The County-Level Geographic Representation of States: A Comprehensive Overview
Related Articles: The County-Level Geographic Representation of States: A Comprehensive Overview
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The County-Level Geographic Representation of States: A Comprehensive Overview. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The County-Level Geographic Representation of States: A Comprehensive Overview
State maps displaying county boundaries are fundamental geographic tools offering a granular view of administrative divisions within a state. These maps provide a spatial framework crucial for understanding demographic distributions, resource allocation, electoral processes, and numerous other facets of state governance and societal organization. Their utility extends across various sectors, impacting policy decisions, research endeavors, and public engagement.
Understanding the Cartographic Representation
County boundaries, as depicted on these maps, represent legally defined territorial units. The shapes and sizes of counties vary significantly across states, reflecting historical factors, geographical features, and evolving administrative practices. Some states feature large, sparsely populated counties, while others have numerous smaller counties, often reflecting denser population concentrations. The maps typically incorporate a range of geographical information, including rivers, lakes, major roads, and sometimes, even elevation data, providing context for the county boundaries. Color-coding, shading, and other cartographic techniques are frequently employed to highlight specific data related to each county, such as population density, income levels, or voting patterns.
Data Integration and Analysis
The value of these maps lies in their ability to integrate and visualize diverse datasets. By overlaying demographic data, economic indicators, or environmental information onto the county map, analysts can identify spatial patterns and correlations. This capability is crucial for informed decision-making in various fields. For instance, public health officials can use this information to track disease outbreaks and allocate resources effectively. Similarly, urban planners can leverage this data for infrastructure development, considering population distribution and resource availability. Agricultural researchers might use county-level data to analyze crop yields and optimize farming practices. The possibilities are extensive and span across numerous sectors.
