Understanding the Global Grid: Latitude Lines and Their Significance
Related Articles: Understanding the Global Grid: Latitude Lines and Their Significance
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Global Grid: Latitude Lines and Their Significance. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Global Grid: Latitude Lines and Their Significance

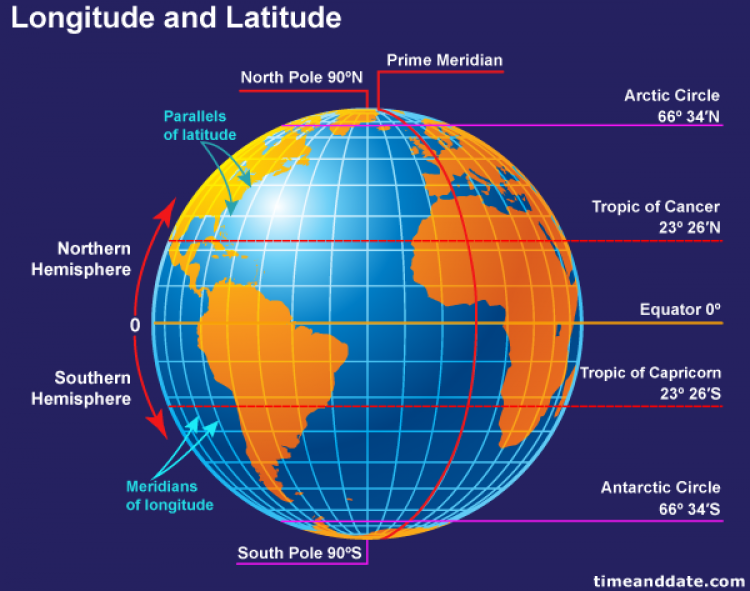
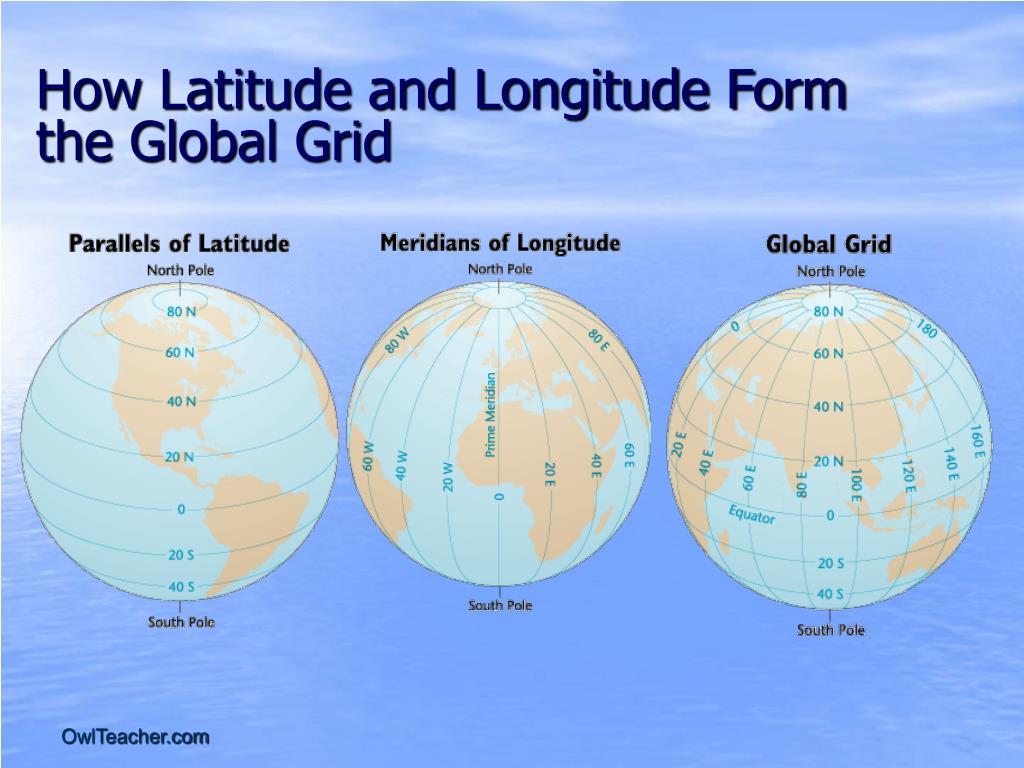
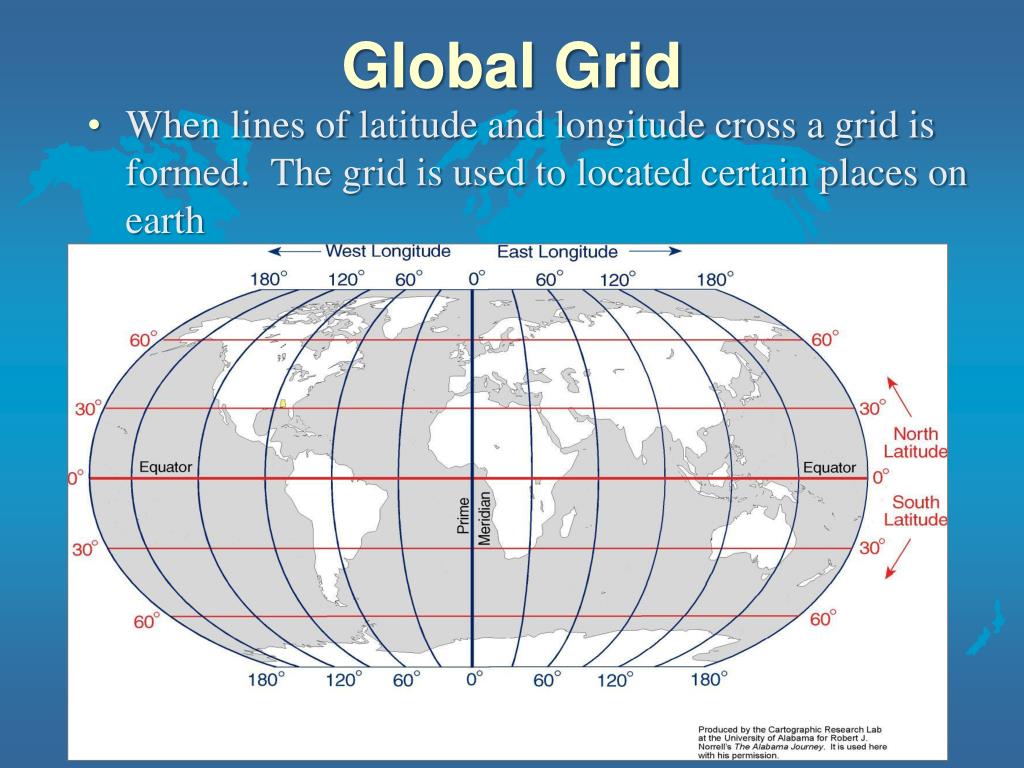
A world map displaying latitude lines provides a fundamental framework for understanding global geography. These horizontal lines, parallel to the Equator, are crucial for precise location identification and numerous applications across various disciplines. The system, based on a spherical coordinate system, allows for the precise measurement of distances, the calculation of time zones, and the analysis of climatic patterns, among other uses.
The Equator, at 0 degrees latitude, divides the Earth into the Northern and Southern Hemispheres. Lines of latitude, also known as parallels, extend north and south of the Equator, reaching 90 degrees at the North and South Poles. Each degree of latitude represents approximately 111 kilometers (69 miles) at the surface, though this distance slightly varies due to the Earth’s slightly oblate spheroid shape. Subdivisions of degrees into minutes and seconds further enhance precision in location specification.
