The Map of the First Crusade: A Visual Narrative of Faith, Conquest, and Change
Related Articles: The Map of the First Crusade: A Visual Narrative of Faith, Conquest, and Change
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Map of the First Crusade: A Visual Narrative of Faith, Conquest, and Change. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Map of the First Crusade: A Visual Narrative of Faith, Conquest, and Change

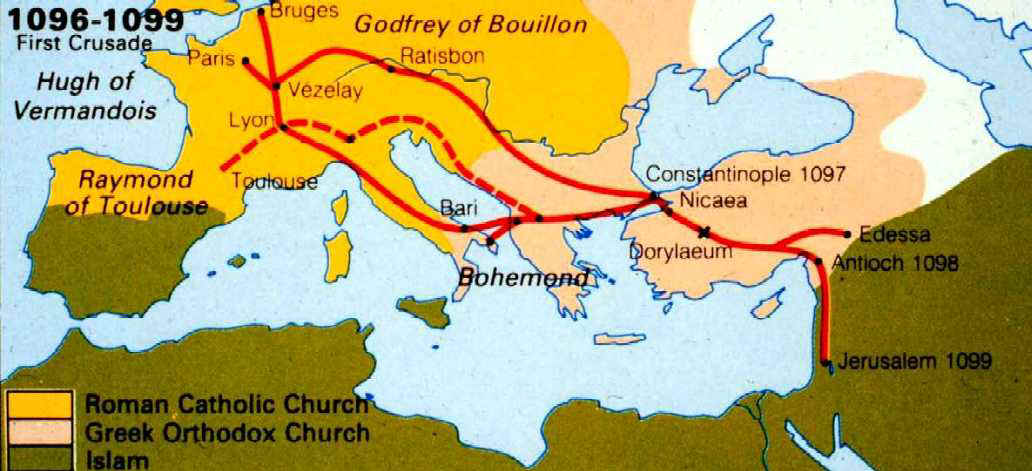
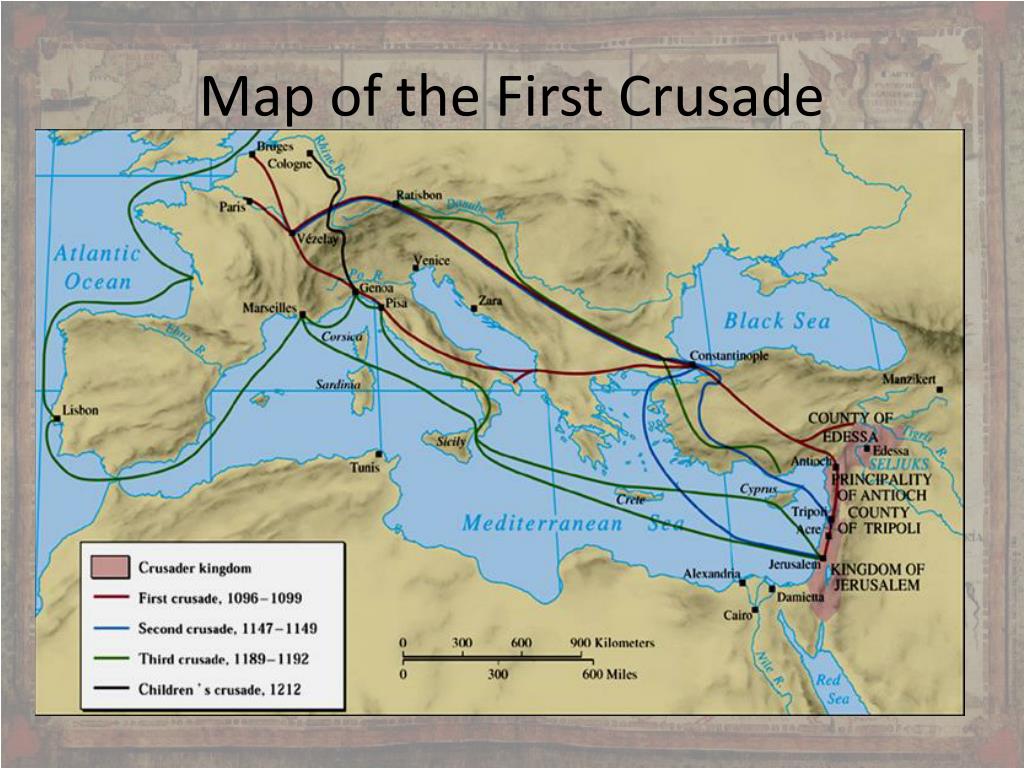
The First Crusade, a pivotal moment in European history, is often depicted through the lens of a map. This visual representation, more than just a geographical outline, serves as a powerful tool for understanding the complex tapestry of events that unfolded between 1095 and 1099. It reveals the vast distances traversed, the diverse landscapes encountered, and the strategic decisions made by the crusaders.