Applications Across Diverse Fields
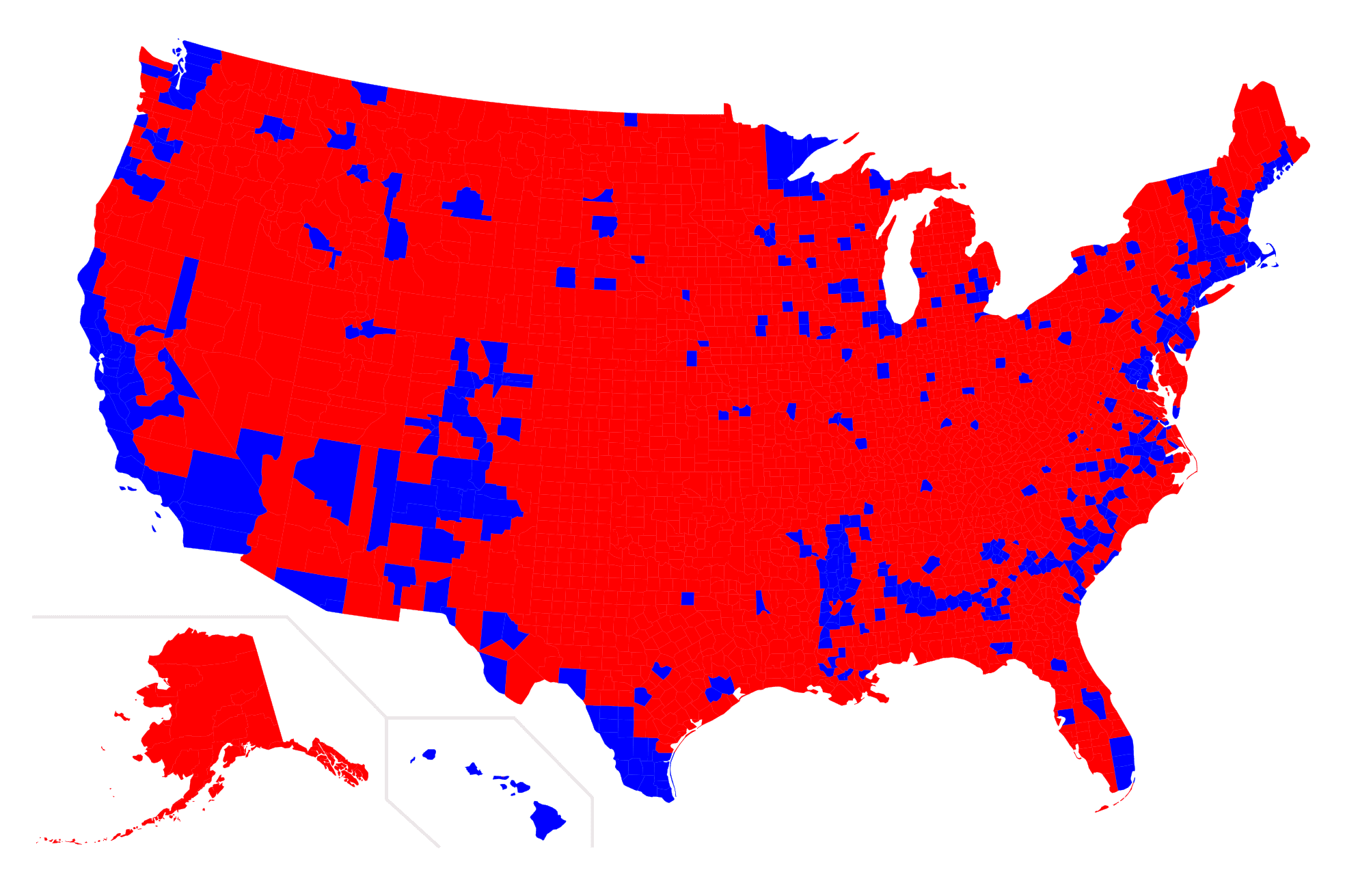
The applications of county-level geographic representations are multifaceted and deeply embedded within the fabric of societal operations. In the realm of politics, these maps are indispensable for understanding electoral districts and analyzing voting patterns. They provide a visual representation of the political landscape, facilitating the analysis of election outcomes and the identification of key demographic trends that influence voting behavior. In the legal field, these maps are used to define jurisdictional boundaries, helping to clarify legal responsibilities and facilitate the administration of justice. Furthermore, emergency response agencies utilize these maps to coordinate disaster relief efforts, ensuring that resources are directed to the areas most in need.
Historical Context and Evolution
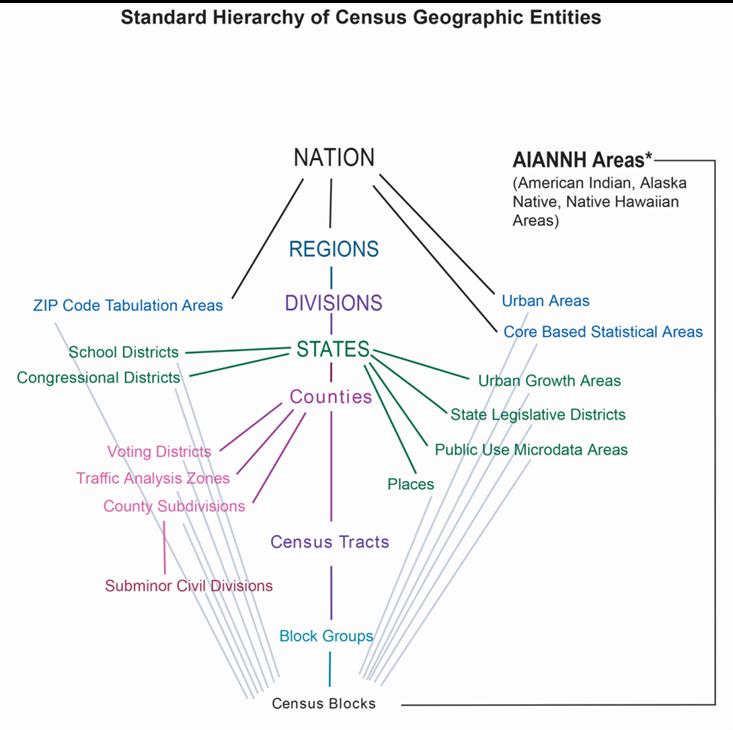
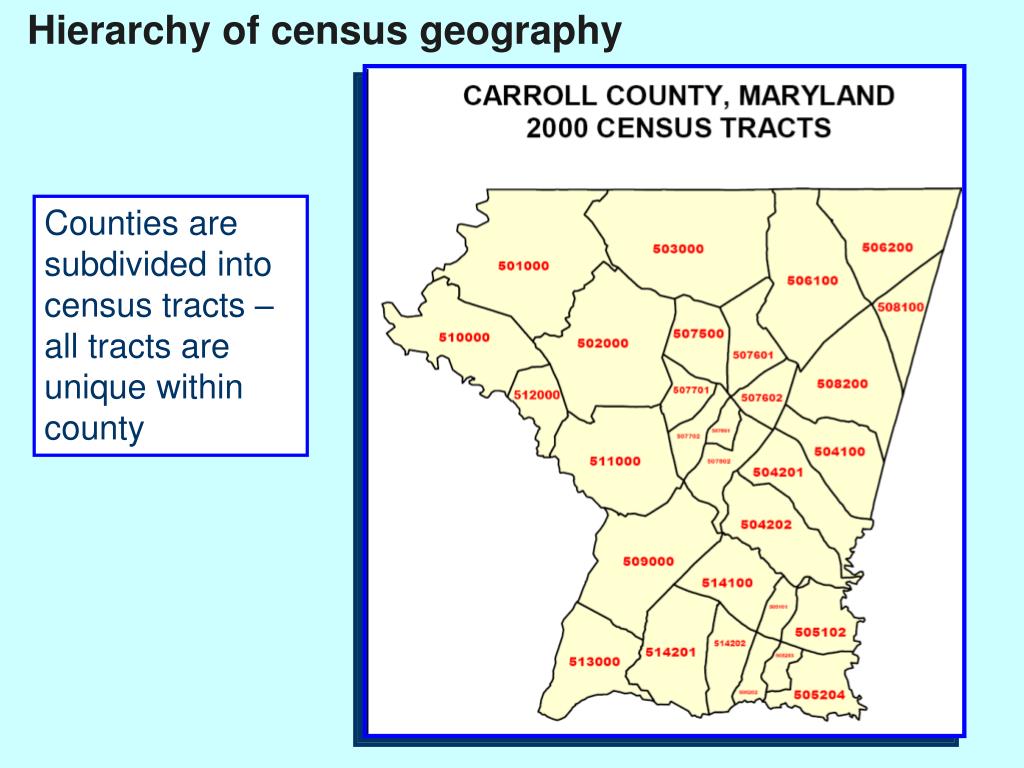
The county system itself has a rich historical context, evolving over centuries to reflect changes in population distribution, economic activities, and political structures. The boundaries depicted on contemporary maps are often the result of a long and complex process of adjustments and revisions, reflecting historical land grants, settlements, and political compromises. Understanding this historical context is essential for interpreting the current configuration of counties and appreciating the nuances of their geographical representation. The evolution of these boundaries also highlights the dynamic nature of administrative divisions and their adaptation to changing societal needs.
Technological Advancements and Data Accessibility
Technological advancements have significantly enhanced the accessibility and utility of these maps. Geographic Information Systems (GIS) technology allows for the creation of interactive maps, enabling users to zoom, pan, and query data at various levels of detail. Online platforms provide readily accessible county-level data, fostering greater transparency and facilitating data-driven decision-making. This increased accessibility empowers researchers, policymakers, and the public with the tools necessary to analyze spatial patterns and draw informed conclusions.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What is the difference between a county and a parish? While both are administrative divisions, the terms "county" and "parish" are used interchangeably in some states, while others use them to represent distinct types of administrative units.
