A Visual Journey Through Africa: Unveiling the Continent’s Geography and Significance
Related Articles: A Visual Journey Through Africa: Unveiling the Continent’s Geography and Significance
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Visual Journey Through Africa: Unveiling the Continent’s Geography and Significance. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Visual Journey Through Africa: Unveiling the Continent’s Geography and Significance
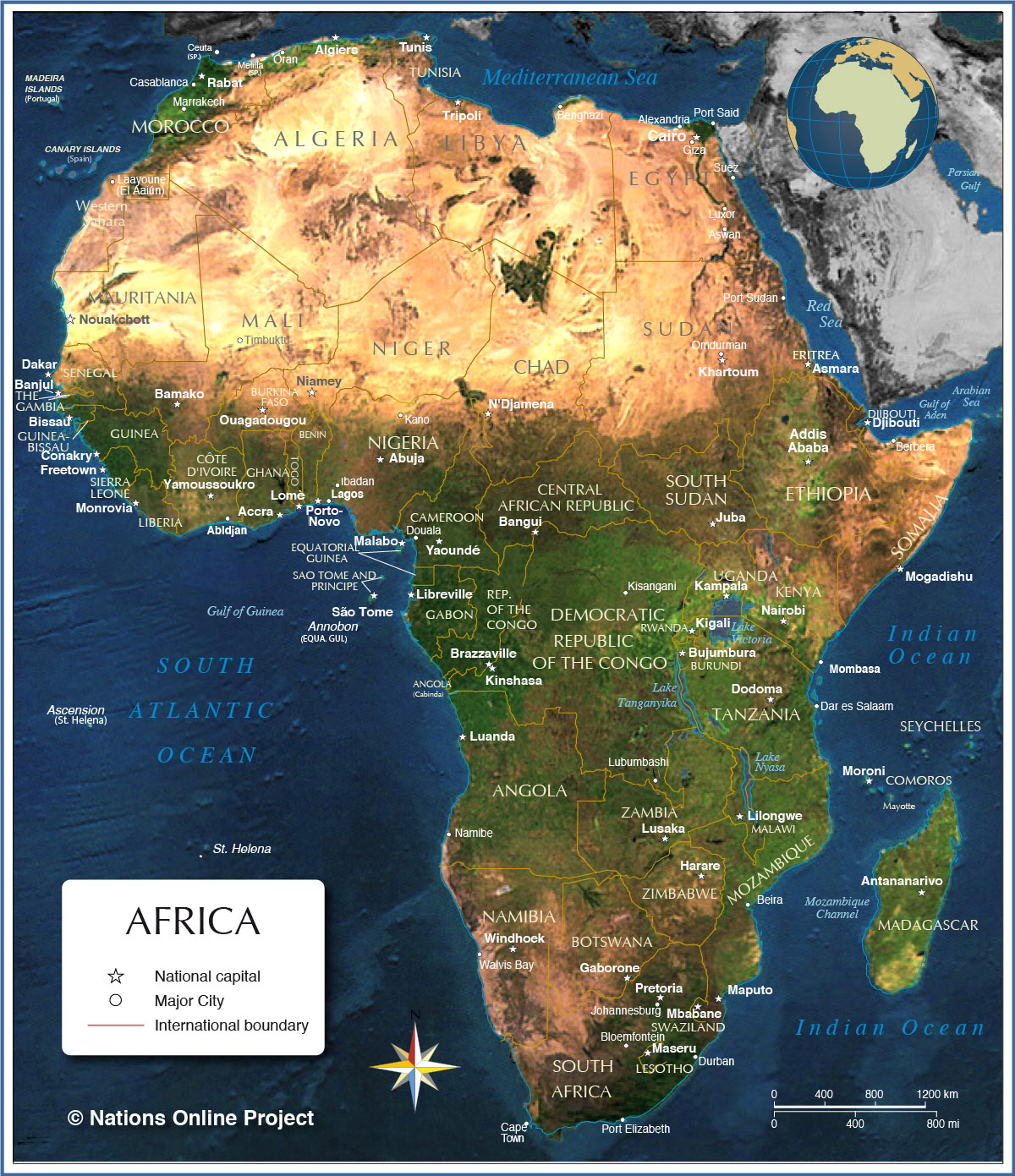
The African map, a vibrant tapestry of colors and shapes, holds within its lines a story of immense diversity, rich history, and profound cultural significance. It is a powerful visual representation of a continent that has shaped the world in countless ways. This article delves into the intricacies of the African map, exploring its geographical features, historical context, and the profound impact it has on our understanding of the world.
A Continent of Contrasts: Geographical Diversity
The African map immediately reveals the continent’s remarkable geographical diversity. From the snow-capped peaks of Mount Kilimanjaro to the vast expanse of the Sahara Desert, from the lush rainforests of the Congo Basin to the arid plains of the Kalahari, Africa encompasses a remarkable range of landscapes.
Mountain Ranges and High Plateaus: The continent boasts impressive mountain ranges, including the Atlas Mountains in North Africa, the Ethiopian Highlands, and the Drakensberg Mountains in Southern Africa. These mountain ranges, along with high plateaus like the East African Plateau, play a crucial role in shaping the continent’s climate and ecosystems.
Rivers and Lakes: Africa is home to some of the world’s most significant rivers, including the Nile, the Congo, and the Niger. These rivers serve as lifelines for communities, providing vital water resources for agriculture, transportation, and sustenance. The continent also features numerous large lakes, such as Lake Victoria, Lake Tanganyika, and Lake Malawi, which support diverse aquatic ecosystems and contribute to the region’s biodiversity.
