Charting the Spice Islands: A Journey Through the East Indies Map
Related Articles: Charting the Spice Islands: A Journey Through the East Indies Map
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Charting the Spice Islands: A Journey Through the East Indies Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Charting the Spice Islands: A Journey Through the East Indies Map

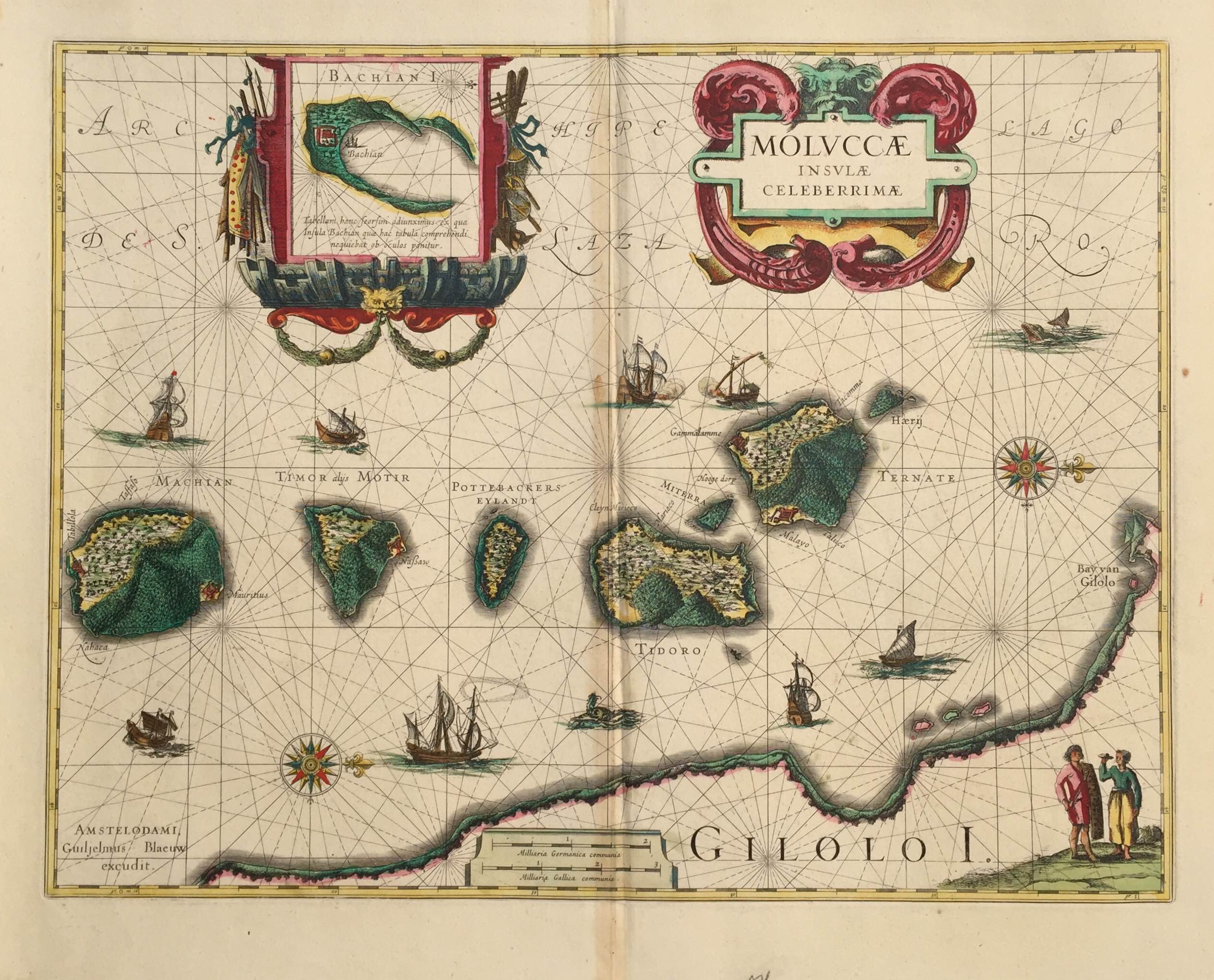
The term "East Indies" evokes images of exotic spices, opulent trade, and the vibrant tapestry of cultures that once flourished across a vast expanse of the Asian archipelago. While the geographical boundaries of the East Indies have shifted over time, the term generally encompasses the islands of Southeast Asia, including Indonesia, Malaysia, Singapore, Brunei, East Timor, and parts of the Philippines.
