The Czech Republic’s Geographic Context: A Central European Powerhouse
Related Articles: The Czech Republic’s Geographic Context: A Central European Powerhouse
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Czech Republic’s Geographic Context: A Central European Powerhouse. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Czech Republic’s Geographic Context: A Central European Powerhouse

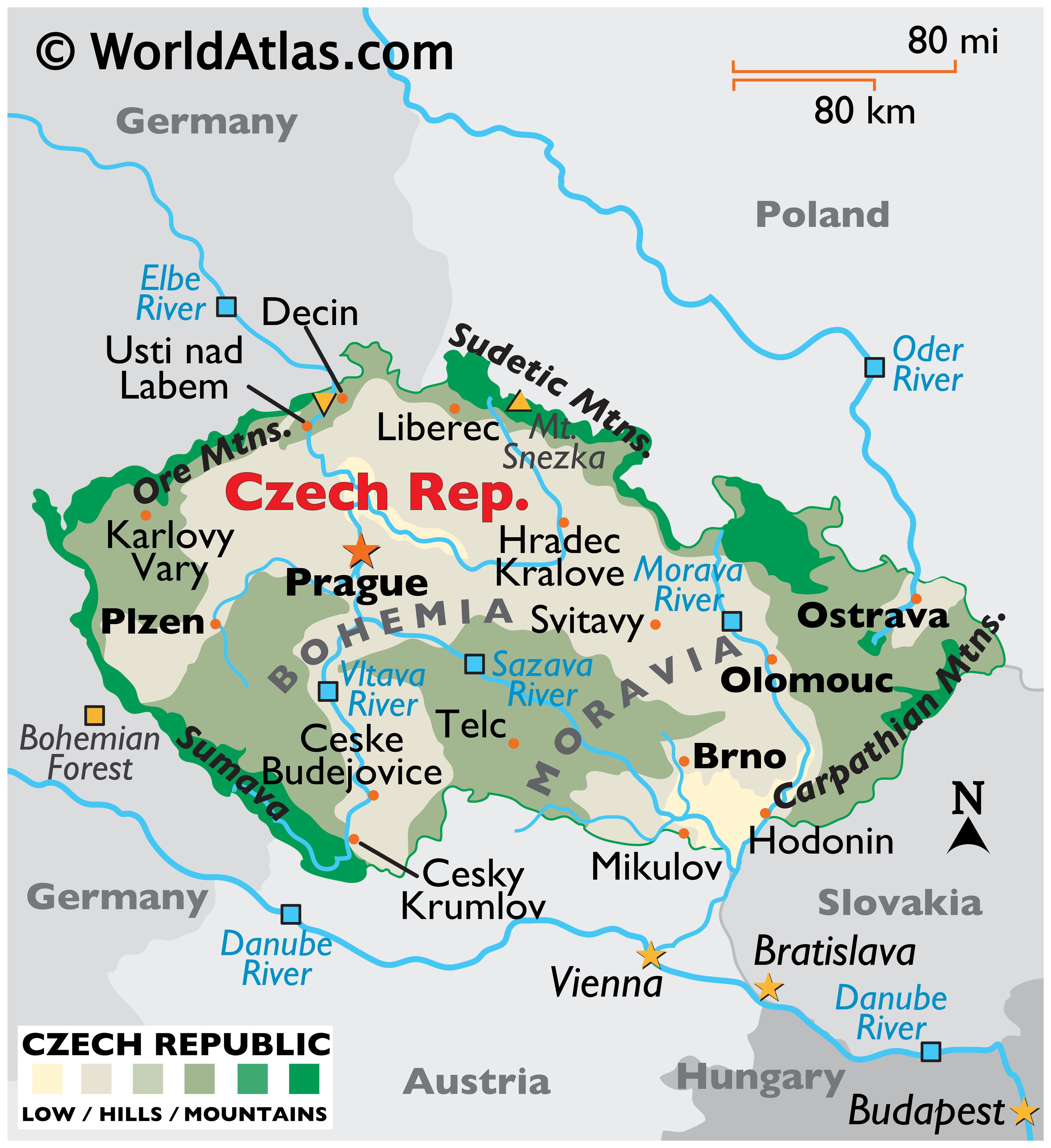
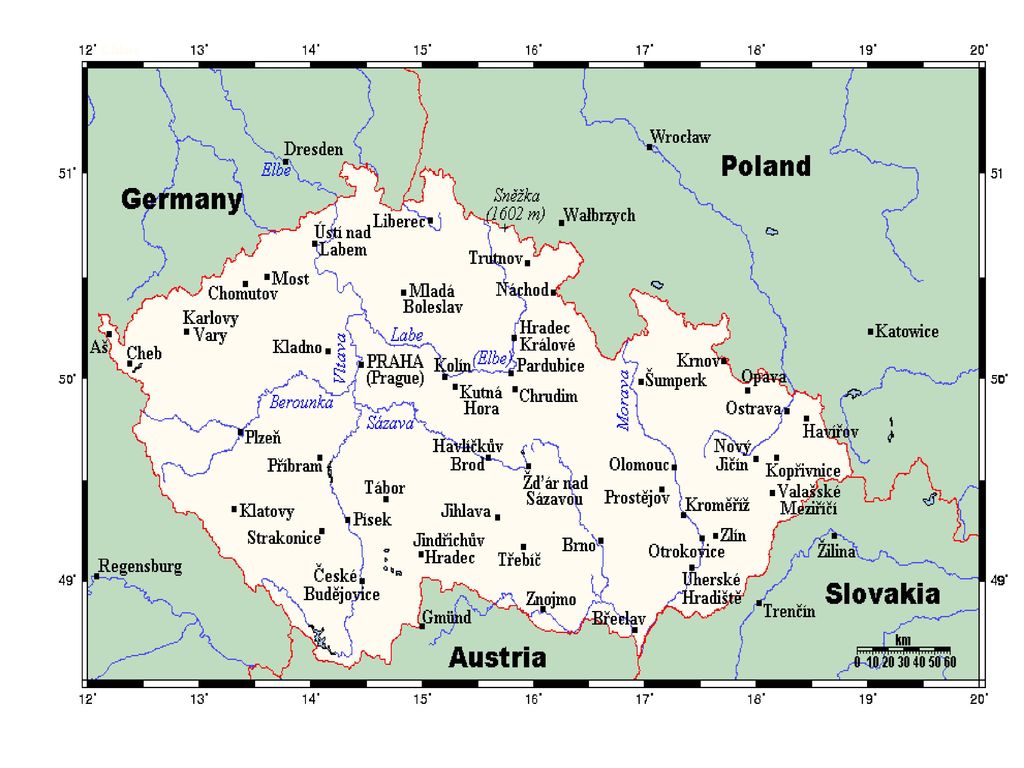
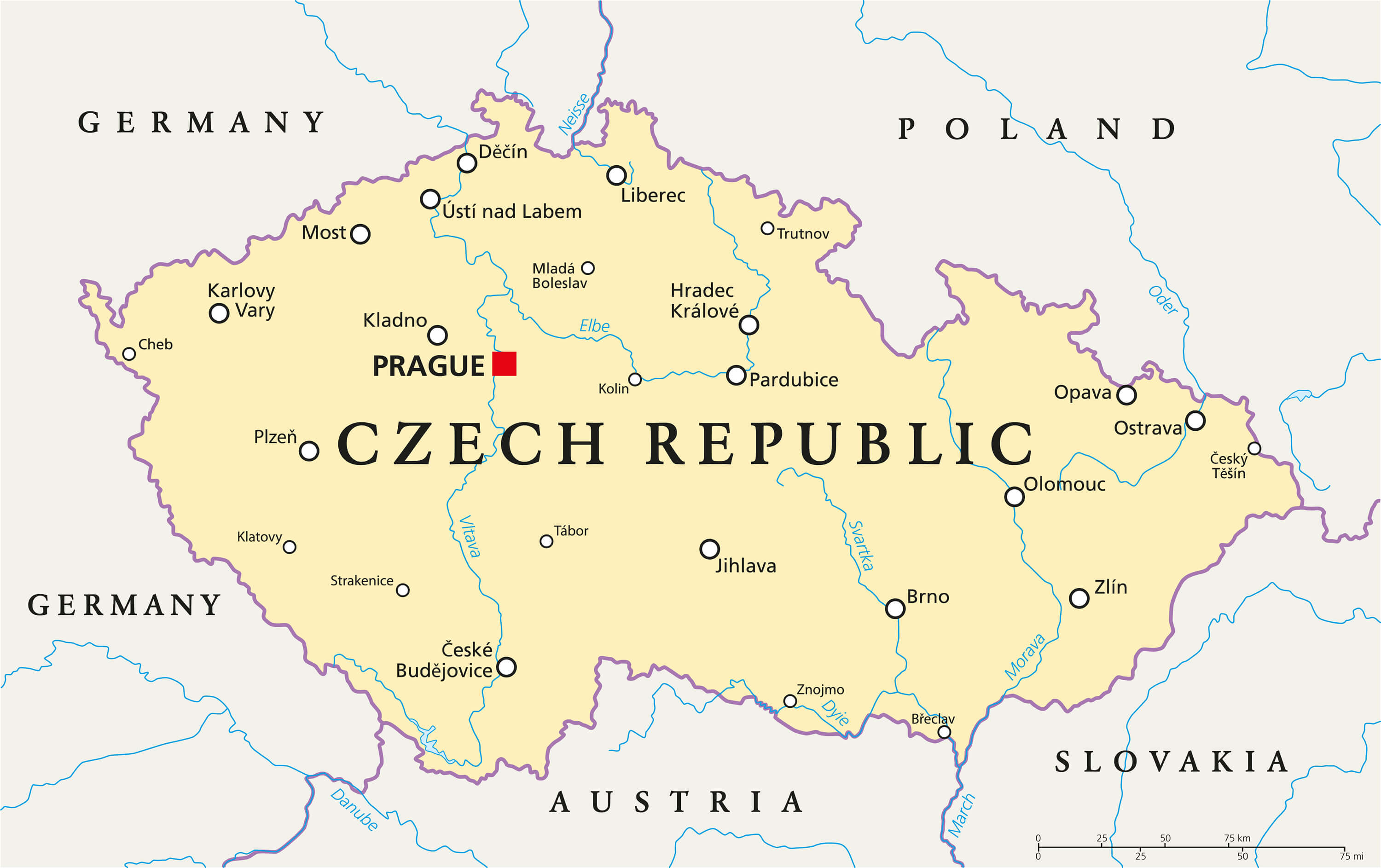
The Czech Republic occupies a strategically significant location in Central Europe, nestled between Germany to the west, Austria to the south, Slovakia to the east, and Poland to the north. This landlocked position, while limiting direct maritime access, has historically placed the nation at the crossroads of major European trade routes and cultural influences. Its relatively compact size – approximately 78,866 square kilometers – belies its historical importance and contemporary influence.
