The Complex Tapestry of Ethnicity in the Middle East: A Geographic and Historical Overview
Related Articles: The Complex Tapestry of Ethnicity in the Middle East: A Geographic and Historical Overview
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Complex Tapestry of Ethnicity in the Middle East: A Geographic and Historical Overview. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Complex Tapestry of Ethnicity in the Middle East: A Geographic and Historical Overview

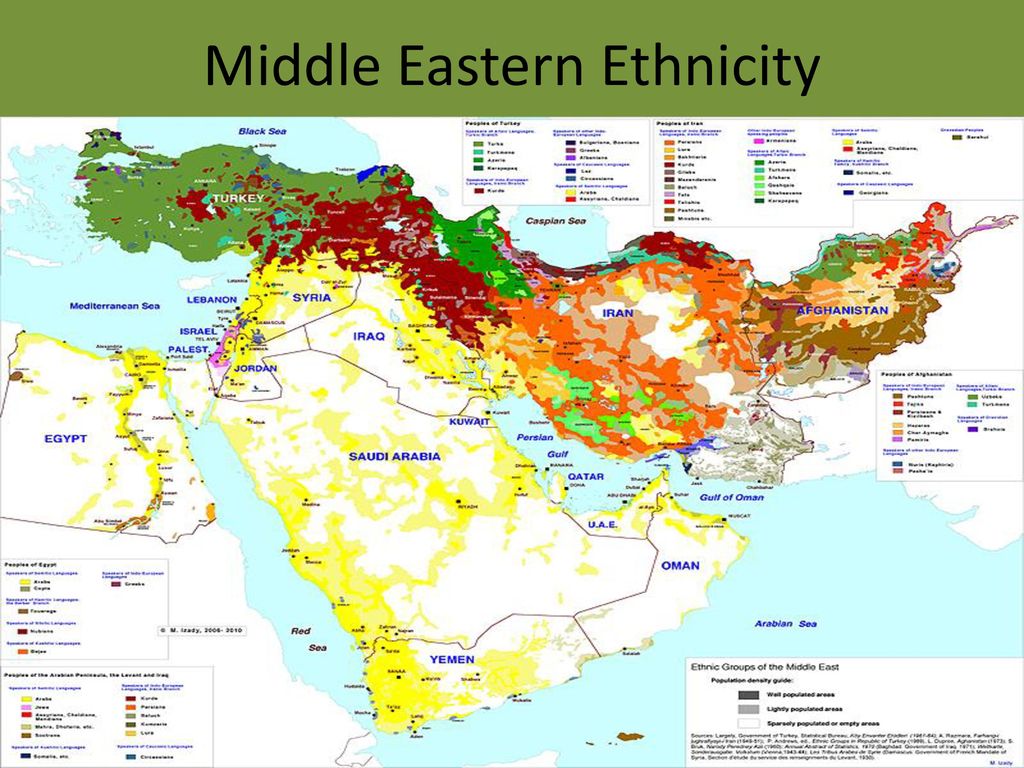
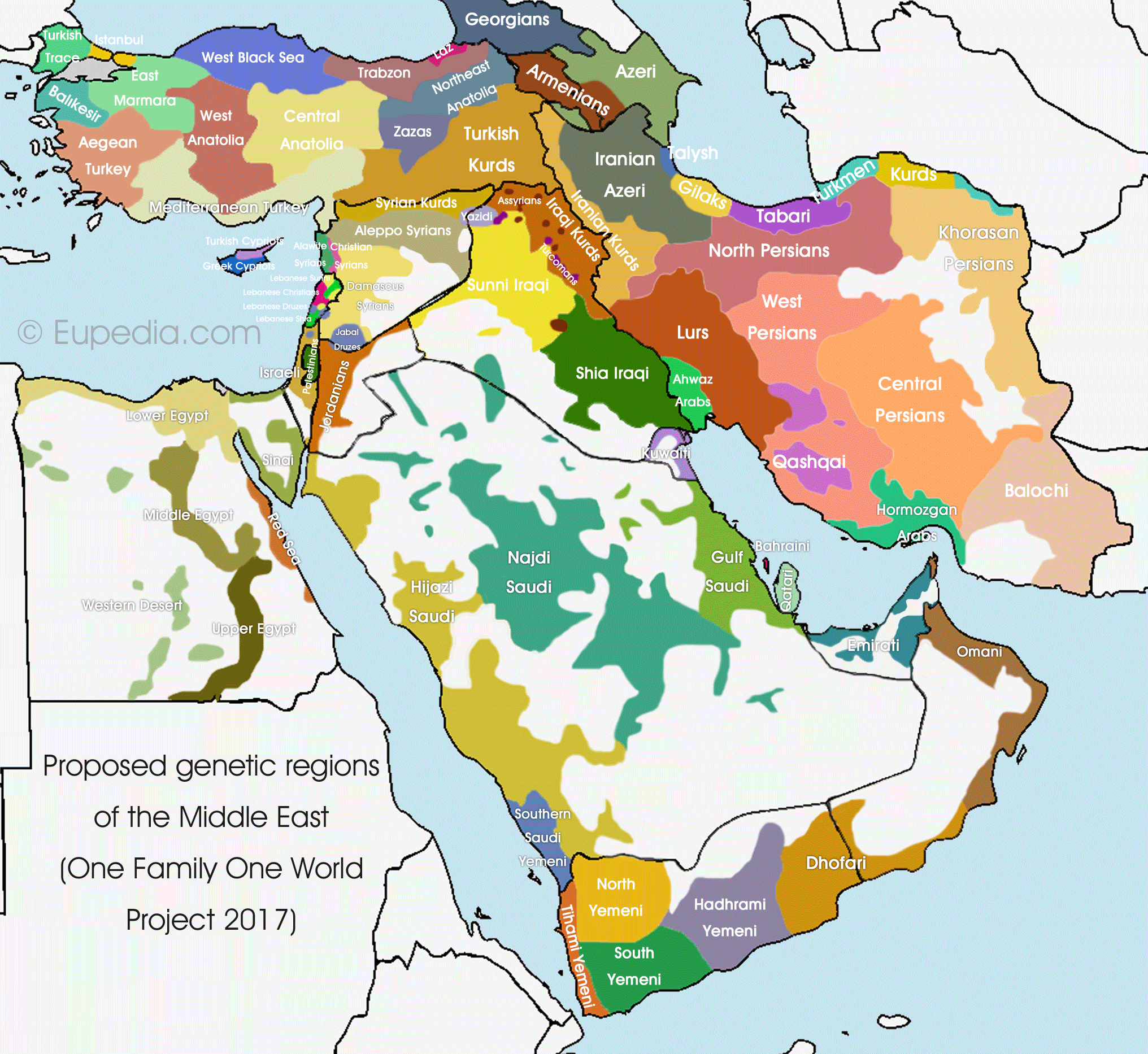
The Middle East, a region encompassing a vast swathe of land from North Africa to Central Asia, is a melting pot of cultures, languages, and ethnicities. This intricate mosaic of human diversity has shaped the region’s history, politics, and social landscape. Understanding the ethnic map of the Middle East is crucial for navigating its complex realities and appreciating the richness of its cultural heritage.
A Region Defined by Mobility and Exchange:
The Middle East has historically been a crossroads of civilizations, with various empires, migrations, and trade routes converging within its borders. This constant movement of people and ideas has led to a dynamic and multifaceted ethnic landscape.
-
Ancient Origins: The region’s ethnic tapestry is rooted in ancient civilizations, including the Sumerians, Akkadians, Babylonians, Assyrians, Persians, and Egyptians. These civilizations left behind a legacy of languages, religions, and cultural practices that continue to influence the region today.
-
Waves of Migration: Throughout history, the Middle East has witnessed numerous migrations, including the arrival of the Arabs in the 7th century, the Turkic expansion in the 11th century, and the influx of refugees and migrants in recent decades. These migrations have enriched the region’s ethnic diversity, adding new layers to its cultural fabric.
