Navigating the Depths: A Comprehensive Look at the Tasman Sea
Related Articles: Navigating the Depths: A Comprehensive Look at the Tasman Sea
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Depths: A Comprehensive Look at the Tasman Sea. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Depths: A Comprehensive Look at the Tasman Sea

The Tasman Sea, a vast expanse of water separating Australia and New Zealand, holds a unique position in the global maritime landscape. It is a body of water steeped in history, teeming with diverse marine life, and playing a crucial role in the region’s climate and economy. Understanding the Tasman Sea’s geography, its ecological significance, and its historical and modern-day importance requires a comprehensive exploration.
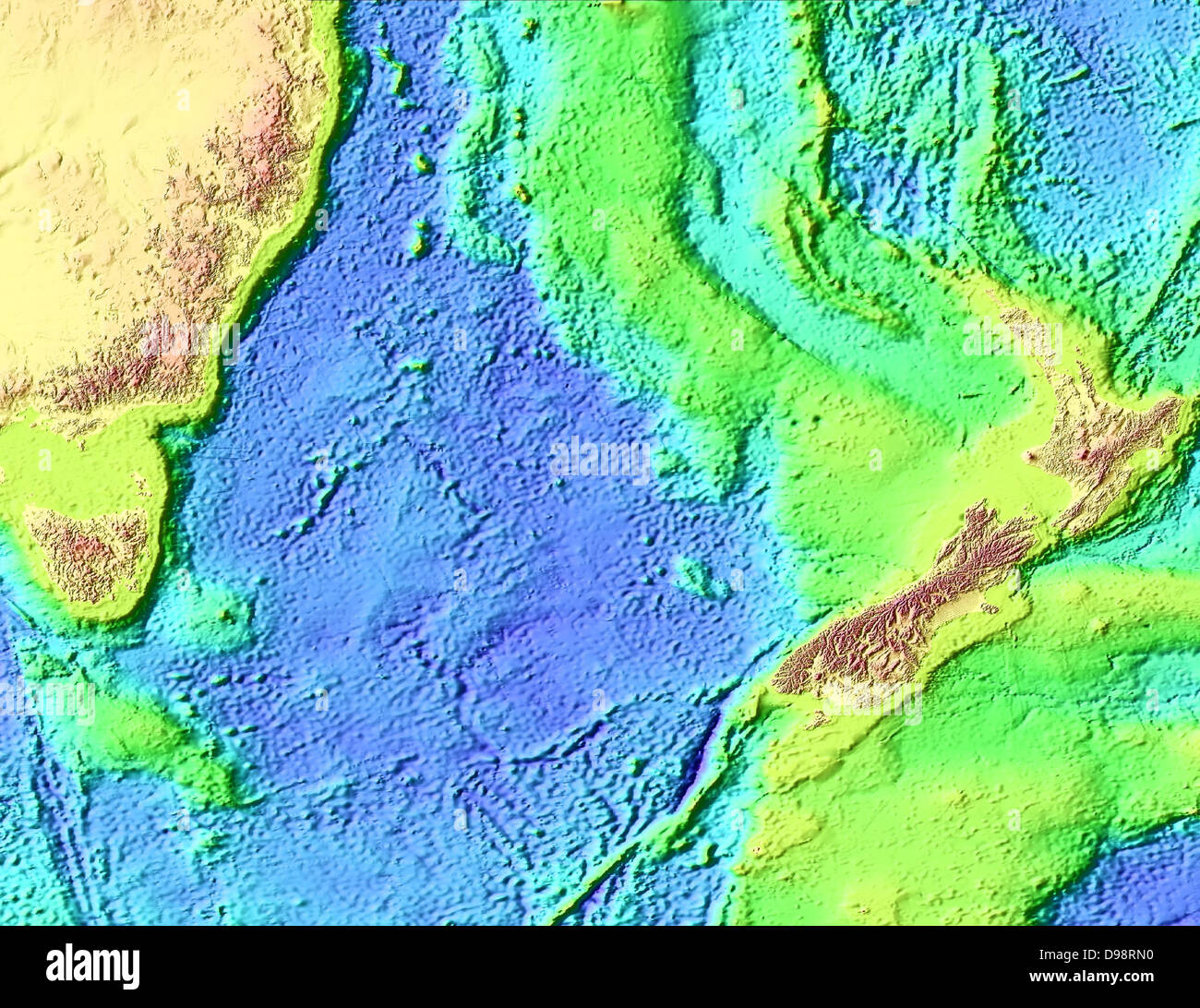
A Geographic Overview
The Tasman Sea, named after the Dutch explorer Abel Janszoon Tasman who first charted it in 1642, stretches for approximately 2,000 kilometers (1,243 miles) at its widest point. It encompasses an area of roughly 2,000,000 square kilometers (772,204 square miles), making it one of the largest marginal seas on Earth. The sea’s boundaries are defined by the eastern coastline of Australia, the southern coastline of New Zealand, and a series of underwater ridges and trenches.
The Tasman Sea’s depth varies considerably, ranging from shallow coastal areas to deep trenches exceeding 5,000 meters (16,404 feet) in depth. The most prominent feature is the Tasman Fracture Zone, a series of trenches and rises that runs along the sea’s western edge. This zone is a major tectonic boundary, where the Australian and Pacific plates collide, resulting in frequent seismic activity and volcanic eruptions.
A Tapestry of Marine Life
The Tasman Sea is a rich and diverse ecosystem, home to a wide array of marine life. Its waters are a haven for various species of fish, including tuna, marlin, and sharks. Whales, dolphins, and seals are also common residents of the sea, migrating along its currents and feeding in its nutrient-rich waters.
