Navigating the Waterways: A Comprehensive Guide to the UK’s Inland Waterways Network
Related Articles: Navigating the Waterways: A Comprehensive Guide to the UK’s Inland Waterways Network
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Waterways: A Comprehensive Guide to the UK’s Inland Waterways Network. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Waterways: A Comprehensive Guide to the UK’s Inland Waterways Network

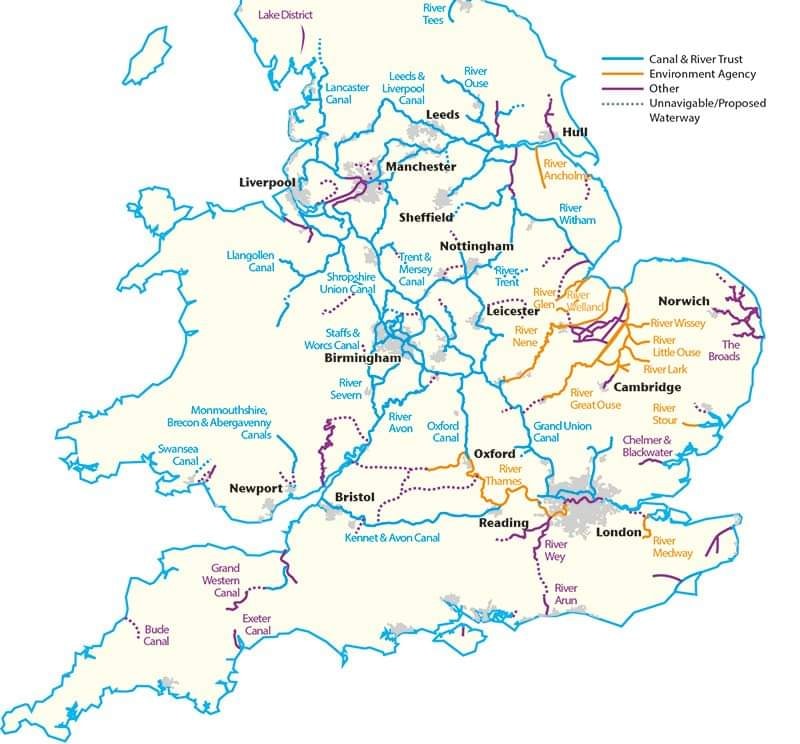
The intricate network of canals and rivers crisscrossing the British Isles constitutes a significant part of the nation’s heritage and infrastructure. Understanding this network requires a thorough grasp of its geography, history, and practical applications. Detailed cartographic representations of this system, often referred to as canal maps, are indispensable tools for navigation, planning, and appreciating the historical and environmental significance of these waterways.
Historical Development and Geographic Scope:
The development of the UK’s canal system spanned centuries, beginning in the late 17th and early 18th centuries with the construction of canals primarily to transport coal and other heavy goods. The Industrial Revolution fueled further expansion, creating a complex network connecting major industrial centers and ports. This network, however, wasn’t uniformly planned; different companies and regions developed their own sections, resulting in variations in dimensions, lock mechanisms, and overall design. Consequently, a comprehensive map needs to reflect this historical evolution, showing not only the current navigable waterways but also the remnants of abandoned or silted-up canals, offering a richer understanding of the network’s history.
Modern canal maps account for this complexity. They typically include details such as:
- Navigable Waterways: Clearly marked canals, rivers, and navigable sections, indicating their precise course, dimensions (width, depth), and any restrictions on navigation.
- Locks and Weirs: The location and type of locks are crucial for navigation planning. Maps typically indicate the number of locks along a particular stretch of waterway, their rise or fall, and any specific operational requirements. Weirs, which control water levels, are also prominently featured.
- Bridges and Tunnels: These structures represent potential obstacles or constraints. Maps indicate their location, type (e.g., swing bridge, fixed bridge), and any height or width restrictions.
- Points of Interest: Many maps incorporate points of interest along the canals, such as marinas, mooring locations, pubs, shops, historical landmarks, and nature reserves. This enhances the map’s utility for leisure boating and tourism.
- Water Levels: Current water levels are often indicated, particularly crucial during periods of drought or heavy rainfall. This information ensures safe navigation and avoids potential hazards.
- Topography: The surrounding terrain is often represented, providing context for the waterways and aiding in route planning. This includes hills, valleys, and other geographical features.
- Scale and Legend: A clear scale and a comprehensive legend are essential for accurate interpretation. These ensure that distances, dimensions, and symbols are easily understood.
The Importance of Accurate Cartography:
Accurate and up-to-date cartography is paramount for several reasons:
- Safe Navigation: Detailed maps are essential for safe navigation, particularly for inexperienced boaters. They help avoid hazards, plan routes effectively, and ensure safe passage through locks and other structures.
- Route Planning: Planning a canal journey requires careful consideration of distances, lock timings, and potential obstacles. Maps allow for efficient route planning, optimizing travel time and minimizing delays.
- Emergency Services: Emergency services, such as rescue teams, rely on accurate maps to locate boats in distress and respond effectively.
- Maintenance and Management: Canal authorities utilize maps for maintenance planning, identifying areas requiring dredging, repair, or other interventions.
- Environmental Management: Maps contribute to environmental monitoring and management, helping to identify ecologically sensitive areas and plan for sustainable waterway management.
- Tourism and Recreation: Detailed maps are indispensable for promoting tourism and recreation along the canals. They help boaters discover new routes, explore interesting places, and plan enjoyable trips.
Frequently Asked Questions:
-
What types of maps are available? A variety of maps cater to different needs, from simple overview maps to highly detailed charts suitable for navigation. Paper maps, digital maps, and online resources are all commonly available.
-
Where can maps be obtained? Maps are available from various sources, including canal and river trust websites, nautical chart suppliers, and online retailers.
-
Are the maps regularly updated? Reputable map providers regularly update their maps to reflect changes in the canal network, such as new constructions, closures, or alterations to locks and bridges.
-
What information should a good map include? A good map should include all the elements mentioned earlier: navigable waterways, locks, bridges, points of interest, water levels, topography, scale, and a comprehensive legend.
-
Are there any free map resources available? Several organizations offer free online maps, though the level of detail may vary.
-
How do I interpret the symbols on a canal map? Each map will have a legend explaining the meaning of its symbols. Familiarizing oneself with the legend is crucial for accurate interpretation.
Tips for Utilizing Canal Maps:
- Check the map’s publication date: Ensure the map is up-to-date to avoid outdated information.
- Understand the scale and legend: Accurately interpreting distances and symbols is crucial for safe navigation.
- Plan the route carefully: Consider factors such as lock timings, bridge heights, and water levels.
- Carry a backup map: Having a paper copy in addition to a digital map is advisable.
- Consult local information: Supplement map information with local knowledge and advice.
- Be aware of weather conditions: Weather can significantly impact navigation.
- Respect the environment: Adhere to responsible boating practices.
Conclusion:
The UK’s canal network represents a significant part of the nation’s history, infrastructure, and natural environment. Detailed and accurate cartographic representations of this network are crucial for safe navigation, efficient route planning, environmental management, and the promotion of tourism and leisure activities. By understanding the historical context, geographical scope, and practical applications of these cartographic resources, individuals and organizations can fully appreciate and utilize this vital aspect of the British landscape. Continuous investment in updating and improving these maps ensures the safe and sustainable use of this invaluable resource for generations to come.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Waterways: A Comprehensive Guide to the UK’s Inland Waterways Network. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!