A Journey of Faith and Ambition:
The map of the First Crusade begins in Western Europe, where Pope Urban II’s impassioned plea for a "Holy War" ignited a fervor for liberation of the Holy Land from Seljuk Turk control. From various points across France, Germany, Italy, and even England, crusader armies embarked on their perilous journey to the East.
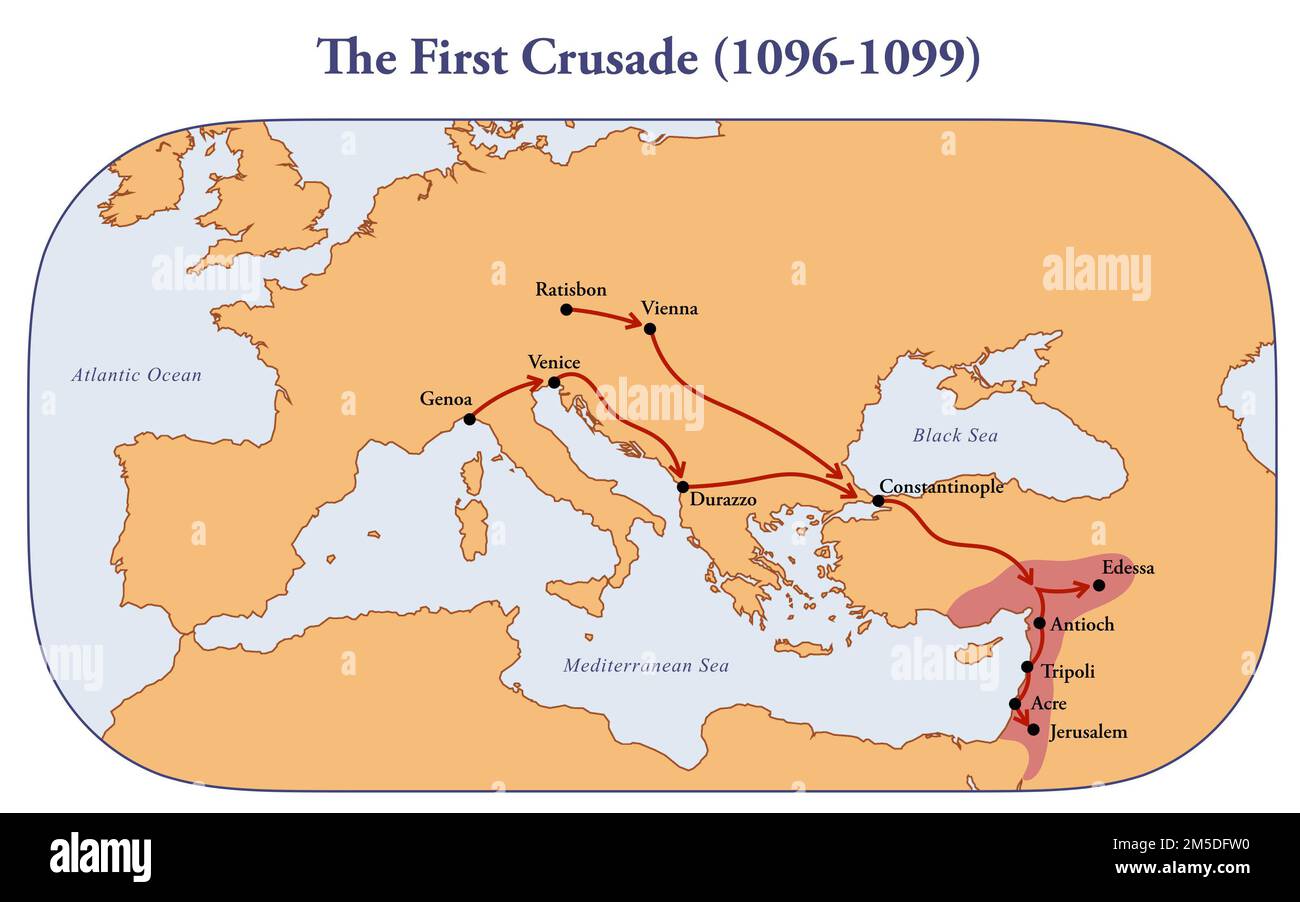
The Routes of Conquest:
The map illustrates the multiple routes taken by the crusaders. The main path, known as the "Land Route," led through the Byzantine Empire, traversing the Balkan Peninsula and into Anatolia. This route, fraught with challenges and potential conflict with the Byzantines, highlights the intricate political landscape of the time.
