Uncovering the Lifeblood of the Great Plains: A Look at the Ogallala Aquifer
Related Articles: Uncovering the Lifeblood of the Great Plains: A Look at the Ogallala Aquifer
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Uncovering the Lifeblood of the Great Plains: A Look at the Ogallala Aquifer. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Uncovering the Lifeblood of the Great Plains: A Look at the Ogallala Aquifer
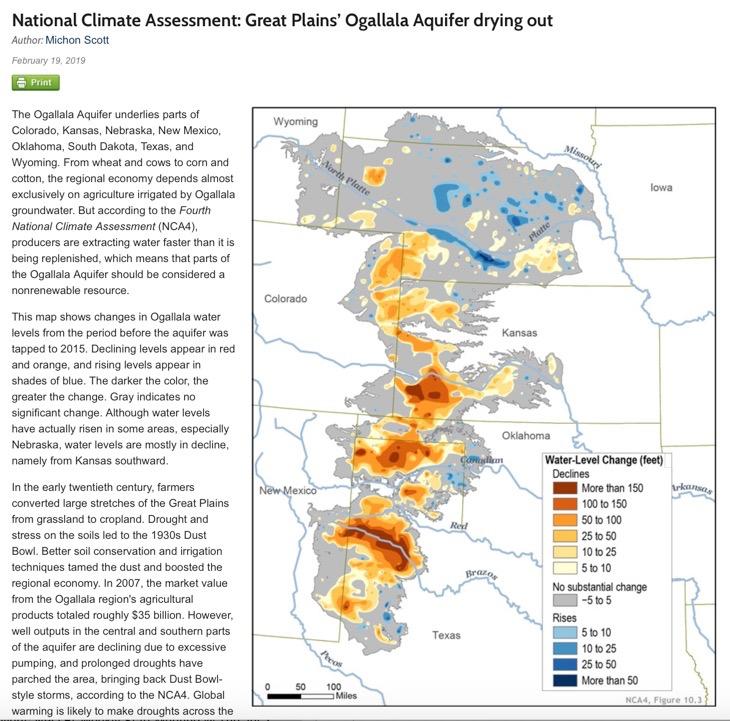
The Ogallala Aquifer, often referred to as the High Plains Aquifer, is a vast, underground reservoir of water stretching across eight states in the central United States: South Dakota, Nebraska, Wyoming, Colorado, Kansas, Oklahoma, New Mexico, and Texas. This geological treasure, formed over millennia by the accumulation of sediment and water, serves