Geocaching, the modern-day treasure hunt, has captivated millions around the globe. Armed with a GPS device or smartphone and a sense of adventure, geocachers seek hidden containers called "geocaches" placed in a wide variety of locations, from urban parks to remote wilderness areas. At the heart of this activity lies the geocache map, a crucial tool that guides treasure hunters towards their hidden prizes. Understanding how to effectively use and interpret geocache maps is essential for a successful and enjoyable geocaching experience.
This article delves into the world of geocache maps, exploring their various forms, functionalities, and the information they provide. We’ll cover everything from the basics of map reading to advanced techniques for optimizing your geocaching adventures.
The Foundation: Understanding Geocaching and its Coordinates
Before diving into the intricacies of geocache maps, it’s important to understand the fundamental principles of geocaching. Geocaches are hidden containers that typically contain a logbook for finders to sign, and sometimes small trinkets for trade. The location of each geocache is recorded using geographic coordinates, specifically latitude and longitude.
-
Latitude: Measures the angular distance, in degrees, north or south of the equator. Latitude lines run horizontally around the Earth. The equator is at 0 degrees latitude, while the North and South Poles are at 90 degrees north and 90 degrees south, respectively.
-
Longitude: Measures the angular distance, in degrees, east or west of the Prime Meridian. Longitude lines run vertically from pole to pole. The Prime Meridian, which passes through Greenwich, England, is at 0 degrees longitude. Longitude ranges from 0 to 180 degrees east and 0 to 180 degrees west.
These coordinates are presented in a specific format, such as:
- Degrees, Minutes, Seconds (DMS): N 34° 03′ 04.5" W 118° 15′ 16.0"
- Degrees, Decimal Minutes (DDM): N 34° 03.075′ W 118° 15.267′
- Decimal Degrees (DD): 34.05125, -118.25445
Understanding these coordinate formats is crucial because geocache listings provide the coordinates in one of these forms, and you’ll need to be able to input them correctly into your GPS device or geocaching app.
The Evolution of Geocache Maps: From Paper to Digital
In the early days of geocaching, paper maps were the primary tool for navigating to geocache locations. Cachers would manually plot the coordinates on topographic maps and use a compass to determine the direction and distance to the cache. While paper maps are still useful for offline navigation and backup, the digital revolution has transformed the way geocachers utilize maps.
Today, geocache maps are primarily accessed through:
-
Dedicated GPS Devices: Handheld GPS units designed for outdoor navigation often feature built-in mapping capabilities. These devices can display topographic maps, satellite imagery, and geocache locations. They typically offer superior accuracy and battery life compared to smartphones, making them a reliable choice for serious geocachers.
-
Smartphone Geocaching Apps: Numerous geocaching apps are available for both iOS and Android devices. These apps provide access to the geocaching database, display geocache locations on interactive maps, and offer navigation features. They leverage the smartphone’s GPS capabilities and often integrate with online mapping services like Google Maps or OpenStreetMap. Popular apps include the official Geocaching® app, c:geo (Android), and Cachly (iOS).
-
Online Geocaching Platforms: Websites like Geocaching.com provide interactive maps that allow users to search for geocaches, view their locations, and plan their routes. These platforms often offer advanced features like filtering caches by type, difficulty, terrain, and size.
Key Features and Functionalities of Geocache Maps
Regardless of the platform you choose, geocache maps share several key features and functionalities:
-
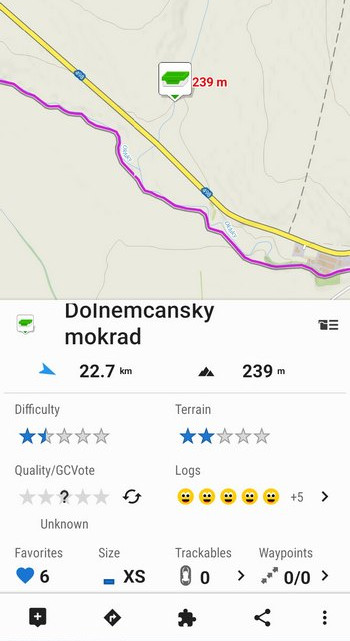
Displaying Geocache Locations: The primary function of a geocache map is to visually represent the locations of geocaches. Geocaches are typically marked with icons that indicate their type (e.g., Traditional, Multi-Cache, Mystery Cache). The icons may also be color-coded to indicate the cache’s status (e.g., Found, Not Found, Archived).
