us bank map
Related Articles: us bank map
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to us bank map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Financial Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to the U.S. Bank Map
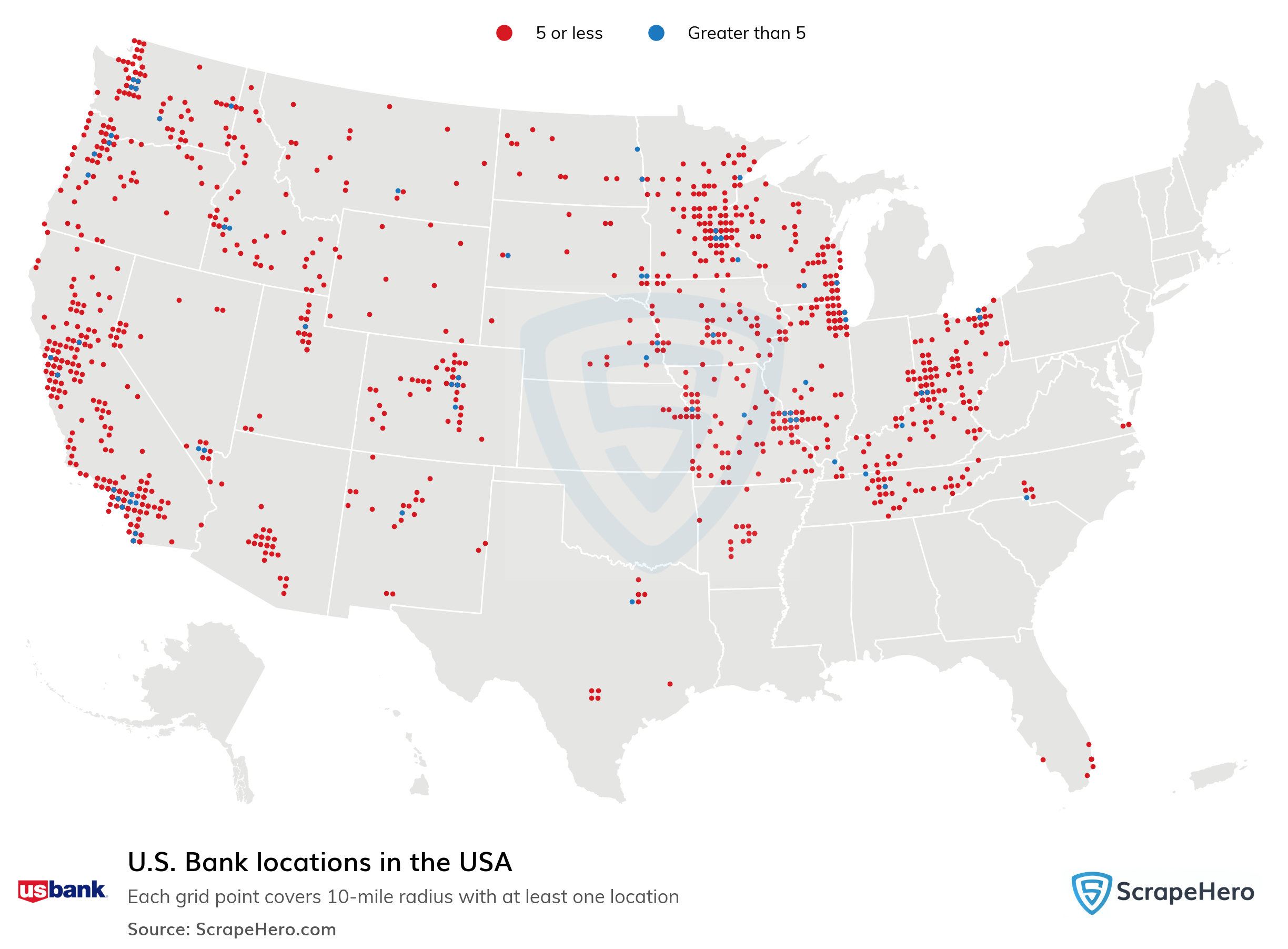
The United States banking system is a complex network of institutions, each serving a unique role in facilitating financial transactions, managing assets, and providing essential financial services to individuals and businesses. Understanding the structure and dynamics of this system is crucial for navigating the financial landscape effectively. This guide aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the U.S. bank map, highlighting its key components, their interrelationships, and the benefits they offer.