-
How are county boundaries determined? County boundaries are established through legal processes, often reflecting historical events, geographical features, and political considerations. These boundaries can be modified through legislative action or court decisions.
-
Where can I access high-resolution county maps? Many governmental agencies and online mapping services provide access to high-resolution county maps and associated data. Specific sources vary by state.
-
How are county maps used in census data collection? County boundaries serve as a fundamental unit for collecting and reporting census data, providing a spatial framework for demographic analysis.
Tips for Utilizing County Maps
-
Consider the map’s scale and projection: The scale and projection used can affect the accuracy and interpretation of spatial relationships.
-
Verify data sources: Always verify the accuracy and reliability of data used to create or annotate the map.
-
Utilize multiple data layers: Overlaying multiple data layers can reveal correlations and patterns that may not be apparent from a single data layer.
-
Consult with experts: For complex analyses, consulting with GIS specialists or other relevant experts can ensure the accurate interpretation and utilization of the data.
Conclusion
State maps displaying county boundaries are essential tools for understanding the spatial organization of states. Their applications span numerous fields, from political analysis to public health, highlighting their significance in various aspects of societal functioning. The increasing accessibility of data and technological advancements continue to enhance the utility of these maps, making them invaluable resources for research, policy-making, and public engagement. Their historical context and ongoing evolution reflect the dynamic nature of administrative divisions and their adaptation to changing societal needs. Understanding and effectively utilizing these maps is crucial for navigating the complexities of state-level governance and societal organization.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The County-Level Geographic Representation of States: A Comprehensive Overview. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!