Maps incorporating latitude lines are essential tools for navigation. Seafaring and air travel heavily rely on these lines to plot courses and determine locations. GPS technology, for example, utilizes latitude and longitude coordinates to pinpoint positions with remarkable accuracy. This capability is critical for emergency services, logistics, and various transportation sectors.
Beyond navigation, latitude lines are instrumental in understanding climate and weather patterns. Solar radiation varies significantly with latitude, influencing temperature and precipitation. Regions near the Equator receive more direct sunlight throughout the year, resulting in consistently high temperatures and abundant rainfall. Conversely, areas closer to the poles experience more extreme seasonal variations and significantly less solar radiation, leading to colder temperatures and potentially less rainfall. Climate models and analyses often utilize latitude as a key parameter for understanding and predicting weather events.
The distribution of natural resources and ecosystems is also closely linked to latitude. Certain plant and animal species thrive only within specific latitudinal bands, reflecting adaptations to particular climatic conditions. Understanding these latitudinal distributions is crucial for conservation efforts, resource management, and biodiversity studies. Maps displaying latitude lines facilitate the visualization and analysis of these ecological patterns.
Furthermore, the geographical distribution of human populations is significantly influenced by latitude. Historically, population density has been higher in regions with favorable climates, often located within specific latitudinal bands. While urbanization and technological advancements have somewhat lessened this dependence, latitude continues to play a role in shaping population distributions and patterns of human settlement. Analyzing population data in conjunction with latitude lines provides valuable insights into demographic trends and societal development.
The use of latitude lines extends beyond the physical sciences. In the social sciences, these lines facilitate the analysis of geographical data related to political boundaries, economic activities, and social inequalities. Researchers can use latitude as a variable in statistical models to explore the correlation between geographical location and various social phenomena. This approach helps identify potential patterns and relationships that might otherwise be overlooked.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What is the difference between latitude and longitude?
A1: Latitude measures the distance north or south of the Equator, while longitude measures the distance east or west of the Prime Meridian. Latitude lines run east-west, parallel to the Equator, while longitude lines run north-south, converging at the poles. Together, latitude and longitude provide a unique coordinate for every location on Earth.
Q2: How are latitude lines used in time zone determination?
A2: While not directly determining time zones, latitude plays an indirect role. Time zones are primarily defined by longitude, but their boundaries often follow geographical features and political boundaries, which in turn are influenced by latitude-related factors like climate and population distribution.
Q3: Are latitude lines perfectly parallel?
A3: While depicted as parallel on many maps, latitude lines are not perfectly parallel in reality due to the Earth’s slightly oblate spheroid shape. The difference is minimal, however, and generally negligible for most applications.
Q4: What are some limitations of using latitude lines alone for geographical analysis?
A4: Latitude alone provides only a one-dimensional representation of location. For a complete understanding of a location, longitude is essential. Furthermore, elevation and other topographical features significantly influence local conditions and are not directly represented by latitude.
Tips for Utilizing Latitude Lines on Maps
- Understand the scale: Pay attention to the scale of the map to accurately interpret the distances represented by degrees of latitude.
- Consider the map projection: Different map projections distort distances and shapes differently. Be aware of the projection used to avoid misinterpretations.
- Use latitude in conjunction with longitude: For precise location identification and analysis, always use latitude and longitude together.
- Refer to geographical data: Combine latitude information with other geographical data, such as elevation, climate information, and population density, for a comprehensive understanding.
Conclusion
The incorporation of latitude lines on world maps provides a crucial framework for understanding and analyzing a wide range of geographical phenomena. These lines offer a precise system for locating places, facilitating navigation, and enabling the study of climate, ecosystems, and human populations. While limitations exist, the benefits derived from utilizing this fundamental geographical tool remain invaluable across diverse disciplines. A comprehensive understanding of latitude lines and their applications is essential for anyone working with geographical information or seeking a deeper understanding of the Earth’s spatial organization.
![]()




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Global Grid: Latitude Lines and Their Significance. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!