Navigating South America’s Urban Landscape: A Geographic Perspective
Related Articles: Navigating South America’s Urban Landscape: A Geographic Perspective
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating South America’s Urban Landscape: A Geographic Perspective. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating South America’s Urban Landscape: A Geographic Perspective

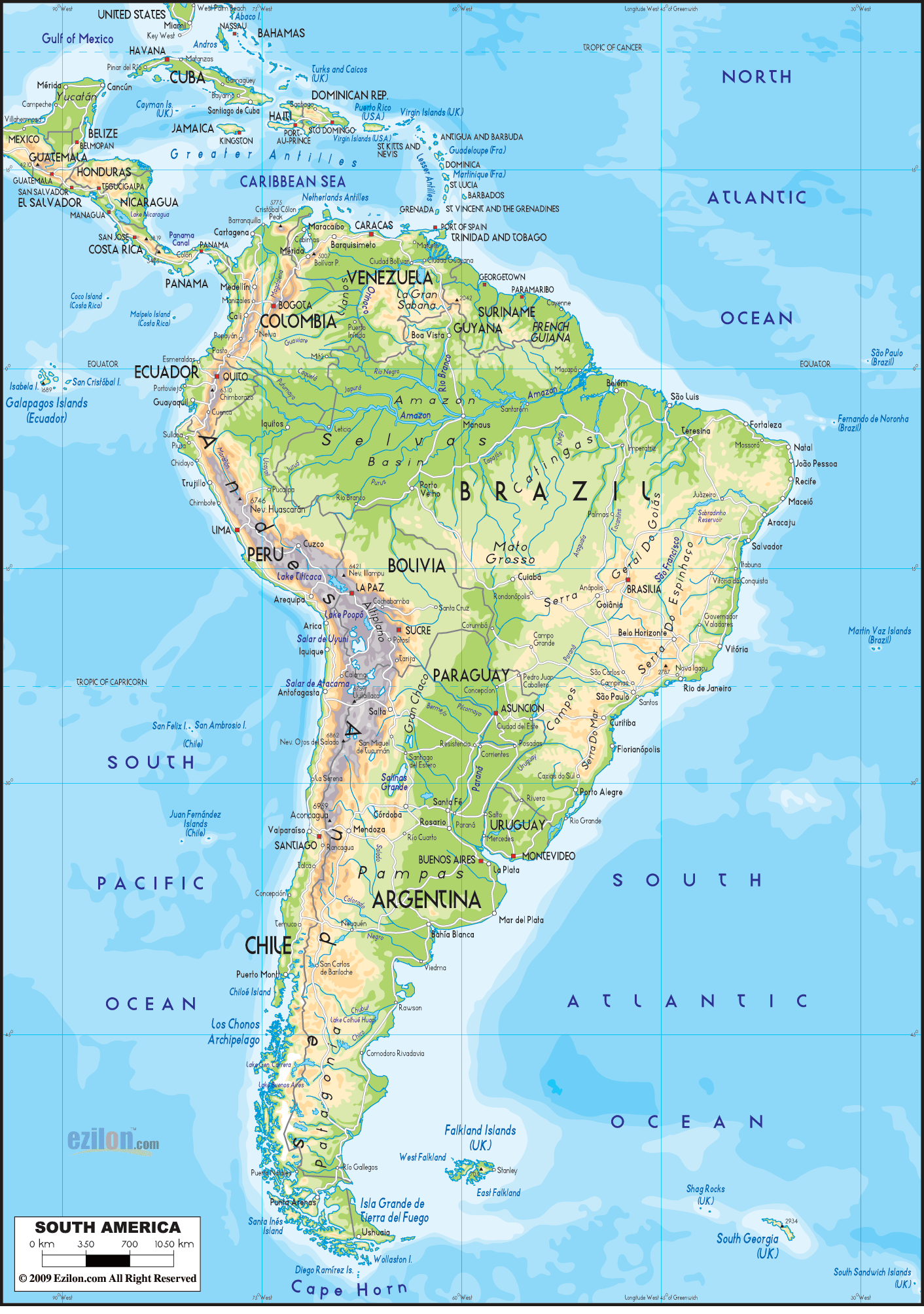
South America, a continent of immense geographical diversity, boasts a complex tapestry of urban centers, ranging from sprawling megacities to smaller, historic towns. Understanding the distribution and characteristics of these cities is crucial for comprehending the continent’s economic, social, and political dynamics. A visual representation of these urban areas provides invaluable insight.