as a critical source of irrigation for agriculture, providing sustenance to the heartland of America. Understanding its geography, significance, and challenges is crucial for ensuring the long-term sustainability of this vital resource.
A Visual Representation of a Hidden Giant
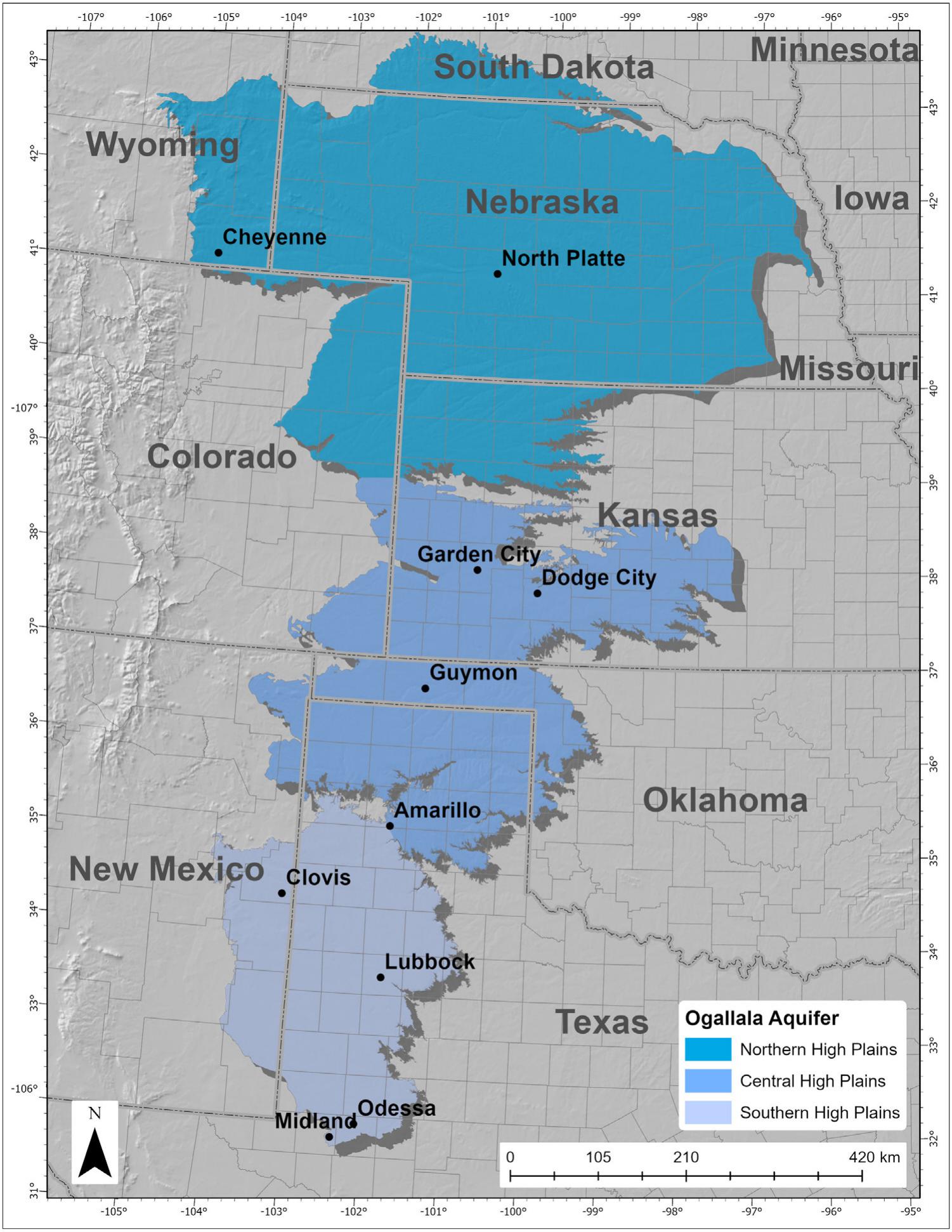
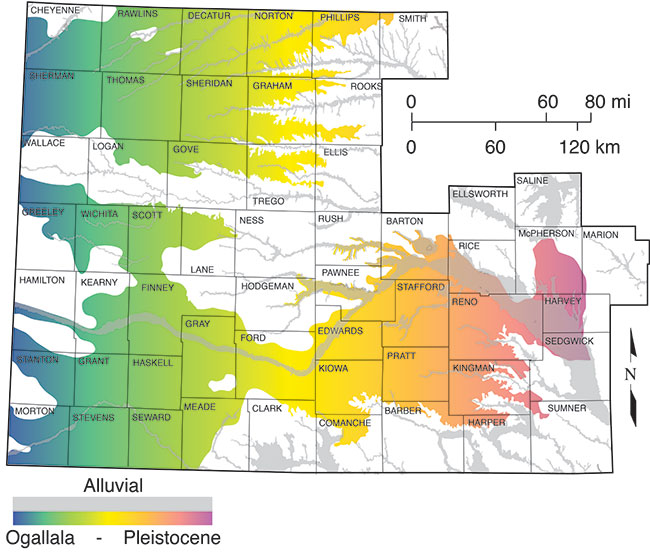
A map of the Ogallala Aquifer reveals a complex landscape of water storage. Its primary area of occurrence lies beneath the Great Plains, extending from the panhandle of Texas to the Dakotas. The aquifer’s thickness varies considerably, ranging from a few feet in the west to over one thousand feet in the east. The water within the aquifer is held within porous rock formations, primarily sand and gravel, and is replenished by rainfall and snowmelt.
