Navigating the Global Landscape: An Examination of Major World City Maps
Related Articles: Navigating the Global Landscape: An Examination of Major World City Maps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Global Landscape: An Examination of Major World City Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Global Landscape: An Examination of Major World City Maps
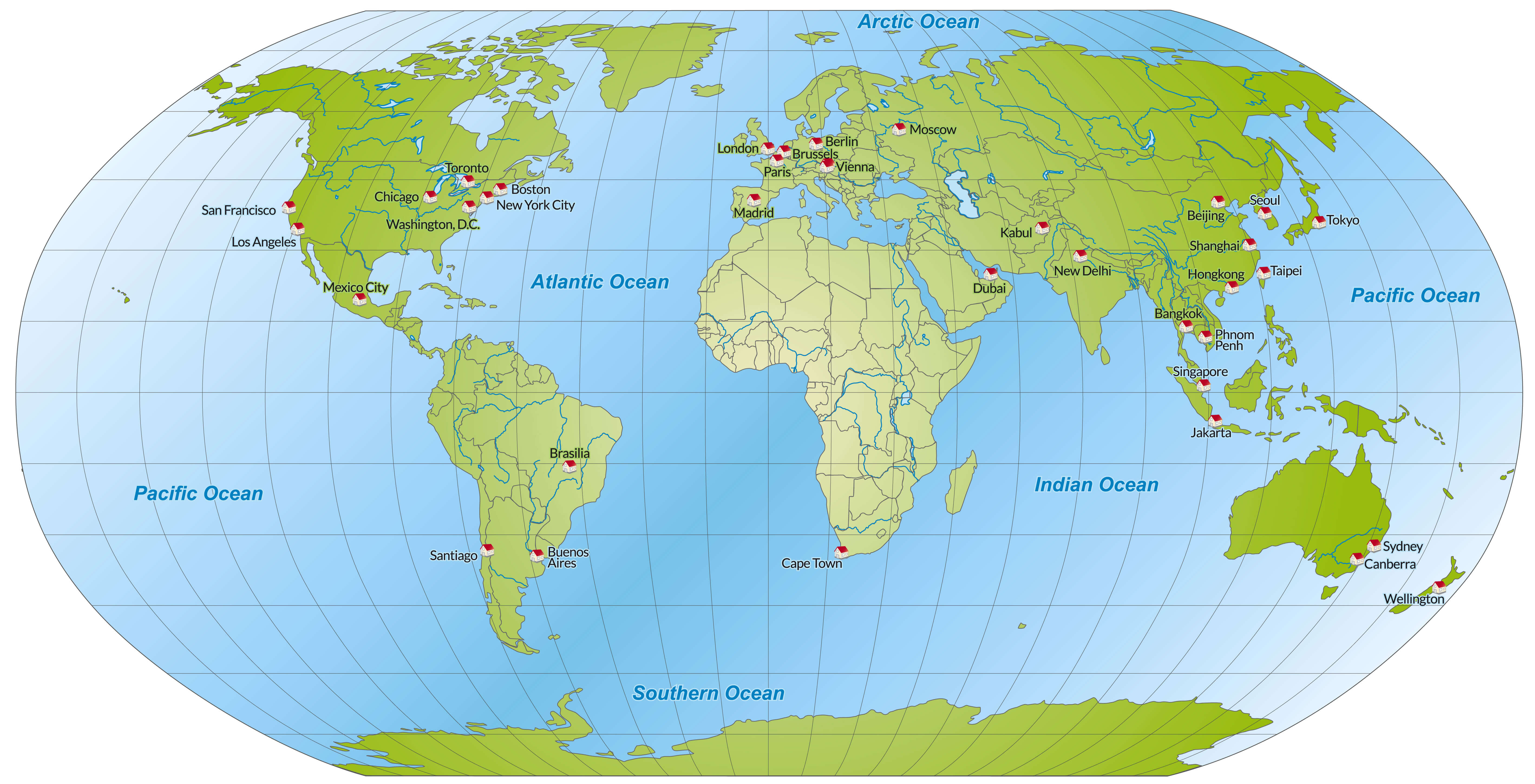
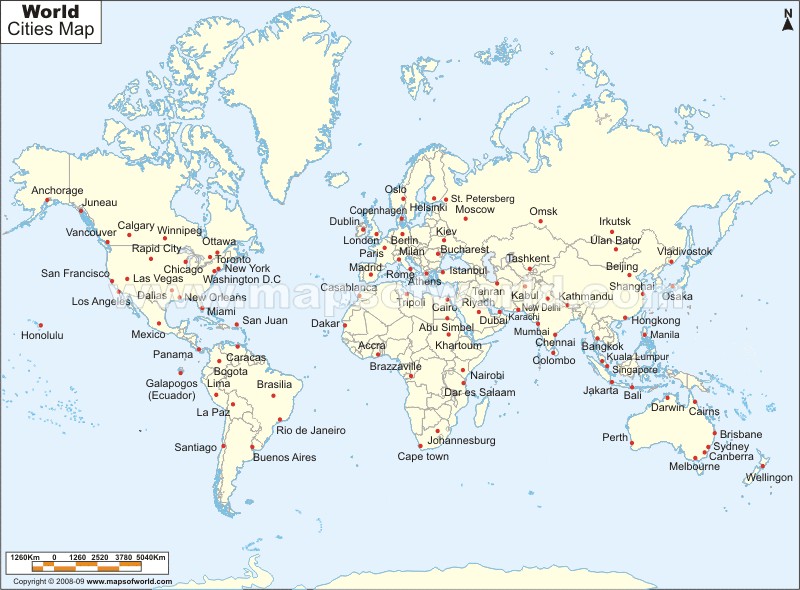
Major world city maps provide a crucial visual representation of global urbanization, offering insights into population distribution, economic activity, and geopolitical influence. These