Deserts and Savannas: The African map prominently displays the vast Sahara Desert, the world’s largest hot desert, which stretches across North Africa. The continent also features other extensive deserts, including the Namib and the Kalahari. In contrast, the savannas, characterized by grasslands and scattered trees, cover a substantial portion of the continent, providing habitat for a vast array of wildlife.
Coastal Regions and Islands: Africa boasts a long coastline, with diverse coastal regions ranging from the sandy beaches of the Mediterranean to the rocky shores of the Atlantic. The continent also encompasses numerous islands, including Madagascar, the Seychelles, and the Comoros, each with unique ecosystems and cultures.
Understanding the Past: Historical Significance
The African map is not merely a geographical representation; it is a powerful tool for understanding the continent’s rich history. It reveals the ancient trade routes that connected different civilizations, the empires that rose and fell, and the movements of people across the continent.
Ancient Civilizations: The map highlights the locations of ancient civilizations, such as the Egyptian civilization, the Kingdom of Kush, and the Aksumite Empire. These civilizations flourished in different regions of the continent, leaving behind lasting legacies in art, architecture, and cultural practices.
Colonialism and Its Impact: The African map also bears the scars of colonialism. The arbitrary lines drawn by European powers in the 19th century, dividing the continent into distinct colonies, continue to influence the political landscape of Africa today. These colonial boundaries often ignored existing cultural and linguistic divisions, leading to conflicts and instability in many post-colonial nations.
The Rise of Nation-States: The African map reflects the emergence of independent nation-states following the decolonization process in the 20th century. The continent now comprises 54 sovereign states, each with its own unique history, culture, and challenges.
A Continent of Diversity: Cultural Tapestry
The African map is a visual representation of the continent’s incredible cultural diversity. It encompasses a wide range of languages, religions, traditions, and artistic expressions.
Linguistic Diversity: Africa is home to over 2,000 languages, making it one of the most linguistically diverse continents in the world. The map reveals the distribution of language families, including Afro-Asiatic, Niger-Congo, and Nilo-Saharan, showcasing the complex linguistic tapestry of the continent.
Religious Diversity: Africa is a continent of diverse religious beliefs, with Christianity, Islam, traditional African religions, and other faiths coexisting within its borders. The map reveals the geographical distribution of these religions, highlighting the religious landscape of the continent.
Artistic Expressions: The African map is a testament to the continent’s vibrant artistic traditions. From the intricate masks of the Yoruba people to the colorful textiles of the Ashanti, from the powerful sculptures of the Dogon to the captivating music of the Maasai, African art reflects the richness and diversity of the continent’s cultural heritage.
Challenges and Opportunities: Looking Towards the Future
The African map also highlights the challenges and opportunities facing the continent in the 21st century. It reveals the vast disparities in development across different regions, the ongoing conflicts and instability in some areas, and the potential for economic growth and social progress.
Economic Development: The map highlights the potential for economic growth in Africa, with its vast natural resources, young population, and growing middle class. However, the continent faces challenges in infrastructure development, access to education and healthcare, and overcoming poverty and inequality.
Environmental Sustainability: The African map also reveals the importance of environmental sustainability for the continent’s future. Climate change, deforestation, and pollution pose significant threats to the environment and the livelihoods of millions of people.
Peace and Security: The map highlights the ongoing conflicts and instability in some parts of Africa, driven by factors such as poverty, inequality, and ethnic tensions. Achieving peace and security is crucial for the continent’s development and prosperity.
FAQs about the African Map
1. What are the largest countries in Africa by land area?
The largest countries in Africa by land area are:
- Algeria
- Democratic Republic of the Congo
- Sudan
- Libya
- Chad
2. What are the most densely populated countries in Africa?
The most densely populated countries in Africa are:
- Rwanda
- Burundi
- Mauritius
- Comoros
- Seychelles
3. What are the major mountain ranges in Africa?
The major mountain ranges in Africa include:
- Atlas Mountains
- Ethiopian Highlands
- Drakensberg Mountains
- Ruwenzori Mountains
- Mount Kilimanjaro
4. What are the main rivers in Africa?
The main rivers in Africa include:
- Nile River
- Congo River
- Niger River
- Zambezi River
- Orange River
5. What are the major deserts in Africa?
The major deserts in Africa include:
- Sahara Desert
- Namib Desert
- Kalahari Desert
6. What are the major lakes in Africa?
The major lakes in Africa include:
- Lake Victoria
- Lake Tanganyika
- Lake Malawi
- Lake Chad
- Lake Turkana
7. What are the major islands in Africa?
The major islands in Africa include:
- Madagascar
- Seychelles
- Comoros
- Mauritius
- Réunion
Tips for Using the African Map
- Explore the continent’s diversity: Use the map to learn about the different landscapes, cultures, and languages found across Africa.
- Trace historical events: The map can help you understand the historical movements of people, the rise and fall of empires, and the impact of colonialism.
- Identify geographical features: The map provides a visual representation of the continent’s major rivers, mountains, deserts, and lakes.
- Compare and contrast regions: Use the map to compare and contrast different regions of Africa, such as North Africa, West Africa, and Southern Africa.
- Gain a global perspective: The map helps you understand Africa’s place in the world and its connections to other continents.
Conclusion
The African map is more than just a geographical representation; it is a powerful tool for understanding the continent’s rich history, diverse cultures, and complex challenges. It serves as a reminder of the continent’s immense potential and the importance of fostering peace, development, and sustainability for the benefit of all its people. By studying and appreciating the African map, we gain a deeper understanding of this fascinating continent and its profound impact on the world.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Visual Journey Through Africa: Unveiling the Continent’s Geography and Significance. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!