Geographically, the country is characterized by a diverse landscape. The Bohemian Massif, a geological formation dominating the western and central regions, features rolling hills, mountains, and fertile plains. This area is historically associated with Bohemia, the heartland of the Czech lands. To the east, the Moravian-Silesian region offers a different terrain, with the Carpathian Mountains forming a natural boundary with Slovakia. This varied topography has shaped the country’s agricultural practices, industrial development, and cultural identity. The Vltava and Elbe rivers, along with numerous smaller tributaries, are crucial for transportation, irrigation, and hydropower generation.
This central location has profoundly shaped the Czech Republic’s history. The nation has been a frequent battleground and a pivotal player in significant historical events, from the Holy Roman Empire to the Austro-Hungarian Empire and beyond. Its position facilitated both the spread of ideas and the movement of populations, resulting in a rich cultural tapestry influenced by various European traditions. This historical legacy continues to inform the nation’s present-day character.
The Czech Republic’s geographic situation also holds considerable economic significance. Its proximity to major European markets provides easy access to export opportunities. The country’s well-developed transportation infrastructure, including a robust network of roads, railways, and waterways, further enhances its connectivity. This facilitates the movement of goods and services, supporting a vibrant and diversified economy. The nation’s strategic location has also made it an attractive destination for foreign investment.
FAQs regarding the Czech Republic’s Geographic Position:
-
Q: Is the Czech Republic easily accessible from other European countries?
- A: Yes, the Czech Republic boasts excellent road and rail connections to neighboring countries and major European cities, making it easily accessible by land. International airports in Prague and other cities provide convenient air links.
-
Q: What are the major geographical features influencing the Czech Republic’s economy?
- A: The fertile plains of Bohemia support significant agricultural production. The abundance of rivers provides hydropower and facilitates transportation. The country’s central location offers easy access to major European markets, fostering trade and investment.
-
Q: How has the Czech Republic’s landlocked status affected its development?
- A: While lacking direct access to the sea, the Czech Republic has overcome this limitation through its efficient transportation infrastructure and strategic alliances, ensuring strong economic ties with maritime nations. Its central location within Europe compensates for the absence of coastal access.
-
Q: What are the main climate zones in the Czech Republic?
- A: The Czech Republic experiences a temperate continental climate, characterized by warm summers and cool winters. Variations exist across the country due to altitude and geographical features.
Tips for understanding the Czech Republic’s geographic context:
- Consult detailed maps: Utilize topographic maps and satellite imagery to visualize the country’s diverse landscape and understand its regional variations.
- Study historical maps: Examining historical maps can illustrate the country’s shifting borders and its role in broader European contexts throughout history.
- Analyze infrastructure data: Explore data on transportation networks, industrial zones, and agricultural regions to grasp the relationship between geography and economic activity.
- Research climate data: Understanding climate patterns and their impact on agriculture and other sectors offers a more complete picture of the country’s geographic profile.
Conclusion:
The Czech Republic’s geographic location firmly positions it as a pivotal nation within Central Europe. Its central location, diverse landscape, and well-developed infrastructure contribute significantly to its economic strength and cultural richness. Understanding this geographic context is crucial for appreciating the country’s historical trajectory, its present-day realities, and its potential for future development. The interplay between its geography, history, and economy creates a unique and compelling national identity. Further exploration of its geographical features and their impact on various aspects of Czech society reveals a nuanced and fascinating picture of this Central European nation.
![Map of Czech Republic [Czechia] - GIS Geography](https://gisgeography.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/09/Czech-Republic-Regions-Map.jpg)




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Czech Republic’s Geographic Context: A Central European Powerhouse. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!