cartographic representations, ranging from simple point-based displays to complex layered visualizations, are indispensable tools for a variety of disciplines, from urban planning and international relations to logistics and tourism. Their utility stems from their ability to condense vast amounts of geographical and demographic information into easily digestible formats.
The design and functionality of these maps vary considerably depending on their intended purpose. Some prioritize sheer scale and location, showing only the largest metropolitan areas as points or simple symbols. Others incorporate detailed information on city boundaries, infrastructure networks (roads, railways, airports), and even demographic breakdowns within city limits. Advanced maps may integrate data on economic indicators (GDP, employment rates), environmental factors (pollution levels, green spaces), or social metrics (crime rates, access to healthcare). The level of detail and the type of data included fundamentally shape the map’s usefulness for specific applications.
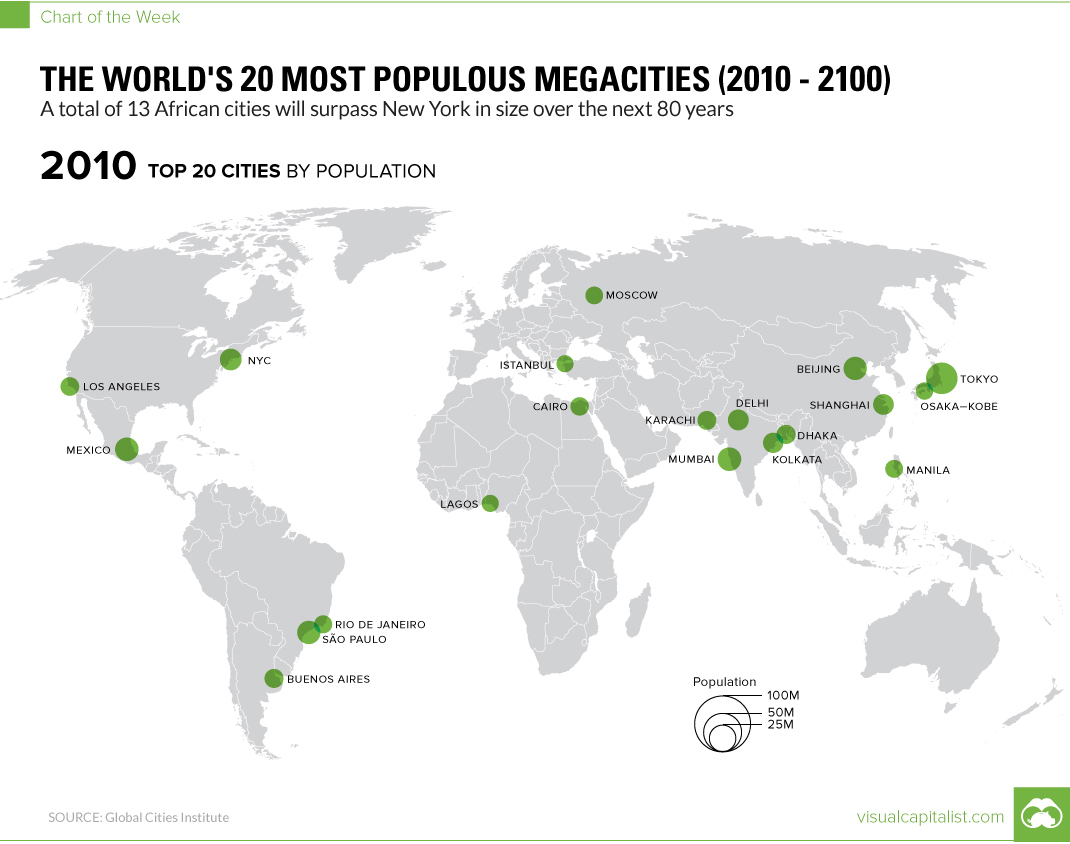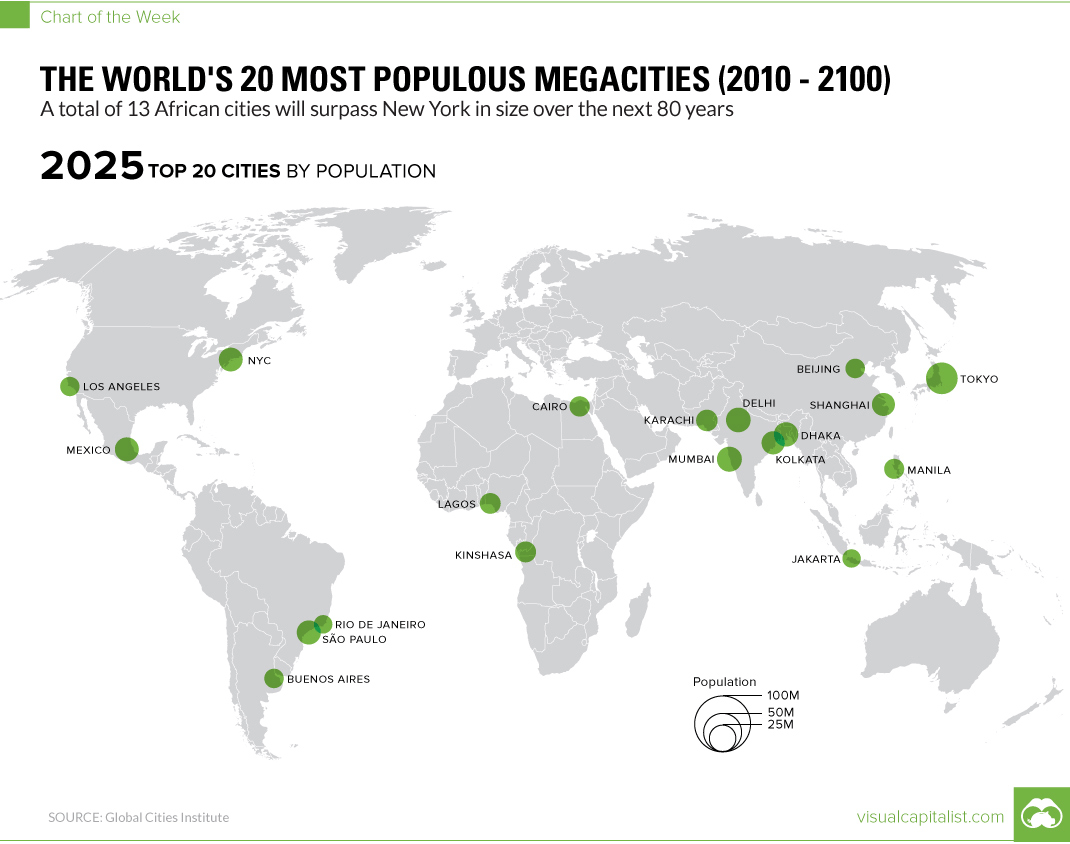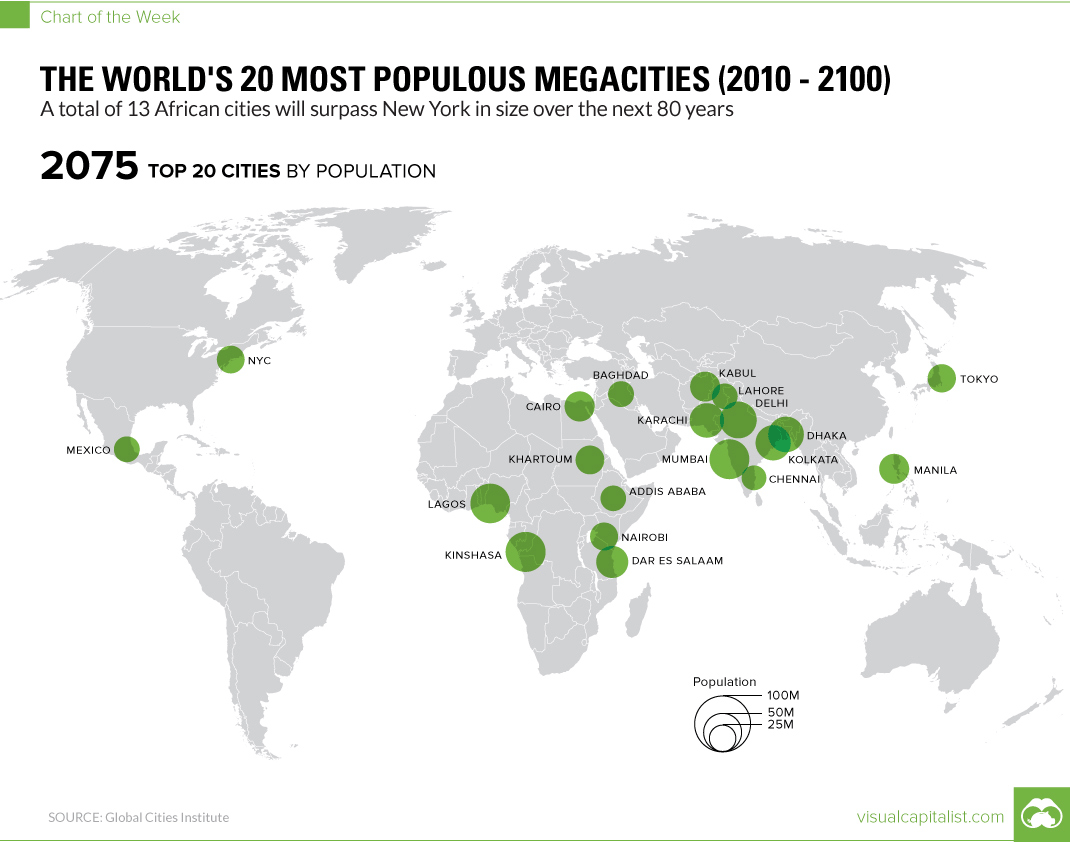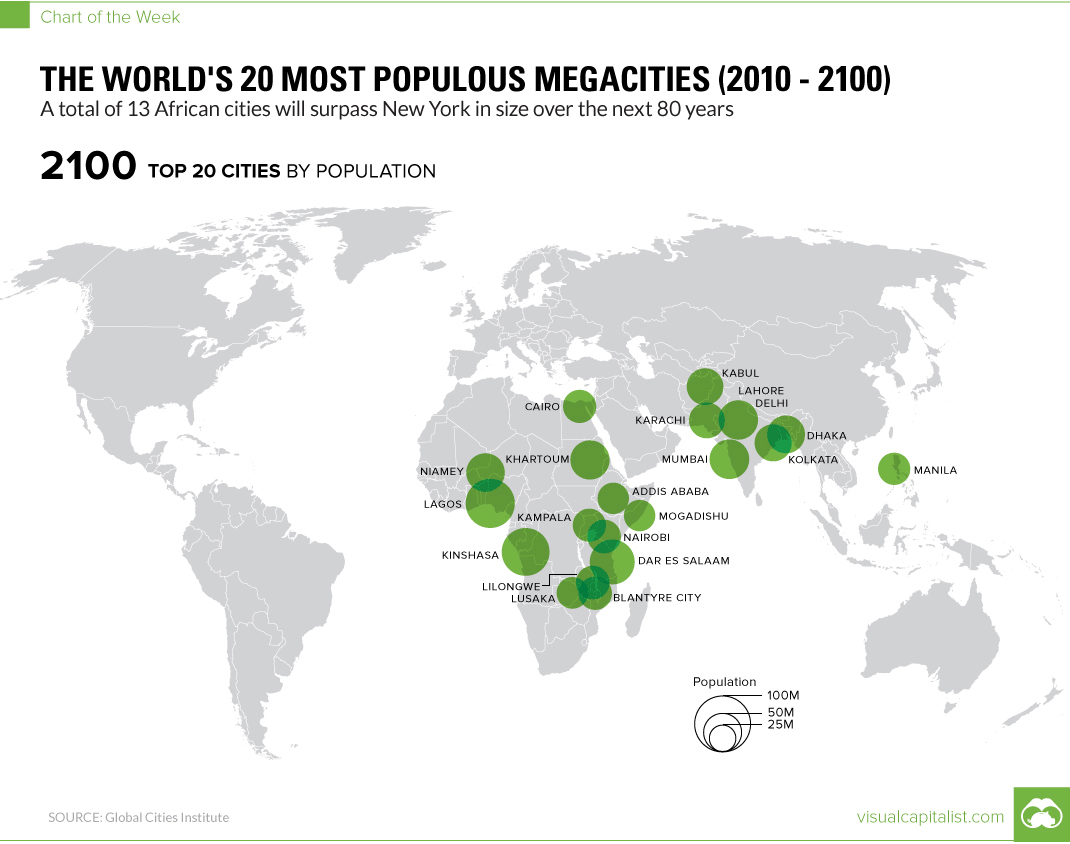
One significant benefit of these visual tools is their ability to highlight global patterns of urbanization. Examination reveals the clustering of major cities along coastlines, near navigable waterways, and in regions with historically favorable climates and resources. This spatial distribution reflects centuries of economic and social development, revealing the intricate interplay between geography and human settlement. Furthermore, these maps readily illustrate the emergence of megacities – urban areas with populations exceeding ten million – and the challenges associated with managing such dense populations, including infrastructure provision, resource allocation, and environmental sustainability.
