A Tapestry of Faith: Understanding the Religious Landscape of the Middle East
Related Articles: A Tapestry of Faith: Understanding the Religious Landscape of the Middle East
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Tapestry of Faith: Understanding the Religious Landscape of the Middle East. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Tapestry of Faith: Understanding the Religious Landscape of the Middle East

The Middle East, a region steeped in history and civilization, is also a vibrant melting pot of religious traditions. Its diverse tapestry of faiths, woven over millennia, has shaped its cultural identity, political dynamics, and social structures. Understanding the religious map of the Middle East is crucial for comprehending the region’s complexities and navigating its intricate relationships.
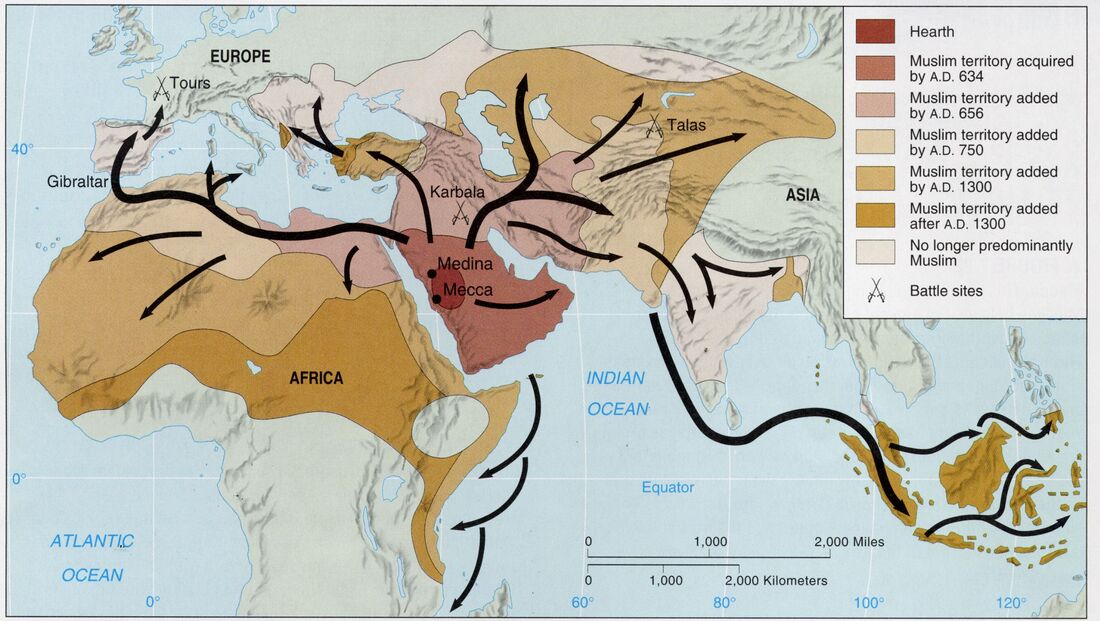
Islam: The Dominant Faith
Islam, the youngest of the Abrahamic faiths, holds the most significant presence in the Middle East. It emerged in the 7th century CE in the Arabian Peninsula, with the prophet Muhammad as its founder. Islam’s central tenets revolve around the belief in one God (Allah) and the submission to His will. The region boasts a diverse Islamic landscape, encompassing Sunni and Shia branches, each with its own theological interpretations and practices.
Sunni Islam dominates in countries like Saudi Arabia, Egypt, and Jordan, while Shia Islam holds sway in Iran, Iraq, and Lebanon. This division has often led to tensions and conflicts, particularly in the context of regional politics.
Christianity: A Long and Rich History
Christianity, the second most prominent religion in the Middle East, boasts an equally rich and complex history. Its origins can be traced back to the life and teachings of Jesus Christ in Judea, now part of Israel. The region witnessed the rise of early Christianity, with significant communities established in areas like Syria, Lebanon, and Palestine.
The Middle East is home to various Christian denominations, including Orthodox, Catholic, and Protestant churches. These denominations often represent distinct theological perspectives and historical experiences, contributing to the region’s religious diversity.
Judaism: Ancient Roots and Modern Identity
Judaism, the oldest of the Abrahamic faiths, finds its roots in the ancient land of Israel. Its history is intricately intertwined with the region’s cultural and political landscape. Judaism’s core principles revolve around the belief in one God, the observance of Mosaic law, and the expectation of a messianic redemption.