-
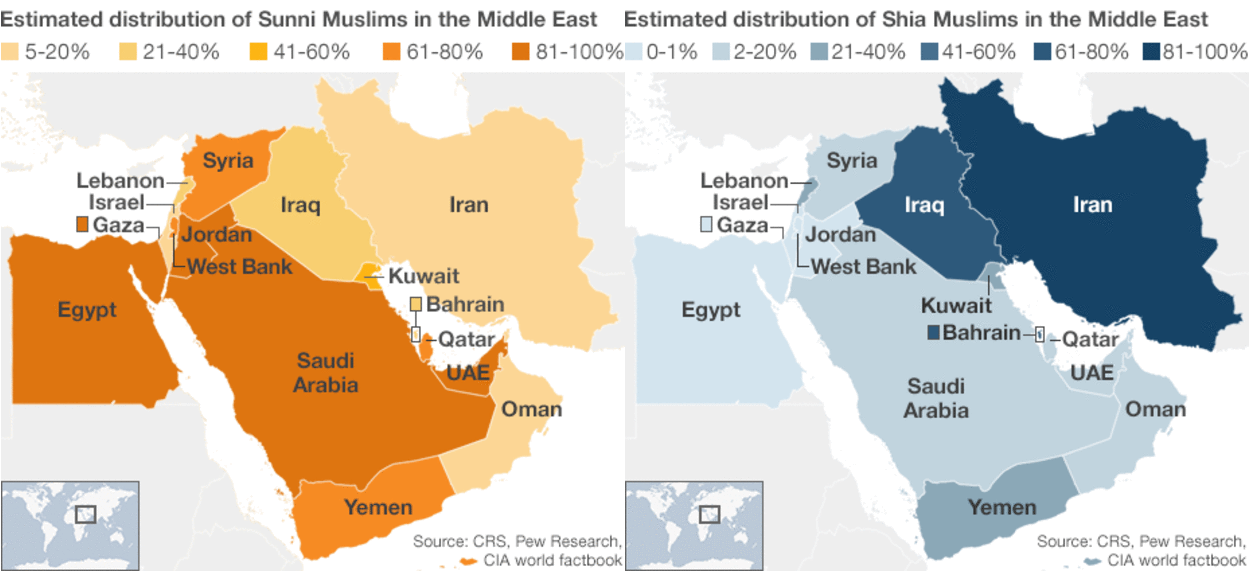
Religious Diversity: The Middle East is home to a wide range of religions, including Islam, Christianity, Judaism, and various ancient faiths. These religions have played a significant role in shaping the region’s ethnic identities, with religious affiliation often intertwining with ethnic belonging.
Mapping the Ethnic Landscape:
Creating a comprehensive ethnic map of the Middle East is a complex undertaking, as ethnic boundaries are often fluid and overlapping. Nevertheless, some broad generalizations can be made based on language, religion, and historical origins:
-
Arabic-Speaking Populations: Arabic is the dominant language in many Middle Eastern countries, including Egypt, Syria, Lebanon, Jordan, Iraq, and the Arabian Peninsula. While sharing a common language, these populations exhibit variations in ethnicity and cultural practices. For instance, in Lebanon, the Arabic-speaking population is further divided into religious groups like Maronites, Sunnis, Shias, and Druze, each with their own unique cultural traditions.
-
Turkish Populations: Turkish is spoken primarily in Turkey, but it also has a significant presence in Cyprus and parts of Syria and Iraq. Turkish populations in the Middle East often have a distinct cultural identity, influenced by their historical ties to the Ottoman Empire.
-
Persian Populations: Persian, spoken in Iran and parts of Afghanistan and Tajikistan, represents another major ethnic group in the Middle East. Persian culture, known for its rich literature, art, and music, is deeply intertwined with its language and historical legacy.
-
Kurds: The Kurdish people, an ethnic group primarily concentrated in southeastern Turkey, northern Iraq, northwestern Iran, and northeastern Syria, constitute a significant but often marginalized population in the Middle East. Kurdish culture, language, and aspirations for autonomy are distinct from the surrounding populations.