Understanding the U.S. Bank Map
The U.S. bank map is a visual representation of the interconnectedness of various financial institutions operating within the country. It encompasses a diverse range of entities, including:
- Commercial Banks: These are the most common type of bank, offering a broad array of financial services to individuals and businesses, including deposit accounts, loans, credit cards, and investment products.
- Savings Banks: These institutions primarily focus on accepting deposits and providing loans, often with a specific emphasis on mortgage lending and community development initiatives.
- Credit Unions: Member-owned financial cooperatives, credit unions offer competitive rates on savings and loans while emphasizing financial education and community outreach.
- Investment Banks: These institutions specialize in financial transactions, including mergers and acquisitions, underwriting securities, and providing investment advice to corporations and governments.
- Non-Bank Financial Companies: This category includes a variety of entities, such as insurance companies, mortgage lenders, and finance companies, offering specialized financial services.
The Role of the Federal Reserve
The Federal Reserve, also known as the Fed, acts as the central bank of the United States. Its primary role is to maintain the stability of the financial system and promote economic growth. The Fed does this by:
- Setting Interest Rates: The Fed influences interest rates through its monetary policy tools, impacting borrowing costs and investment activity across the economy.
- Regulating Banks: The Fed establishes and enforces regulations for banks, ensuring their financial stability and safeguarding the interests of depositors.
- Providing Liquidity: The Fed acts as a lender of last resort, providing liquidity to banks during periods of financial stress.
Navigating the U.S. Bank Map: Key Considerations
When choosing a financial institution, individuals and businesses should consider various factors, including:
- Financial Stability: Opt for institutions with a strong track record of financial stability, as evidenced by their capital adequacy and profitability.
- Product and Service Offerings: Evaluate the range of products and services offered by the institution, ensuring they meet your specific needs and requirements.
- Customer Service: Choose institutions with a reputation for excellent customer service, providing responsive and reliable support.
- Fees and Charges: Carefully review the fees and charges associated with different products and services, comparing them across institutions to find the most cost-effective options.
- Location and Convenience: Consider the accessibility of branches and ATMs, particularly if you prefer in-person banking.
- Technology and Digital Services: Evaluate the institution’s digital capabilities, including mobile banking apps, online account management, and other convenient features.
The Importance of Understanding the U.S. Bank Map
Having a solid understanding of the U.S. bank map and the various financial institutions within it empowers individuals and businesses to make informed decisions regarding their finances. This knowledge enables them to:
- Choose the right financial institutions: By understanding the different types of banks and their strengths, individuals and businesses can select institutions that best meet their specific financial needs.
- Access competitive products and services: Knowledge of the competitive landscape allows individuals and businesses to compare rates, fees, and features across institutions, ensuring they obtain the most favorable terms.
- Navigate financial challenges: Understanding the structure of the financial system allows individuals and businesses to navigate periods of economic uncertainty or personal financial challenges with greater confidence.
- Make informed investment decisions: Familiarity with the different types of financial institutions and their investment products empowers individuals and businesses to make informed investment decisions aligned with their risk tolerance and financial goals.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What are the benefits of using a bank?
A: Banks provide a range of benefits, including:
- Safeguarding deposits: Banks offer FDIC insurance, protecting deposits up to $250,000 per depositor, per insured bank.
- Convenience and accessibility: Banks offer a wide network of branches and ATMs, providing easy access to funds.
- Financial services: Banks provide a comprehensive suite of financial services, including deposit accounts, loans, credit cards, and investment products.
- Financial advice and guidance: Banks often offer financial advice and guidance, assisting customers with managing their finances effectively.
Q: What is the difference between a commercial bank and a credit union?
A: While both offer similar financial services, key differences include:
- Ownership: Commercial banks are for-profit entities, while credit unions are member-owned cooperatives.
- Focus: Commercial banks typically focus on profitability, while credit unions prioritize member service and community outreach.
- Rates: Credit unions often offer more competitive rates on savings and loans, as they prioritize member benefits.
Q: How do I choose the right bank for me?
A: When choosing a bank, consider your specific financial needs and preferences, including:
- Type of accounts needed: Savings, checking, money market, etc.
- Loan requirements: Mortgage, auto, personal, business loans.
- Investment goals: Retirement planning, college savings, etc.
- Location and accessibility: Branch network, ATM availability.
- Technology and digital services: Mobile banking, online account management.
- Fees and charges: Compare rates and fees across institutions.
Tips for Navigating the U.S. Bank Map
- Research and compare: Take the time to research different financial institutions and compare their products, services, and fees.