-
Navigation: Geocache maps provide navigation tools to guide you from your current location to the geocache. This includes displaying your current position, calculating the distance and bearing to the cache, and providing turn-by-turn directions.
-
Map Types and Layers: Most geocache maps offer a variety of map types, including:
- Road Maps: Show roads, streets, and other transportation infrastructure.
- Satellite Imagery: Provide a bird’s-eye view of the terrain.
- Topographic Maps: Display elevation contours and other terrain features.
- Hybrid Maps: Combine satellite imagery with road overlays.
In addition to map types, geocache maps often allow you to overlay additional layers, such as:
- Geocache Logs: Display recent logs from other geocachers, providing insights into the cache’s condition and accessibility.
- Waypoints: Allow you to mark specific locations of interest, such as parking spots, trailheads, or points of reference.
- Public Land Boundaries: Show the boundaries of national parks, forests, and other public lands.
-
Filtering and Searching: Geocache maps allow you to filter and search for geocaches based on various criteria, such as:
- Cache Type: Traditional, Multi-Cache, Mystery Cache, etc.
- Difficulty: A rating from 1 to 5, indicating the mental challenge of finding the cache.
- Terrain: A rating from 1 to 5, indicating the physical difficulty of reaching the cache.
- Size: Micro, Small, Regular, Large.
- Attributes: Hints about the cache’s location or characteristics (e.g., "Available in Winter," "Needs Maintenance").
-
Offline Maps: Downloading offline maps is crucial for geocaching in areas with limited or no internet connectivity. This allows you to access map data and navigate to geocaches even when you’re off the grid.
Tips for Effectively Using Geocache Maps
To maximize your geocaching success, consider these tips for effectively using geocache maps:
-
Calibrate Your GPS Device: Ensure that your GPS device or smartphone is properly calibrated to provide accurate location data.
-
Understand Map Symbols and Legends: Familiarize yourself with the symbols and legends used on your chosen map platform. This will help you interpret the map information correctly.
-
Pay Attention to Terrain Ratings: The terrain rating provides valuable information about the physical challenges involved in reaching the cache. Choose caches that are within your physical capabilities.
-
Read Geocache Logs: Before heading out, read the recent logs from other geocachers. This can provide valuable insights into the cache’s condition, accessibility, and any potential hazards.
-
Use Waypoints: Mark important locations, such as parking spots or trailheads, as waypoints on your map. This can help you navigate back to your starting point after finding the cache.
-
Plan Your Route: Before embarking on your geocaching adventure, plan your route carefully. Consider the distance, terrain, and estimated time required to reach each cache.
-
Download Offline Maps: If you’re geocaching in an area with limited internet connectivity, download offline maps to ensure that you can navigate to the caches.
-
Carry a Backup Map and Compass: While digital maps are convenient, it’s always a good idea to carry a backup paper map and compass in case your GPS device fails or runs out of battery.
-
Respect the Environment: Geocaching is an outdoor activity, so it’s important to respect the environment and leave no trace. Avoid disturbing vegetation, wildlife, or private property.
Beyond the Basics: Advanced Techniques for Geocache Mapping
For experienced geocachers, advanced mapping techniques can enhance the geocaching experience:
-
Geocaching Toolbars and Plugins: Several toolbars and plugins are available for web browsers that add geocaching functionality to online mapping services. These tools can help you analyze geocache clusters, identify potential hiding spots, and plan multi-cache routes.
-
Geocaching with GIS Software: Geographic Information System (GIS) software can be used to create custom geocache maps, analyze spatial data, and perform advanced route planning.
-
Creating Your Own Geocaches: Understanding geocache mapping principles is essential for creating your own geocaches. When hiding a geocache, you’ll need to accurately record its coordinates and choose a location that is both challenging and accessible.
Conclusion: The Geocache Map as Your Guide to Adventure
Geocache maps are an indispensable tool for modern-day treasure hunters. From simple road maps to sophisticated digital platforms, they provide the information and navigation tools needed to locate hidden geocaches around the world. By understanding the principles of map reading, utilizing the features of geocache mapping platforms, and employing advanced techniques, geocachers can unlock a world of adventure and exploration. So, grab your GPS device or smartphone, fire up your geocache map, and embark on your next treasure hunting expedition. The world is waiting to be explored, one geocache at a time.