The sea’s diverse habitats, from shallow coral reefs to deep-sea canyons, support a complex web of life. The presence of cold, nutrient-rich currents from the Antarctic region contributes to the abundance of phytoplankton, the base of the marine food chain. This abundance fuels the thriving populations of zooplankton, which in turn support larger fish and marine mammals.
Navigational Significance and Historical Significance
The Tasman Sea has played a pivotal role in the history of maritime exploration and trade. It was a vital route for early explorers, connecting Europe to the Pacific and facilitating the discovery of new lands. In the 19th and 20th centuries, the sea became a crucial trade route for shipping goods between Australia and New Zealand, connecting the two countries economically and culturally.
Today, the Tasman Sea remains a significant shipping route, carrying goods between Australia, New Zealand, and other parts of the world. It also plays a vital role in the tourism industry, attracting divers, surfers, and anglers from across the globe.
Climate and Environmental Concerns
The Tasman Sea plays a crucial role in the regional climate, acting as a heat sink and a source of moisture for the surrounding continents. Its currents influence weather patterns in Australia and New Zealand, bringing rain to coastal regions and moderating temperatures.
However, the Tasman Sea is facing increasing environmental pressures. Climate change is leading to rising sea temperatures, ocean acidification, and changes in marine ecosystems. Overfishing, pollution, and habitat destruction also pose threats to the sea’s biodiversity and ecological balance.
Exploring the Tasman Sea: A Deeper Dive
To gain a deeper understanding of the Tasman Sea, it is essential to explore specific aspects of its geography, ecology, and history. Here are some key areas to focus on:
1. The Tasman Fracture Zone: This tectonic boundary is a defining feature of the Tasman Sea, influencing its depth, topography, and seismic activity. Understanding its formation and impact on the surrounding environment is crucial for comprehending the sea’s geological history and its potential for future natural hazards.
2. Marine Biodiversity: The Tasman Sea harbors a remarkable diversity of marine life, ranging from microscopic plankton to large whales. Studying the distribution, abundance, and interactions of these species provides insights into the sea’s ecological health and its vulnerability to human activities.
3. Historical Exploration: The Tasman Sea has been a focal point for maritime exploration for centuries. Examining the journeys of early explorers, their discoveries, and their impact on the region sheds light on the sea’s historical significance and its role in shaping global understanding of the Pacific.
4. Climate Change Impacts: The Tasman Sea is experiencing the effects of climate change, including rising sea temperatures, ocean acidification, and changes in marine ecosystems. Investigating these impacts helps assess the vulnerability of the sea’s biodiversity and its potential for adaptation.
5. Human Activities and Sustainability: The Tasman Sea is subject to various human activities, including shipping, fishing, and tourism. Evaluating the environmental impacts of these activities and promoting sustainable practices is crucial for ensuring the long-term health and productivity of the sea.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the major currents in the Tasman Sea?
The Tasman Sea is influenced by several major currents, including the East Australian Current, the Tasman Front, and the Subtropical Convergence. These currents play a vital role in transporting heat, nutrients, and marine life throughout the region.
2. What are the main islands in the Tasman Sea?
The Tasman Sea is characterized by the presence of several islands, including Tasmania, Norfolk Island, and Lord Howe Island. These islands offer unique ecosystems and provide important habitats for various species.
3. What are the major ports in the Tasman Sea?
The Tasman Sea is home to several important ports, including Sydney, Melbourne, Auckland, and Wellington. These ports serve as hubs for international trade and transport, connecting the region to the global maritime network.
4. What are the major threats to the Tasman Sea’s environment?
The Tasman Sea faces a range of environmental threats, including climate change, overfishing, pollution, and habitat destruction. These threats pose significant risks to the sea’s biodiversity and its ability to support marine life.
5. What are the efforts being made to protect the Tasman Sea?
Various efforts are underway to protect the Tasman Sea’s environment, including the establishment of marine protected areas, the implementation of sustainable fishing practices, and the reduction of pollution from land-based sources.
Tips for Exploring the Tasman Sea
1. Research and Plan Your Trip: Before embarking on any exploration of the Tasman Sea, it is essential to conduct thorough research and plan your trip carefully. Consider factors such as weather conditions, tides, and the availability of resources.
2. Seek Expert Guidance: If you are interested in diving, fishing, or other activities in the Tasman Sea, seek guidance from experienced professionals. They can provide valuable insights into safety precautions, local regulations, and the best spots to explore.
3. Respect the Environment: When exploring the Tasman Sea, it is crucial to respect the environment and minimize your impact. Avoid littering, disturbing marine life, and damaging sensitive habitats.
4. Support Conservation Efforts: Contribute to the protection of the Tasman Sea by supporting organizations dedicated to marine conservation. These organizations work to address threats such as overfishing, pollution, and habitat loss.
5. Learn and Educate Others: Share your knowledge of the Tasman Sea with others, promoting awareness of its importance and the need for its protection. By educating others, you can contribute to broader efforts to conserve this vital ecosystem.
Conclusion
The Tasman Sea is a vast and complex body of water, playing a crucial role in the region’s climate, economy, and biodiversity. Its geographical features, ecological significance, and historical importance make it a fascinating subject of study and exploration. Understanding the Tasman Sea’s interconnectedness with the surrounding continents and its vulnerability to human activities is essential for promoting its sustainable management and ensuring its long-term health. By fostering a deeper appreciation for this remarkable ecosystem, we can contribute to its protection and preservation for future generations.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Depths: A Comprehensive Look at the Tasman Sea. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!