-
Berber Populations: In North Africa, Berber populations, primarily in Morocco, Algeria, and Tunisia, represent a distinct ethnic group with their own language, culture, and traditions. Berber identity is often intertwined with local tribal affiliations and regional variations.
-
Other Ethnic Groups: The Middle East is also home to numerous other ethnic groups, including Assyrians, Armenians, Circassians, and various nomadic tribes, each with their own unique cultural heritage and historical experiences.
The Importance of Understanding Ethnic Diversity:
Understanding the ethnic map of the Middle East is crucial for several reasons:
-
Political Stability: Ethnic tensions and conflicts are a recurring feature of the Middle East’s political landscape. Acknowledging and understanding the complexities of ethnic identities is essential for promoting peaceful coexistence and resolving conflicts.
-
Cultural Appreciation: The region’s rich cultural diversity is a source of inspiration and beauty. Recognizing and celebrating the unique traditions and heritage of different ethnic groups fosters cultural understanding and appreciation.
-
Economic Development: Ethnic diversity can be a source of economic strength, as it can lead to innovation, creativity, and a broader range of skills and perspectives. Promoting inclusive economic policies that benefit all ethnic groups is essential for sustainable development.
-
Human Rights: Respecting the rights of all ethnic groups is fundamental to building a just and equitable society. This includes ensuring equal access to education, healthcare, and other essential services, regardless of ethnic background.
FAQs on the Ethnic Map of the Middle East:
1. What are the main challenges associated with mapping ethnicities in the Middle East?
Mapping ethnicities in the Middle East is challenging due to the fluidity and overlapping nature of ethnic boundaries. Ethnic identities can be fluid, influenced by factors such as religion, language, cultural practices, and historical experiences. Moreover, political boundaries often do not align with ethnic divisions, leading to complexities in defining and mapping ethnic groups.
2. How has the ethnic map of the Middle East evolved over time?
The ethnic map of the Middle East has been constantly evolving due to migrations, conquests, and intermingling of cultures. The arrival of the Arabs in the 7th century, the Turkic expansion in the 11th century, and the influx of refugees and migrants in recent decades have all contributed to the region’s dynamic ethnic landscape.
3. What are the implications of ethnic diversity for the future of the Middle East?
Ethnic diversity can be a source of strength and resilience for the Middle East, but it also poses challenges. Managing ethnic tensions, promoting inclusivity, and ensuring equal opportunities for all ethnic groups are crucial for the region’s future.
4. How can we promote understanding and tolerance between different ethnic groups in the Middle East?
Promoting understanding and tolerance between different ethnic groups in the Middle East requires a multi-faceted approach. This includes fostering dialogue and communication, promoting cultural exchange programs, educating individuals about the diverse cultures and histories of the region, and advocating for policies that promote equality and inclusivity.
Tips for Navigating the Ethnic Landscape of the Middle East:
-
Be mindful of generalizations: Avoid making generalizations about entire ethnic groups, as individuals within each group have diverse experiences and perspectives.
-
Engage in respectful dialogue: Approach conversations about ethnicity with sensitivity and respect, listening attentively to different viewpoints.
-
Learn about different cultures: Take the time to learn about the history, culture, and traditions of different ethnic groups in the Middle East. This will help you develop a deeper understanding and appreciation for the region’s diversity.
-
Support organizations promoting cultural understanding: Consider supporting organizations that work to bridge cultural divides and promote peaceful coexistence between different ethnic groups.
Conclusion:
The ethnic map of the Middle East is a testament to the region’s rich history, cultural diversity, and ongoing dynamism. Understanding this intricate tapestry is essential for navigating the region’s complexities, fostering peaceful coexistence, and promoting a future where all ethnic groups can thrive. By embracing the region’s diversity and working towards a future of mutual understanding and respect, the Middle East can harness its cultural richness to build a brighter future for all its people.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Complex Tapestry of Ethnicity in the Middle East: A Geographic and Historical Overview. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!