The Ogallala Aquifer: A Vital Resource Facing Challenges
Related Articles: The Ogallala Aquifer: A Vital Resource Facing Challenges
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Ogallala Aquifer: A Vital Resource Facing Challenges. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Ogallala Aquifer: A Vital Resource Facing Challenges

The Ogallala Aquifer, also known as the High Plains Aquifer, is a vast underground reservoir of water stretching across eight states in the central United States: South Dakota, Nebraska, Wyoming, Colorado, Kansas, Oklahoma, Texas, and New Mexico. This aquifer is a vital resource, providing water for agriculture, drinking, and industry, supporting a significant portion of the nation’s food production.
Mapping the Ogallala Aquifer: Understanding its Depths and Extent
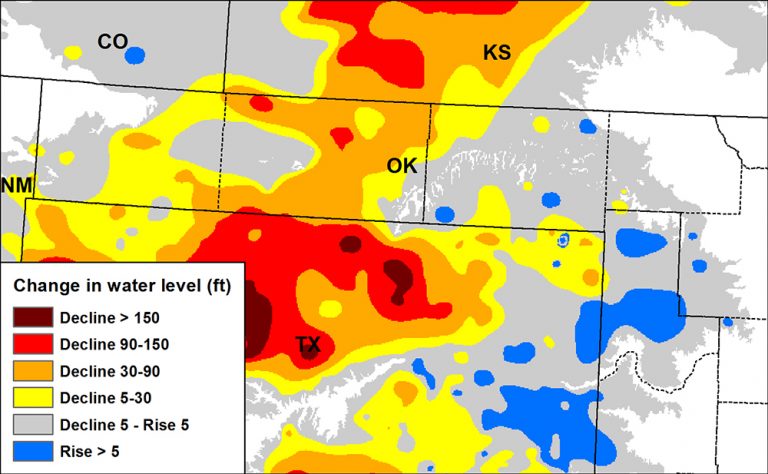
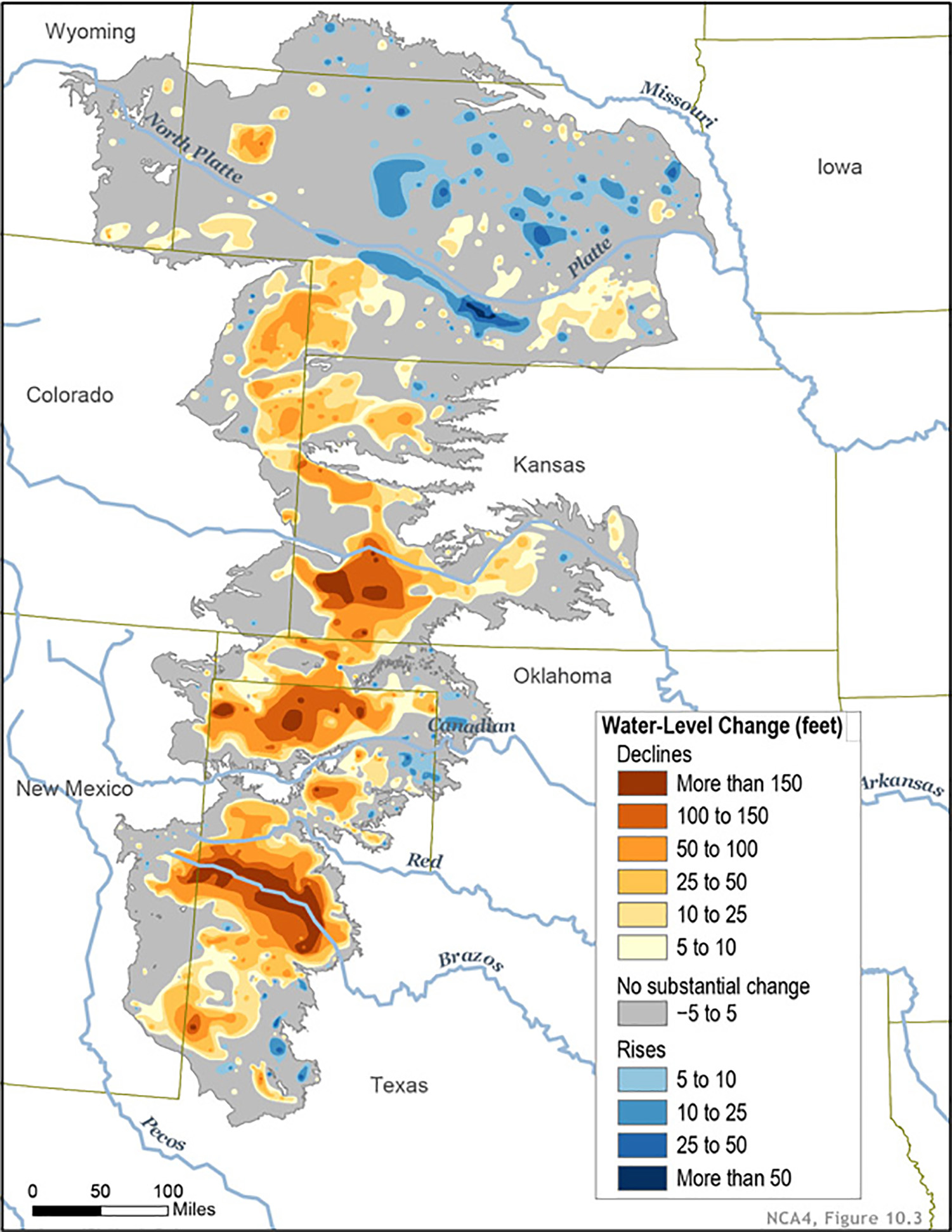
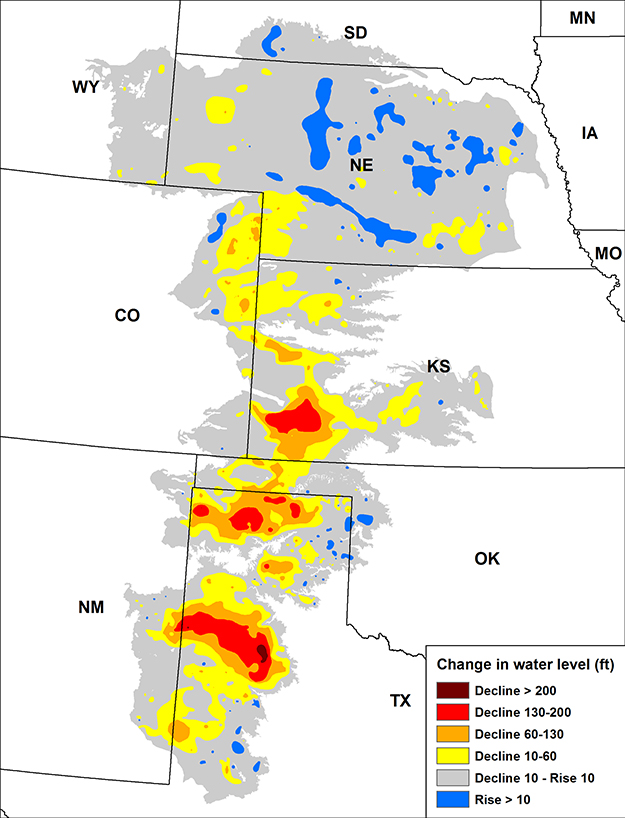
Visualizing the Ogallala Aquifer through maps provides crucial insights into its vastness, water levels, and the challenges it faces. These maps typically depict the aquifer’s boundaries, its depth, and the amount of water stored within it.
Types of Maps:
- Boundary Maps: These maps illustrate the geographical extent of the aquifer, highlighting the states it encompasses and the areas where it is most prevalent. They provide a general overview of the aquifer’s presence.
- Depth Maps: These maps show the thickness of the aquifer, indicating the depth of the water-bearing layer. They are crucial for understanding the potential water storage capacity of the aquifer and identifying areas with greater water reserves.
- Water Level Maps: These maps display the elevation of the water table within the aquifer. They reveal areas where water levels are declining, indicating overpumping or drought conditions.
- Recharge Maps: These maps show the areas where the aquifer is being replenished naturally, highlighting the sources of water entering the system. Understanding recharge patterns is critical for sustainable management of the aquifer.
Importance of the Ogallala Aquifer:
The Ogallala Aquifer is a lifeline for the Great Plains region, playing a crucial role in:
- Agriculture: The aquifer provides irrigation water for vast agricultural fields, supporting the production of major crops like corn, wheat, and cotton. This agricultural output contributes significantly to the national food supply.