- Read the fine print: Carefully review the terms and conditions of any financial product or service before signing up.
- Ask questions: Don’t hesitate to ask questions about any aspect of banking that you don’t understand.
- Seek professional advice: Consider consulting a financial advisor for personalized guidance on managing your finances.
- Stay informed: Keep up-to-date on industry trends and developments that may impact your financial decisions.
Conclusion
The U.S. bank map is a dynamic and evolving landscape, reflecting the ever-changing needs of individuals and businesses. By understanding the different types of financial institutions and their roles, individuals and businesses can make informed decisions about their financial well-being, ensuring they access the products and services that best meet their unique needs and goals. Navigating this complex financial landscape requires careful research, comparison, and a commitment to financial literacy. By taking an active and informed approach, individuals and businesses can effectively leverage the resources available within the U.S. banking system to achieve their financial aspirations.


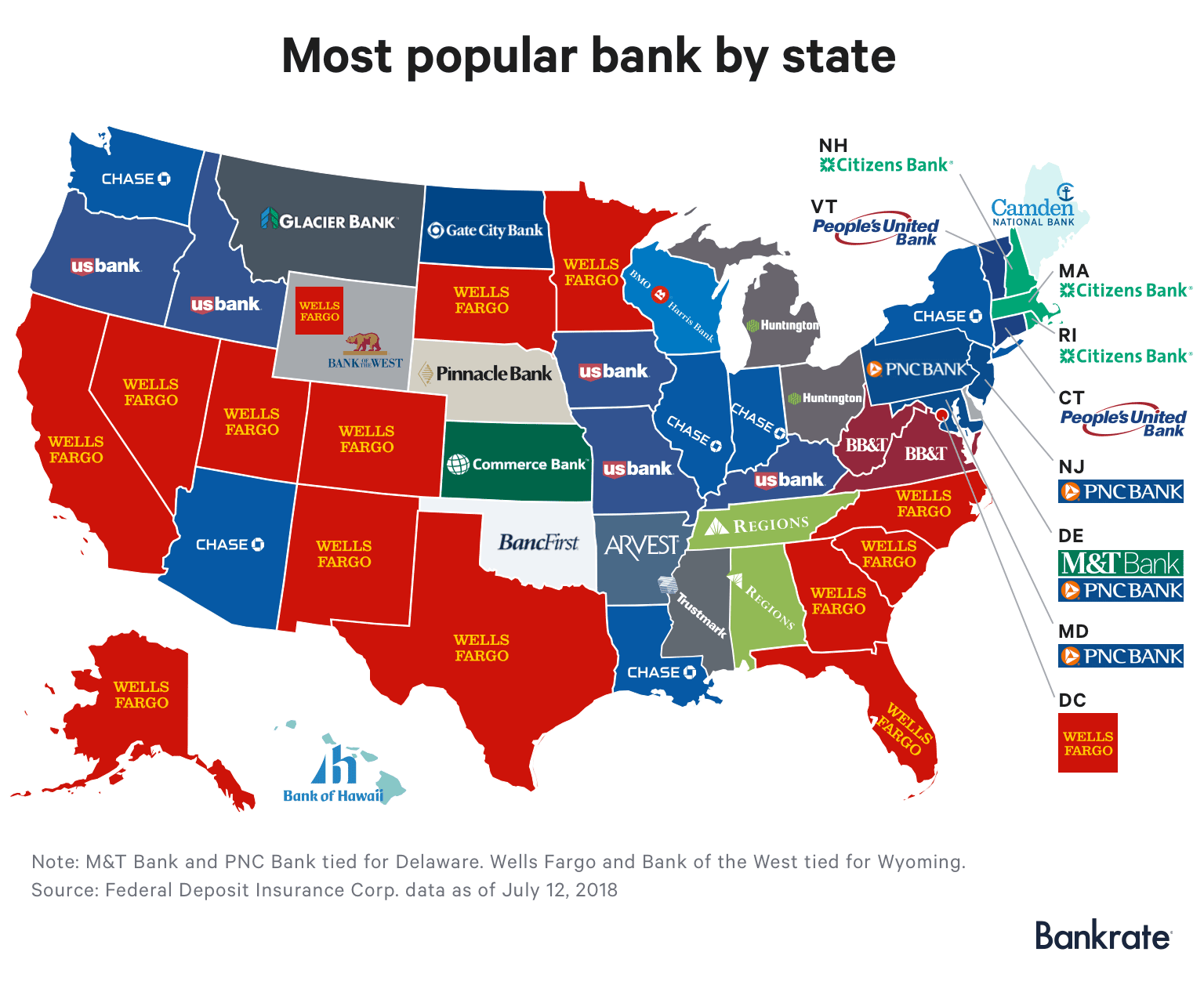
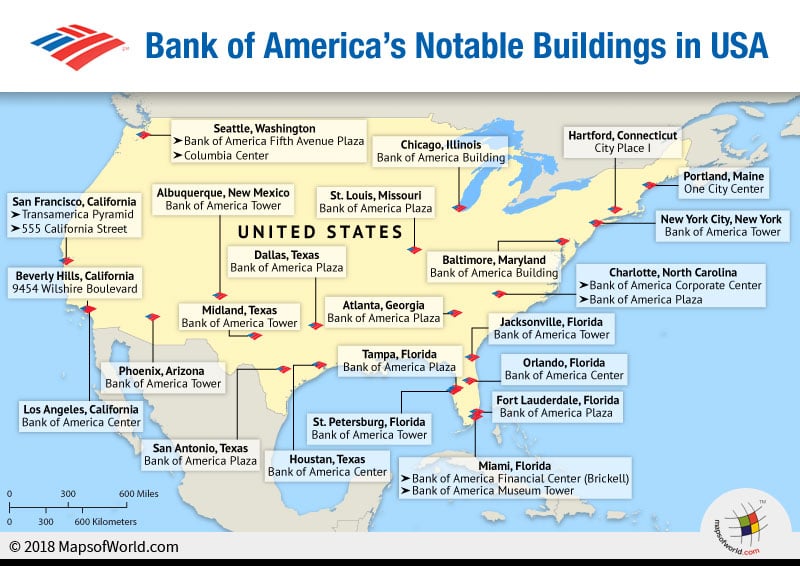
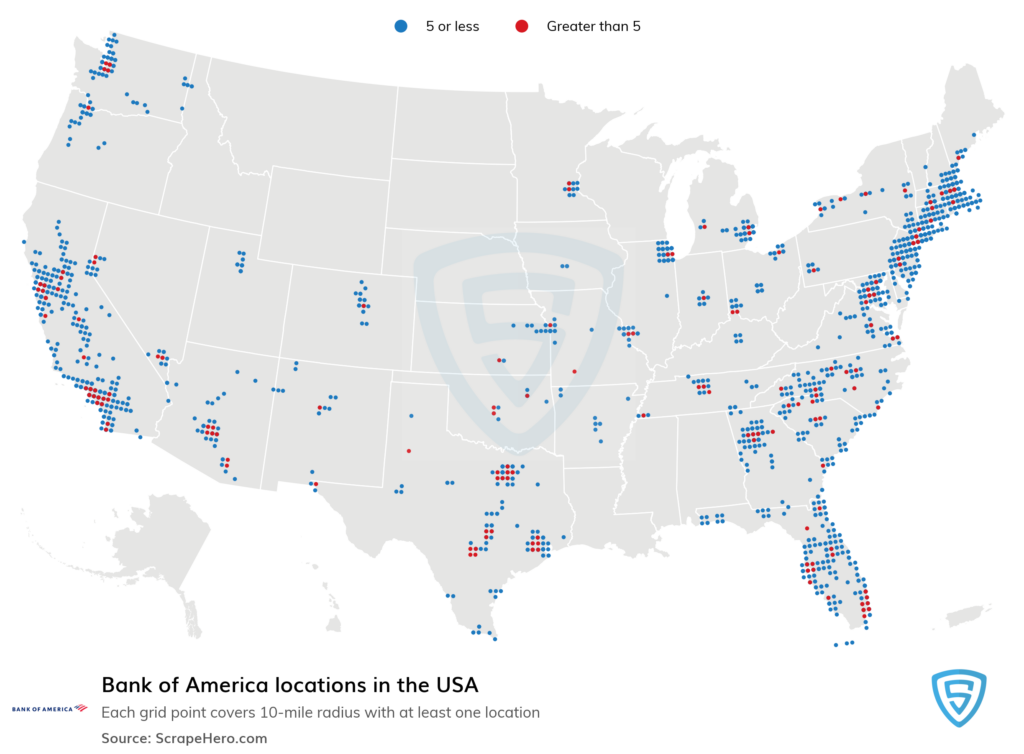
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_WhatDo_the_Federal_Reserve_Banks_Do_May_2020-01-08af2fa345a440ff9df4c83495ad4328.jpg)
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into us bank map. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!