The "Sea Route," another prominent path, saw crusaders embarking from various Italian ports, navigating the Mediterranean Sea to reach the Levant. This route, while safer than the land journey, was still vulnerable to pirate attacks and unpredictable weather conditions.
Strategic Points and Battles:
The map is dotted with significant locations, each representing a pivotal moment in the crusade’s narrative. The city of Nicaea, captured from the Seljuks in 1097, served as a crucial staging ground for the crusaders. The Battle of Dorylaeum, a decisive victory against the Seljuk Turks, further solidified their progress.
The capture of Antioch, a major city in Syria, marked a turning point in the crusade. The siege, lasting over seven months, was a testament to the determination and resilience of the crusaders. The Battle of Harim, fought in 1098, further expanded their territorial gains.
The Ultimate Goal: Jerusalem:
The map culminates at Jerusalem, the ultimate objective of the First Crusade. The siege of the city, lasting for forty days, was a brutal and bloody affair. The capture of Jerusalem in 1099, followed by the massacre of its inhabitants, marked a turning point in the crusade’s legacy, forever associating it with violence and bloodshed.
The Legacy of the Map:
The map of the First Crusade is more than just a visual representation of a historical event. It serves as a window into the motivations, strategies, and consequences of this momentous undertaking. It reveals the intricate web of alliances and rivalries, the challenges faced by the crusaders, and the enduring impact of their actions on the Middle East and Europe.
FAQs by Map of the First Crusade:
Q: Why is the map of the First Crusade important?
A: The map provides a visual narrative of the crusade’s journey, highlighting the strategic decisions, geographic challenges, and pivotal battles that shaped the course of events. It offers a valuable tool for understanding the complex dynamics of the First Crusade.
Q: What were the major routes taken by the crusaders?
A: The major routes were the "Land Route" through the Byzantine Empire and the "Sea Route" across the Mediterranean Sea. Each route presented unique challenges and influenced the course of the crusade.
Q: What were the key battles fought during the First Crusade?
A: The battles of Dorylaeum, Antioch, and Harim were crucial victories for the crusaders, demonstrating their military prowess and strategic planning.
Q: What was the significance of capturing Jerusalem?
A: The capture of Jerusalem, the ultimate objective of the First Crusade, marked a symbolic victory for Christendom. However, it also led to violence and bloodshed, leaving a lasting impact on the region.
Q: What were the lasting consequences of the First Crusade?
A: The First Crusade had a profound impact on the Middle East and Europe. It established Crusader states in the Levant, sparked a series of subsequent crusades, and fostered religious and cultural exchanges between East and West.
Tips by Map of the First Crusade:
- Visualize the journey: Utilize the map to trace the crusaders’ path, imagining the landscapes they traversed and the challenges they faced.
- Identify key locations: Focus on the strategic importance of cities like Nicaea, Antioch, and Jerusalem, understanding their role in the crusade’s narrative.
- Study the battles: Explore the battles depicted on the map, understanding their significance in shaping the outcome of the crusade.
- Connect the map to historical sources: Use primary and secondary sources to gain deeper insights into the events depicted on the map.
- Consider the broader context: Analyze the map within the context of the larger historical landscape, understanding the political, religious, and social factors that influenced the First Crusade.
Conclusion by Map of the First Crusade:
The map of the First Crusade serves as a powerful visual tool for understanding a pivotal moment in European history. It reveals the complex dynamics of faith, conquest, and change, offering insights into the motivations, strategies, and consequences of this momentous undertaking. By studying the map, we gain a deeper appreciation for the historical context and enduring legacy of the First Crusade.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Map of the First Crusade: A Visual Narrative of Faith, Conquest, and Change. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!