Understanding Manitoba’s Geographic Context: A Cartographic Analysis
Related Articles: Understanding Manitoba’s Geographic Context: A Cartographic Analysis
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Understanding Manitoba’s Geographic Context: A Cartographic Analysis. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding Manitoba’s Geographic Context: A Cartographic Analysis
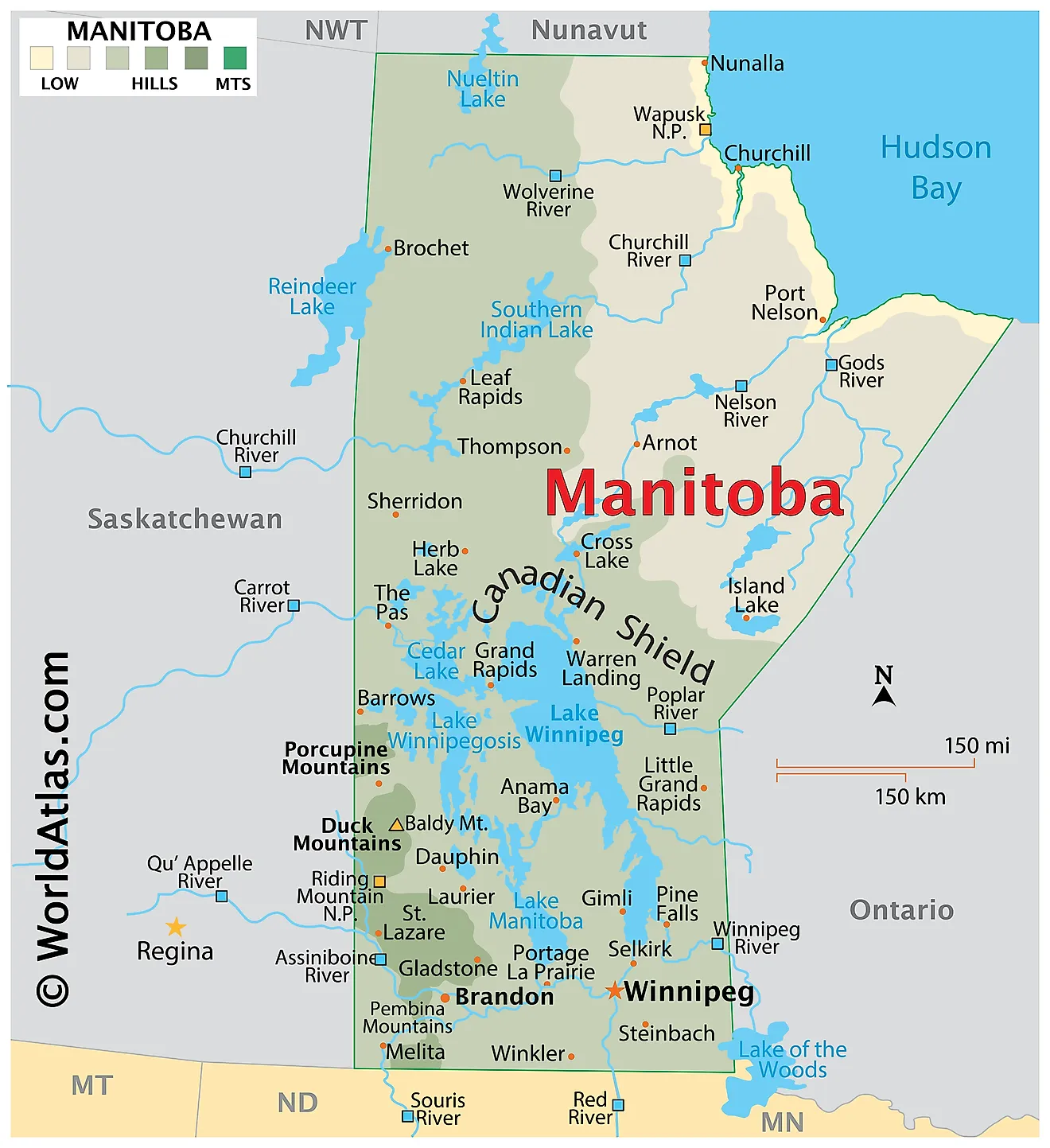
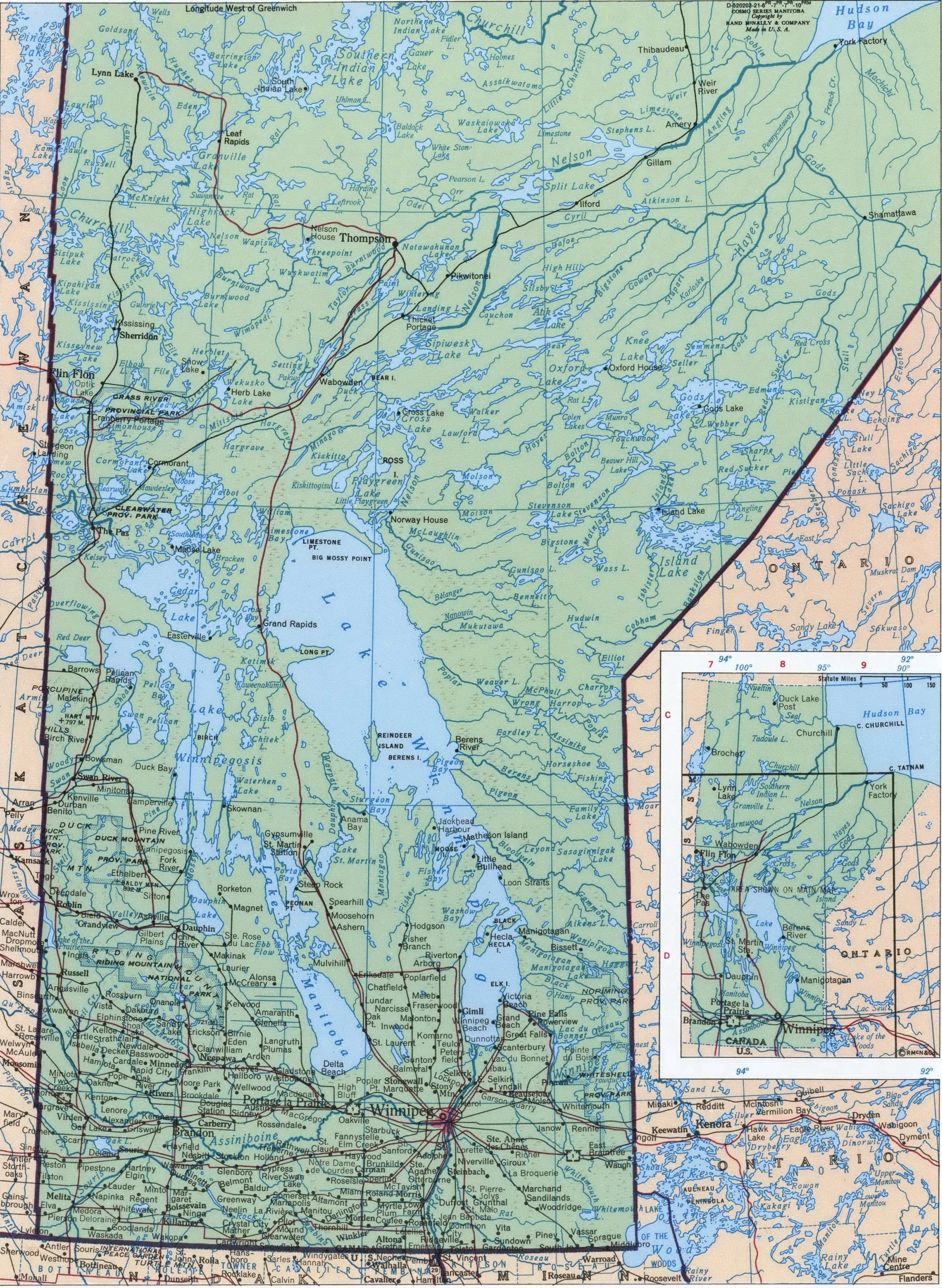
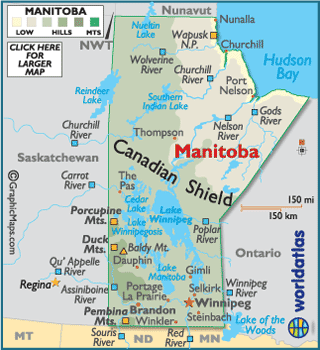
Manitoba, a central Canadian province, occupies a unique geographical position. Its cartographic representation reveals a province characterized by diverse landscapes and significant resource potential. Located in the Prairie Provinces, it stretches from the boreal forests of the north to the fertile plains of the south, encompassing a substantial portion of the Canadian Shield and the Hudson Bay Lowlands. This diverse topography significantly influences the province’s economy, ecology, and population distribution.
