A Journey Through Time: Exploring the Historical Provinces of France
Related Articles: A Journey Through Time: Exploring the Historical Provinces of France
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Journey Through Time: Exploring the Historical Provinces of France. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Journey Through Time: Exploring the Historical Provinces of France
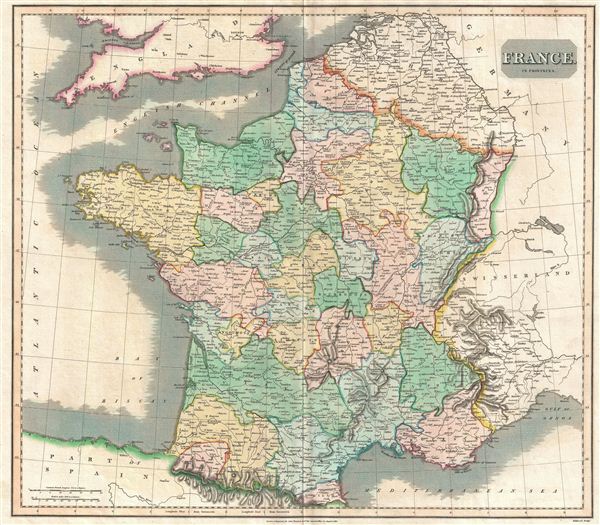
France, a nation steeped in history and cultural diversity, boasts a rich tapestry woven from its diverse regional identities. These identities are deeply intertwined with the historical provinces that once defined the country’s political and administrative landscape. While modern France is divided into 18 administrative regions, understanding the historical provinces offers a unique perspective on its cultural heritage, linguistic nuances, and architectural styles.
A Glimpse into the Past: The Historical Provinces of France
The historical provinces of France emerged over centuries, shaped by evolving political boundaries, dynastic alliances, and regional identities. These provinces, often referred to as "pays" or "paysages," were not merely administrative units but reflected distinct cultural, linguistic, and historical characteristics.
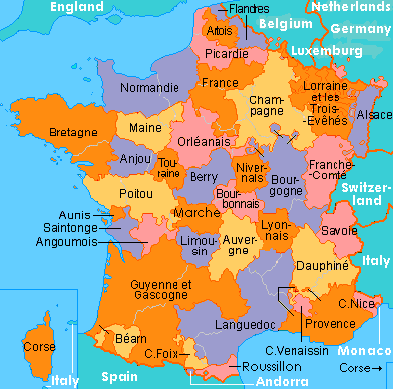
Mapping the Provinces:
1. The Northern Provinces:
-
Picardy: Situated in the north of France, Picardy is renowned for its rolling countryside, fertile plains, and historic cities like Amiens and Saint-Quentin. Its cultural heritage is deeply rooted in the wool trade, its distinctive dialect, and its strong connection to the Hundred Years’ War.
-
Normandy: Known for its dramatic coastline, picturesque countryside, and historic cities like Rouen and Caen, Normandy is a region steeped in Viking heritage. Its cultural identity is marked by its distinct dialect, its rich culinary traditions, and its pivotal role in the D-Day landings during World War II.
-
Île-de-France: Encompassing Paris and its surrounding areas, Île-de-France is the heart of France, both politically and culturally. It boasts a vibrant mix of historical monuments, modern architecture, and diverse cultural institutions.
-
Champagne-Ardenne: This region is renowned for its sparkling wine, its rolling hills, and its historical cities like Reims and Troyes. Its cultural identity is linked to its rich agricultural heritage, its traditional Champagne production, and its significant role in the French Revolution.
2. The Western Provinces:
-
Brittany: Situated on the Atlantic coast, Brittany is a region with a strong Celtic heritage. Its cultural identity is marked by its distinct language, its traditional music and dance, and its picturesque coastal towns.
-
Pays de la Loire: This region, known for its rolling countryside, historic cities like Nantes and Angers, and its picturesque coastline, is home to the Loire Valley, a UNESCO World Heritage Site renowned for its magnificent castles.
-
Poitou-Charentes: This region, located on the Atlantic coast, is known for its vineyards, its historic cities like Poitiers and La Rochelle, and its beautiful beaches. Its cultural identity is linked to its maritime heritage, its Cognac production, and its rich Roman and medieval history.
3. The Eastern Provinces:
-
Alsace: Situated on the border with Germany, Alsace is a region with a distinct cultural identity, influenced by both French and German traditions. Its cultural heritage is marked by its unique dialect, its traditional cuisine, and its picturesque villages.
-
Lorraine: This region, known for its industrial heritage, its historic cities like Nancy and Metz, and its rolling countryside, is home to the Moselle Valley, a region renowned for its vineyards.
-
Franche-Comté: This region, located in the eastern part of France, is known for its mountainous terrain, its historic cities like Besançon and Dole, and its traditional cheese production.
4. The Southern Provinces:
-
Provence: Situated in the south of France, Provence is a region renowned for its beautiful landscapes, its sunny climate, and its historic cities like Marseille and Avignon. Its cultural identity is marked by its unique dialect, its vibrant art scene, and its traditional Provençal cuisine.