The East Indies map, a cartographic representation of this region, holds immense historical and cultural significance. It served as a vital tool for navigation, trade, and exploration, shaping the course of global history and leaving an enduring legacy on the world.
The Evolution of the East Indies Map:
The earliest known representations of the East Indies emerged in the 1st century AD with the work of Greek geographers like Ptolemy. These maps, based on limited accounts and hearsay, depicted the region as a land of mythical creatures and exaggerated geographic features.
During the Age of Exploration, European powers, particularly the Portuguese and Dutch, embarked on ambitious voyages to the East Indies, driven by a insatiable thirst for spices like cloves, nutmeg, and pepper. These expeditions led to the creation of more accurate maps, fueled by detailed observations and firsthand accounts.
The Dutch, in particular, established a powerful colonial presence in the region, creating detailed cartographic records that helped them control trade routes and exploit the region’s resources. Their maps, often based on meticulous surveys and scientific observations, contributed significantly to the advancement of cartography and geographical knowledge.
The Importance of the East Indies Map:
The East Indies map played a crucial role in shaping global trade and exploration. It enabled European powers to navigate the complex waterways and treacherous seas of the region, facilitating the transportation of valuable commodities like spices, textiles, and precious metals.
Beyond its commercial significance, the East Indies map provided crucial insights into the region’s diverse geography, cultures, and natural resources. It allowed European cartographers and scholars to study the intricate network of islands, the unique ecosystems, and the diverse societies that inhabited the region.
The Cultural Impact of the East Indies Map:
The East Indies map also had a profound cultural impact, influencing art, literature, and popular imagination. European artists and writers, inspired by accounts of the region’s exotic wonders, created works that captured the allure and mystique of the East Indies.
These representations, often romanticized and idealized, contributed to the development of Orientalism, a complex and often problematic discourse that shaped Western perceptions of the East.
The Legacy of the East Indies Map:
The legacy of the East Indies map extends far beyond its historical significance. It serves as a reminder of the interconnectedness of the world and the enduring impact of trade and exploration on human societies.
The map also underscores the importance of cartography as a tool for understanding and navigating the world. It highlights the power of maps to shape our perceptions, influence our actions, and connect us to different cultures and places.
FAQs about the East Indies Map:
1. What is the difference between the East Indies and the West Indies?
The East Indies refers to the islands of Southeast Asia, while the West Indies encompasses the islands of the Caribbean Sea. The two regions were historically linked by European trade routes, and both were targeted by European colonial powers for their valuable resources.
2. Who were the major European powers involved in the East Indies trade?
The Portuguese, Dutch, British, and Spanish were the main European powers involved in the East Indies trade. Each nation sought to establish control over key trade routes and exploit the region’s resources.
3. What were the main commodities traded in the East Indies?
Spices, particularly cloves, nutmeg, and pepper, were highly sought after commodities in the East Indies. Other valuable goods included textiles, precious metals, and exotic woods.
4. How did the East Indies map contribute to the development of cartography?
The maps created by European explorers and traders in the East Indies incorporated new techniques and scientific observations, leading to advancements in cartography. These maps helped to refine techniques for measuring distances, charting coastlines, and mapping the interior of continents.
5. What are some examples of artistic and literary works influenced by the East Indies map?
The East Indies map inspired numerous artistic and literary works, including:
- "The Arabian Nights" (collection of Middle Eastern folk tales)
- "The Tempest" (Shakespearean play)
- "The Adventures of Robinson Crusoe" (novel by Daniel Defoe)
- Paintings by Dutch masters like Rembrandt and Vermeer
Tips for Studying the East Indies Map:
- Examine the map’s historical context: Consider the time period, the cartographer’s perspective, and the political and economic factors that influenced the map’s creation.
- Analyze the map’s symbols and conventions: Pay attention to the use of colors, lines, and symbols to represent different features, such as landmasses, waterways, and cities.
- Compare different versions of the map: Examine how the East Indies map evolved over time, reflecting changes in knowledge, exploration, and political power.
- Connect the map to other historical sources: Integrate the map with historical documents, accounts, and artifacts to gain a comprehensive understanding of the region’s history and culture.
Conclusion:
The East Indies map stands as a testament to the enduring power of cartography to shape our understanding of the world. It serves as a window into the past, offering insights into the complex interplay of trade, exploration, and cultural exchange that shaped the global landscape. By studying the East Indies map, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the interconnectedness of human societies and the enduring legacy of the region’s rich history and culture.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Charting the Spice Islands: A Journey Through the East Indies Map. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!