A visual examination of the province’s boundaries reveals its approximate rectangular shape, bordered by Ontario to the east, Saskatchewan to the west, Nunavut to the north, and the United States (North Dakota and Minnesota) to the south. The significant presence of numerous lakes, rivers, and wetlands is immediately apparent. Lake Winnipeg, one of the largest freshwater lakes in the world, dominates the central and eastern regions, significantly shaping the province’s hydrological system and influencing transportation routes. The Nelson River, originating from Lake Winnipeg, flows northwards towards Hudson Bay, highlighting the province’s connection to the Arctic watershed. Other prominent rivers, such as the Assiniboine and Red Rivers, traverse the southern plains, contributing to the fertile agricultural lands.
The northern portion of the province is largely characterized by the Canadian Shield, a vast expanse of Precambrian rock formations, abundant in mineral resources. This region is sparsely populated, primarily due to its challenging terrain and harsh climate. In contrast, the southern portion, situated within the Prairie region, features fertile soils ideal for agriculture, supporting a denser population and intensive agricultural practices. This agricultural heartland is a key contributor to Manitoba’s economy, producing significant quantities of grains, oilseeds, and livestock.
The cartographic representation of Manitoba also underscores its strategic location. Situated at the crossroads of major transportation routes, the province serves as a crucial link between eastern and western Canada. The Trans-Canada Highway traverses the southern portion, facilitating trade and communication. Furthermore, the province’s access to major waterways, including the Hudson Bay and the Great Lakes, has historically played a significant role in its economic development. This accessibility continues to influence its transportation network and trade relationships.
The province’s varied topography is not only reflected in its physical features but also in its ecological diversity. The boreal forests of the north provide habitat for a wide range of wildlife, while the grasslands of the south support different plant and animal communities. This biodiversity is crucial for maintaining ecological balance and supporting various industries, such as forestry and tourism. The cartographic portrayal of Manitoba underscores the importance of conservation efforts to protect this diverse ecosystem.
Frequently Asked Questions:
-
What is the approximate size of Manitoba? Manitoba’s land area is approximately 553,556 square kilometers.
-
Which major cities are located in Manitoba? Winnipeg, the provincial capital, is the largest city. Other significant urban centers include Brandon, Thompson, and Portage la Prairie.
-
What are the primary economic activities in Manitoba? Agriculture, mining, manufacturing, and resource extraction are key contributors to Manitoba’s economy.
-
What is the climate like in Manitoba? Manitoba experiences a continental climate with significant variations between seasons. Summers are warm, while winters are long and cold.
-
What are the major transportation routes in Manitoba? The Trans-Canada Highway, major railway lines, and navigable waterways form the backbone of Manitoba’s transportation infrastructure.
Tips for Understanding Manitoba’s Geography:
-
Utilize detailed topographic maps to understand elevation changes and the distribution of physical features.
-
Consult climate maps to appreciate the regional variations in temperature and precipitation.
-
Explore thematic maps focusing on population density, economic activity, and resource distribution for a comprehensive understanding.
-
Utilize online geographical information systems (GIS) for interactive exploration and data analysis.
-
Consider studying historical maps to understand the evolution of settlement patterns and transportation networks.
Conclusion:
The cartographic representation of Manitoba provides a fundamental understanding of the province’s unique geographical characteristics. Its diverse landscapes, strategic location, and rich resources significantly influence its economic development, social structure, and ecological integrity. A thorough understanding of this geographical context is crucial for informed decision-making regarding resource management, infrastructure development, and economic planning within the province. Further exploration using various cartographic tools and data sources will yield a more nuanced and comprehensive appreciation of Manitoba’s complex geographical reality.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Manitoba’s Geographic Context: A Cartographic Analysis. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!