The geographical distribution of South American cities reveals significant patterns. Coastal regions, particularly along the Atlantic and Pacific coasts, exhibit higher population densities and a greater concentration of major urban areas. This is attributable to historical factors such as early colonization, port development, and access to trade routes. Buenos Aires, Argentina; Rio de Janeiro and São Paulo, Brazil; and Lima, Peru, exemplify this coastal concentration. These cities, often acting as economic hubs, have attracted significant internal migration and contributed to the growth of surrounding metropolitan areas.
Inland areas, while less densely populated overall, also contain important cities. These cities often serve as regional centers, connecting agricultural hinterlands to national and international markets. Examples include Bogotá, Colombia, located in the Andes Mountains, and Brasília, Brazil, a purpose-built capital strategically positioned in the interior. The location of inland cities frequently reflects factors such as resource availability, strategic geopolitical considerations, or historical settlement patterns.
The size and function of South American cities vary considerably. Megacities like São Paulo and Buenos Aires are global players, influencing international finance, trade, and culture. Their vast populations and extensive infrastructure present both opportunities and challenges, including issues of urban sprawl, inequality, and environmental sustainability. Smaller cities, however, often retain a more distinct character, reflecting regional traditions and economic activities. These smaller urban centers are vital for maintaining economic and social balance within the continent’s diverse regions.
A detailed examination of the cartographic representation of these urban areas reveals further insights. The visualization highlights the interconnectedness of cities through transportation networks, emphasizing the importance of infrastructure in facilitating trade, communication, and migration. It also underscores regional disparities in development, illustrating areas with high urban density juxtaposed against regions with sparser urban settlements. This visual representation allows for a quick assessment of urban growth patterns, highlighting areas experiencing rapid expansion and those experiencing stagnation or decline.
Furthermore, the visualization aids in understanding the spatial relationship between urban areas and their surrounding environment. It demonstrates the impact of urbanization on natural resources, highlighting the encroachment of cities on agricultural lands, forests, and water bodies. This visual depiction is crucial for informed urban planning and environmental management strategies.
Frequently Asked Questions:
-
What factors influence the location of South American cities? A multitude of factors contribute, including coastal access, navigable rivers, resource availability (minerals, agriculture), defensible terrain, and historical events such as colonization and migration patterns.
-
How does the visualization of South American cities aid in understanding regional development disparities? The visual representation clearly shows the unequal distribution of urban populations and infrastructure, highlighting areas with concentrated development and those experiencing underdevelopment. This allows for a better understanding of regional economic disparities and the need for targeted development initiatives.
-
What are the challenges associated with the growth of megacities in South America? Rapid urbanization in megacities presents challenges such as housing shortages, inadequate infrastructure (transportation, sanitation, water supply), increased pollution, and social inequalities.
-
How can cartographic representations of South American cities be used for urban planning? Visualizations are essential tools for urban planning, enabling the identification of growth patterns, infrastructure needs, and potential environmental impacts. This allows for the development of more effective and sustainable urban development strategies.
Tips for Utilizing a South American City Map:
-
Consider the map’s scale and projection: Different maps use varying scales and projections, which can affect the accuracy of distance and area measurements. Choose a map appropriate for the specific analysis required.
-
Analyze the spatial distribution of cities: Observe the clustering of cities in specific regions and identify any patterns or relationships between their locations and geographic features.
-
Examine the transportation networks: Assess the connectivity between cities through roads, railways, and waterways. This provides insight into trade routes and regional integration.
-
Integrate the map with other data: Combine the map with data on population, economic activity, or environmental factors to gain a more comprehensive understanding of the region.
Conclusion:
A thorough understanding of the geographical distribution and characteristics of South American cities requires a comprehensive approach. Visual representations, specifically maps, offer a powerful tool for analyzing this complex urban landscape. By examining the spatial patterns, understanding the historical context, and considering the challenges and opportunities presented by urbanization, a more nuanced and informed perspective on the continent’s development can be achieved. This knowledge is vital for effective urban planning, economic development strategies, and environmental management, contributing to a more sustainable and equitable future for South America.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating South America’s Urban Landscape: A Geographic Perspective. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!