The geopolitical implications are equally significant. Maps depicting major world cities instantly illuminate the global power dynamics, showing the concentration of economic and political influence in certain regions. The relative size and prominence assigned to cities on a map often reflect their global standing, indicating their importance in international trade, finance, and diplomacy. Analyzing the connections between cities – via flight routes, trade networks, or diplomatic ties – provides further insights into the complex web of global interactions.
Beyond geopolitical analysis, these maps serve practical purposes in diverse sectors. Logistics companies utilize them to optimize supply chains, identifying efficient routes for transporting goods and services across vast distances. Tourism agencies rely on them to showcase destination cities and plan effective marketing campaigns. Urban planners use them to assess the growth and development of cities, identifying areas requiring infrastructure improvements or social interventions. Researchers in various fields, from epidemiology to sociology, utilize these maps as foundational data for their studies, correlating spatial distributions with various social and environmental phenomena.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What is the criteria for defining a "major" world city? The criteria are not universally standardized. Factors considered include population size, economic output, global influence, and the presence of significant international organizations or institutions. Different organizations and researchers may employ varying thresholds, leading to some discrepancies in city rankings.
-
How frequently are major world city maps updated? The frequency of updates depends on the data source and the map’s purpose. Static maps may be updated infrequently, while dynamic, interactive maps can be updated in real-time, reflecting changes in population, economic activity, or infrastructure.
-
What are the limitations of major world city maps? These maps, while informative, offer a simplified representation of complex realities. They may not capture the nuances of internal city structures or the socio-economic disparities within urban areas. Furthermore, the selection of data and the map’s design choices can influence interpretation, potentially leading to biased or misleading conclusions.
-
What projection systems are commonly used in major world city maps? A variety of map projections are employed, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Common choices include Mercator, Gall-Peters, and Robinson projections, each distorting spatial relationships in different ways. The choice of projection should be considered when interpreting distances and relative sizes.
Tips for Utilizing Major World City Maps Effectively
-
Consider the map’s purpose and data sources: Different maps are designed for different purposes. Evaluate the data sources and methodologies employed to ensure the map’s reliability and relevance to your needs.
-
Pay attention to the map’s scale and projection: Understanding the map’s scale and projection is crucial for accurate interpretation of distances and areas.
-
Analyze the map in conjunction with other data sources: Major world city maps should not be considered in isolation. Integrate them with other data sources to gain a more comprehensive understanding of the phenomena under investigation.
-
Be aware of potential biases and limitations: All maps are representations, not perfect reflections of reality. Be mindful of potential biases in data selection and map design that may influence interpretation.
Conclusion
Major world city maps are indispensable tools for understanding global urbanization patterns, geopolitical dynamics, and the intricate interactions between cities across the globe. Their value lies in their ability to synthesize vast amounts of information into easily digestible visual formats, facilitating analysis across diverse disciplines. However, it is crucial to approach these representations critically, acknowledging their limitations and utilizing them in conjunction with other data sources to gain a more comprehensive and nuanced understanding of the complex urban landscapes they depict. Careful consideration of data sources, map projections, and potential biases ensures responsible and effective utilization of these valuable resources.


![Global Navigation Satellite System [Explained]](https://www.advancednavigation.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/03/Tech-Article-GNSS-1600x900-1.png)


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Global Landscape: An Examination of Major World City Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!