimensions.
- Miles (mi): A larger imperial unit, often used for representing long distances.
- Inches (in): A smaller imperial unit, frequently employed in detailed maps and drawings.
- Degrees:
- Decimal Degrees (DD): A unit of angular measurement used for expressing geographic coordinates, representing longitude and latitude.
- Degrees, Minutes, Seconds (DMS): A traditional method for expressing geographic coordinates, using degrees, minutes, and seconds to represent longitude and latitude.
The Significance of Consistent Map Units
Maintaining consistent map units throughout a GIS project is paramount for ensuring accuracy and preventing misinterpretations. Inconsistent units can lead to:
- Spatial Distortion: Distances and areas may be misrepresented, leading to inaccurate spatial analysis.
- Misaligned Data: Data layers with different units may not align properly, creating inconsistencies in spatial relationships.
- Erroneous Calculations: Calculations involving spatial data, such as area calculations or distance measurements, will be inaccurate if units are inconsistent.
Addressing the Importance of Map Units
The significance of map units extends beyond ensuring accuracy. They play a vital role in:
- Data Interpretation: Map units provide context for interpreting spatial information, enabling users to understand the scale and magnitude of features.
- Spatial Analysis: Consistent units are crucial for conducting spatial analysis, allowing for meaningful comparisons and accurate calculations.
- Data Integration: Map units facilitate the integration of data from different sources, ensuring compatibility and consistency.
- Communication and Collaboration: Standardized map units enable clear communication and collaboration among GIS professionals and stakeholders.
Exploring the Benefits of Proper Map Unit Usage
Implementing proper map unit management offers numerous benefits:
- Enhanced Accuracy: Consistent units ensure accurate spatial representation and analysis, reducing the risk of errors and misinterpretations.
- Improved Data Quality: Consistent units contribute to higher data quality, leading to more reliable and trustworthy spatial information.
- Streamlined Workflow: Consistent units simplify data management and analysis, enhancing workflow efficiency and productivity.
- Effective Communication: Standardized units facilitate clear communication and collaboration among GIS professionals and stakeholders.
FAQs Regarding Map Units
1. How can I determine the map units of a dataset?
The map unit information is typically stored within the metadata of a GIS dataset. You can access this information using GIS software or by examining the dataset’s file properties.
2. What happens if I use inconsistent map units in a GIS project?
Using inconsistent map units can lead to spatial distortion, misaligned data, and erroneous calculations, compromising the accuracy and reliability of your analysis.
3. How can I convert map units between different systems?
Most GIS software provides tools for converting map units between different systems, such as metric and imperial. These tools often use pre-defined conversion factors to ensure accurate conversions.
4. What are the best practices for managing map units in a GIS project?
- Establish a standard set of map units for the project and ensure consistency throughout.
- Document the map units used for each dataset and layer.
- Use GIS software tools for converting units when necessary.
- Regularly verify the accuracy of map units and make adjustments as needed.
Tips for Effective Map Unit Management
- Define Project Standards: Establish clear guidelines for map units at the beginning of a project, ensuring consistent usage throughout.
- Utilize Metadata: Document the map units used for each dataset and layer in the metadata, providing valuable information for future reference.
- Leverage GIS Software: Utilize GIS software tools for managing and converting map units, ensuring accuracy and efficiency.
- Validate Data: Regularly verify the accuracy of map units throughout the project to prevent errors and inconsistencies.
Conclusion: The Importance of Map Units in Geographic Information
Map units, though often overlooked, play a crucial role in ensuring the accuracy, consistency, and interpretability of geographic information. By understanding and implementing proper map unit management, GIS professionals can enhance data quality, streamline workflows, and ultimately, contribute to more reliable and trustworthy spatial analysis. Embracing the importance of map units lays the foundation for a robust and reliable GIS environment, fostering effective communication, collaboration, and informed decision-making based on accurate spatial information.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Foundation of Geographic Information: Understanding Map Units. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!