The Middle East remains the heartland of Judaism, with Israel being the only country where it constitutes the majority religion. However, significant Jewish communities also exist in other countries like Lebanon, Iran, and Syria, though their presence has been historically marked by persecution and displacement.
Other Faiths: A Mosaic of Beliefs
While Islam, Christianity, and Judaism dominate the religious map of the Middle East, the region also hosts a variety of other faiths, each contributing to its unique cultural tapestry.
Druze communities, found primarily in Lebanon and Syria, adhere to a syncretic faith that blends elements of Islam, Christianity, and other ancient traditions. Yazidis, often referred to as "Devil Worshippers," hold a distinct religious identity rooted in ancient Mesopotamian beliefs, with their communities primarily concentrated in Iraq.
Zoroastrianism, an ancient Persian religion that predates Islam, has dwindled in recent centuries, with a small number of Zoroastrians still residing in Iran and other parts of the region. Baháʼí Faith, founded in Persia in the 19th century, emphasizes the unity of all religions and promotes a universal message of peace and equality.
Religious Interactions: A Complex Tapestry
The religious landscape of the Middle East is characterized by a complex interplay of cooperation and conflict. While religious tolerance and interfaith dialogue are crucial for fostering peace and stability, historical tensions, political maneuvering, and sectarian divisions often fuel conflicts and complicate relations between different communities.
Historical Conflicts: The region’s history is marked by numerous religious conflicts, including the Crusades, the Ottoman conquest, and the Arab-Israeli conflict. These historical events have left lasting scars and continue to shape the region’s political dynamics and social interactions.
Contemporary Challenges: In the contemporary context, religious tensions are often intertwined with political and economic issues. The rise of religious extremism, sectarian violence, and the persecution of religious minorities pose significant challenges to regional stability and peaceful coexistence.
Importance of Religious Understanding: Understanding the religious map of the Middle East is crucial for fostering interfaith dialogue, promoting tolerance, and resolving conflicts. It requires engaging with the diverse religious traditions, appreciating their shared values, and recognizing the common ground that can bridge differences.
Benefits of Religious Diversity: The religious diversity of the Middle East, while often a source of tension, also represents a source of cultural richness and intellectual dynamism. The interaction of different faiths has historically fostered innovation, artistic expression, and philosophical inquiry.
FAQs: A Deeper Understanding
Q: What is the dominant religion in the Middle East?
A: Islam is the dominant religion in the Middle East, with both Sunni and Shia branches holding significant presence in the region.
Q: What are the main branches of Islam in the Middle East?
A: The two main branches of Islam in the Middle East are Sunni and Shia. Sunni Islam dominates in countries like Saudi Arabia, Egypt, and Jordan, while Shia Islam is prevalent in Iran, Iraq, and Lebanon.
Q: How does Christianity relate to the history of the Middle East?
A: Christianity has a long and rich history in the Middle East, originating in Judea and spreading throughout the region. The region witnessed the rise of early Christianity, and various Christian denominations, including Orthodox, Catholic, and Protestant churches, continue to flourish in the Middle East.
Q: Where is Judaism most prevalent in the Middle East?
A: Judaism is most prevalent in Israel, the only country where it constitutes the majority religion. Significant Jewish communities also exist in other countries like Lebanon, Iran, and Syria.
Q: What are some of the other faiths present in the Middle East?
A: The Middle East is home to various other faiths, including Druze, Yazidi, Zoroastrianism, and Baháʼí Faith, each contributing to the region’s cultural diversity.
Tips for Navigating the Religious Landscape
- Respect and Empathy: Approach religious differences with respect and empathy, recognizing the importance of faith in people’s lives.
- Open Dialogue: Engage in open and honest dialogue with individuals from different religious backgrounds, fostering understanding and building bridges.
- Critical Thinking: Develop a critical understanding of religious narratives, avoiding generalizations and stereotypes.
- Historical Context: Recognize the historical context of religious tensions and conflicts, seeking to learn from the past to build a more peaceful future.
- Focus on Common Ground: Identify shared values and principles that can unite people of different faiths, promoting cooperation and harmony.
Conclusion: A Call for Understanding and Peace
The religious map of the Middle East reflects a complex and dynamic interplay of faiths, traditions, and historical experiences. Understanding this tapestry of beliefs is crucial for navigating the region’s complexities, promoting interfaith dialogue, and fostering a culture of peace and tolerance. By engaging with diverse religious communities, recognizing shared values, and promoting understanding, we can contribute to a more harmonious and just future for the Middle East.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Tapestry of Faith: Understanding the Religious Landscape of the Middle East. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!