- Drinking Water: The aquifer supplies drinking water to numerous towns and cities across the region, ensuring access to clean and safe water for millions of people.
- Industry: The aquifer supports various industries, including livestock production, energy extraction, and manufacturing, contributing to the economic vitality of the region.
Challenges Facing the Ogallala Aquifer:
The Ogallala Aquifer faces significant challenges, primarily due to:
- Overpumping: The aquifer is being pumped out faster than it is being replenished, leading to declining water levels in many areas. This unsustainable practice threatens the long-term viability of the aquifer.
- Drought: Periodic droughts exacerbate the depletion of the aquifer, further reducing water availability and increasing the strain on the resource.
- Pollution: Agricultural runoff, industrial waste, and other sources of pollution can contaminate the aquifer, compromising the quality of water and posing health risks.
Management and Conservation Efforts:
Recognizing the critical importance of the Ogallala Aquifer, various efforts are underway to manage and conserve this vital resource:
- Water Conservation: Implementing water-saving irrigation techniques, such as drip irrigation and precision agriculture, can reduce water usage and slow down depletion.
- Aquifer Recharge: Projects aimed at replenishing the aquifer through artificial recharge methods are being explored, such as capturing and storing rainwater or diverting excess water from rivers.
- Water Management Policies: Governments are implementing policies to regulate water usage, promote water conservation, and ensure equitable access to the aquifer’s resources.
- Public Awareness: Raising public awareness about the importance of the Ogallala Aquifer and the challenges it faces is crucial to fostering responsible water use practices.
FAQs about the Ogallala Aquifer:
1. What is the current state of the Ogallala Aquifer?
The current state of the Ogallala Aquifer varies across its vast extent. While some areas are experiencing significant water level declines, others maintain relatively stable levels. However, overall, the aquifer is facing challenges due to overpumping and drought.
2. How much water is left in the Ogallala Aquifer?
The estimated volume of water remaining in the Ogallala Aquifer varies depending on the source and methodology used for calculation. However, it is generally accepted that the aquifer is losing water at a faster rate than it is being replenished.
3. What are the potential consequences of depleting the Ogallala Aquifer?
Depleting the Ogallala Aquifer could have severe consequences, including:
- Loss of agricultural productivity: Reduced water availability could lead to crop failures and a decline in agricultural production.
- Water shortages: Depleted aquifers could lead to water shortages for drinking and other uses, impacting communities and industries.
- Economic impacts: The depletion of the aquifer could have significant economic impacts, affecting agricultural livelihoods, water-dependent industries, and overall regional development.
4. What can be done to protect the Ogallala Aquifer?
Protecting the Ogallala Aquifer requires a multifaceted approach:
- Water conservation: Implementing water-saving technologies and practices is crucial to reduce water demand.
- Aquifer recharge: Artificial recharge projects can help replenish the aquifer and mitigate depletion.
- Sustainable water management: Effective water management policies are essential to ensure equitable access to water and promote responsible use.
- Public awareness: Raising awareness about the importance of the aquifer and the need for conservation is crucial to fostering responsible water use practices.
Tips for Conserving Water in the Ogallala Aquifer Region:
- Use water-efficient irrigation techniques: Employ drip irrigation, micro-irrigation, and precision agriculture to reduce water use in agricultural fields.
- Install low-flow showerheads and toilets: Conserve water in homes by upgrading fixtures to reduce water consumption.
- Water your lawns efficiently: Water lawns only when necessary and avoid overwatering.
- Collect rainwater: Harvest rainwater for use in gardens and landscaping, reducing reliance on aquifer water.
- Be mindful of water usage: Adopt water-saving habits in all aspects of life, such as shorter showers, turning off the tap while brushing teeth, and using water-efficient appliances.
Conclusion:
The Ogallala Aquifer is a vital resource for the Great Plains region, supporting agriculture, providing drinking water, and driving economic activity. However, the aquifer faces significant challenges due to overpumping, drought, and pollution. Sustainable management and conservation efforts are crucial to ensure the long-term viability of this vital resource. By implementing water-saving technologies, promoting aquifer recharge, and advocating for responsible water use practices, we can safeguard the Ogallala Aquifer for future generations.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Ogallala Aquifer: A Vital Resource Facing Challenges. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!