-
Languedoc-Roussillon: This region, located on the Mediterranean coast, is known for its vineyards, its historic cities like Montpellier and Perpignan, and its beautiful beaches. Its cultural identity is linked to its Catalan heritage, its traditional wine production, and its rich Roman history.
-
Aquitaine: This region, located in the southwest of France, is known for its vineyards, its historic cities like Bordeaux and Toulouse, and its beautiful beaches. Its cultural identity is linked to its Basque heritage, its traditional wine production, and its rich Roman history.
-
Midi-Pyrénées: This region, located in the southwest of France, is known for its mountains, its historic cities like Toulouse and Albi, and its beautiful countryside. Its cultural identity is linked to its Occitan heritage, its traditional cuisine, and its rich Roman history.
5. The Central Provinces:
-
Auvergne: This region, located in the center of France, is known for its volcanic mountains, its historic cities like Clermont-Ferrand and Vichy, and its traditional cheese production.
-
Bourgogne: This region, located in the center of France, is known for its vineyards, its historic cities like Dijon and Beaune, and its beautiful countryside. Its cultural identity is linked to its Burgundian wine production, its traditional cuisine, and its rich Roman history.
6. The Overseas Provinces:
-
Corsica: This island, located in the Mediterranean Sea, is known for its mountainous terrain, its beautiful beaches, and its unique culture.
-
French Guiana: This overseas department, located in South America, is known for its rainforests, its gold mines, and its diverse population.
-
Guadeloupe: This overseas department, located in the Caribbean Sea, is known for its beautiful beaches, its volcanic mountains, and its rich cultural heritage.
-
Martinique: This overseas department, located in the Caribbean Sea, is known for its beautiful beaches, its volcanic mountains, and its rich cultural heritage.
-
Mayotte: This overseas department, located in the Indian Ocean, is known for its coral reefs, its volcanic mountains, and its diverse population.
-
Réunion: This overseas department, located in the Indian Ocean, is known for its volcanic mountains, its beautiful beaches, and its diverse population.
The Enduring Legacy of the Historical Provinces:
While the historical provinces of France are no longer formally recognized, their influence remains deeply embedded in the country’s cultural landscape. They continue to shape regional identities, culinary traditions, architectural styles, and even linguistic variations.
Benefits of Understanding the Historical Provinces:
-
Enriched Travel Experiences: Understanding the historical provinces adds depth and context to travel experiences, allowing visitors to appreciate the unique cultural nuances of each region.
-
Greater Appreciation of French History: The historical provinces provide a framework for understanding the evolution of France as a nation, from its medieval origins to its modern identity.
-
Enhanced Cultural Understanding: Exploring the historical provinces fosters an appreciation for the diverse cultural tapestry of France, recognizing the unique contributions of each region.
FAQs Regarding the Historical Provinces of France:
1. Are the historical provinces still relevant today?
While the historical provinces are no longer formally recognized, their influence remains deeply embedded in the country’s cultural landscape. They continue to shape regional identities, culinary traditions, architectural styles, and even linguistic variations.
2. How do the historical provinces differ from the current administrative regions?
The historical provinces were primarily defined by cultural and historical factors, while the current administrative regions are primarily based on geographical and economic considerations.
3. What are some examples of cultural differences between the historical provinces?
Cultural differences between the historical provinces can be seen in their languages, dialects, cuisine, architecture, and traditions. For example, Brittany is known for its Celtic heritage and distinct language, while Provence is famous for its sunny climate, its unique dialect, and its vibrant art scene.
4. Are there any maps that show the historical provinces of France?
Yes, there are many maps available that show the historical provinces of France. These maps can be found online, in libraries, and in bookstores.
5. Can I visit the historical provinces today?
Yes, you can visit the historical provinces today. The historical provinces are not administrative units, but they are still very much alive in the cultural landscape of France. You can explore the historical provinces by visiting their cities, towns, and villages, and by experiencing their unique cultures.
Tips for Exploring the Historical Provinces of France:
-
Research the historical provinces: Before you travel, research the historical provinces that you plan to visit. Learn about their history, culture, and attractions.
-
Visit local markets: Local markets are a great way to experience the regional cuisine and culture of the historical provinces.
-
Talk to local people: Talking to local people is a great way to learn about the history and culture of the historical provinces.
-
Visit historic sites: Many historical sites in France are located in the historical provinces. Visiting these sites can help you understand the history and culture of the region.
-
Explore the countryside: The countryside of France is beautiful and offers a chance to experience the natural beauty and rural life of the historical provinces.
Conclusion:
The historical provinces of France offer a fascinating window into the country’s rich history and cultural heritage. By understanding the historical provinces, travelers can gain a deeper appreciation for the diverse cultural tapestry of France, adding richness and depth to their travel experiences. These provinces, while no longer formally recognized, continue to influence the country’s identity, offering a glimpse into the past and a reminder of the enduring legacy of regionalism in France.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Journey Through Time: Exploring the Historical Provinces of France. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!