The Ogallala Aquifer: A Lifeline for Agriculture
The Ogallala Aquifer plays a pivotal role in the agricultural economy of the Great Plains. It provides irrigation water for a vast array of crops, including wheat, corn, cotton, and livestock feed. The aquifer’s water is particularly valuable due to its high quality, making it suitable for both human consumption and agricultural use. The aquifer is estimated to supply roughly 30% of the nation’s irrigation water, highlighting its crucial contribution to food production.
A Declining Resource: The Challenges Facing the Ogallala Aquifer
Despite its immense size, the Ogallala Aquifer faces significant challenges. The primary concern is its depletion rate, exceeding the natural replenishment rate. This over-extraction is primarily driven by intensive agricultural practices, where irrigation demands significantly outweigh natural recharge. The aquifer’s water table has been steadily declining in many areas, raising concerns about its long-term sustainability.
Understanding the Impact: A Deeper Dive into the Consequences of Depletion
The depletion of the Ogallala Aquifer has several consequences. The most direct impact is the decline in agricultural productivity, as farmers struggle to access sufficient water for irrigation. This can lead to crop failures, reduced yields, and economic hardship for agricultural communities. Additionally, the lowering of the water table can have detrimental effects on ecosystems, impacting groundwater-dependent vegetation and wildlife.
A Call for Conservation: Strategies for Sustainable Management
Recognizing the gravity of the situation, efforts are underway to address the challenges facing the Ogallala Aquifer. These efforts encompass various strategies, including:
- Water Conservation Technologies: Implementing irrigation technologies like drip irrigation and center pivot systems can significantly reduce water usage.
- Water-Efficient Crops: Cultivating drought-tolerant crops and promoting crop rotation can minimize water demands.
- Recharging the Aquifer: Strategies like capturing rainwater and runoff can contribute to replenishing the aquifer.
- Policy and Regulation: Implementing water management policies and regulations can ensure responsible water use and promote conservation.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions about the Ogallala Aquifer
1. What is the Ogallala Aquifer, and why is it important?
The Ogallala Aquifer is a vast underground reservoir of water crucial for agriculture in the Great Plains. It provides irrigation water for a significant portion of the nation’s food production, making it a vital resource.
2. How is the Ogallala Aquifer being depleted?
The aquifer is being depleted primarily due to over-extraction for irrigation, exceeding the natural replenishment rate.
3. What are the consequences of the Ogallala Aquifer’s depletion?
The depletion of the aquifer can lead to reduced agricultural productivity, economic hardship, and negative impacts on ecosystems.
4. What are some solutions to address the challenges facing the Ogallala Aquifer?
Solutions include implementing water conservation technologies, cultivating water-efficient crops, recharging the aquifer, and enacting water management policies.
5. What is the future of the Ogallala Aquifer?
The future of the Ogallala Aquifer depends on the effectiveness of conservation efforts and the adoption of sustainable water management practices.
Tips for Sustainable Water Use in the Ogallala Aquifer Region
- Adopt water-efficient irrigation methods: Consider drip irrigation, center pivot systems, or other technologies that minimize water waste.
- Practice crop rotation: Rotate water-intensive crops with drought-tolerant varieties to reduce overall water demand.
- Utilize rainwater harvesting: Collect rainwater for irrigation and other uses, reducing reliance on the aquifer.
- Implement soil conservation practices: Healthy soil retains moisture better, minimizing the need for excessive irrigation.
- Promote water conservation awareness: Educate yourself and others about the importance of water conservation and the challenges facing the Ogallala Aquifer.
Conclusion: A Call for Collective Action
The Ogallala Aquifer is a precious resource that has sustained the Great Plains for generations. However, its future is uncertain due to the unsustainable depletion rates. Addressing this challenge requires a collective effort from farmers, policymakers, and communities. By implementing conservation strategies, promoting sustainable practices, and fostering a culture of water stewardship, we can ensure the long-term viability of this vital resource for future generations.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Uncovering the Lifeblood of the Great Plains: A Look at the Ogallala Aquifer. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!