Understanding the Geographic Distribution of American Indian Reservations
Related Articles: Understanding the Geographic Distribution of American Indian Reservations
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Geographic Distribution of American Indian Reservations. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Geographic Distribution of American Indian Reservations
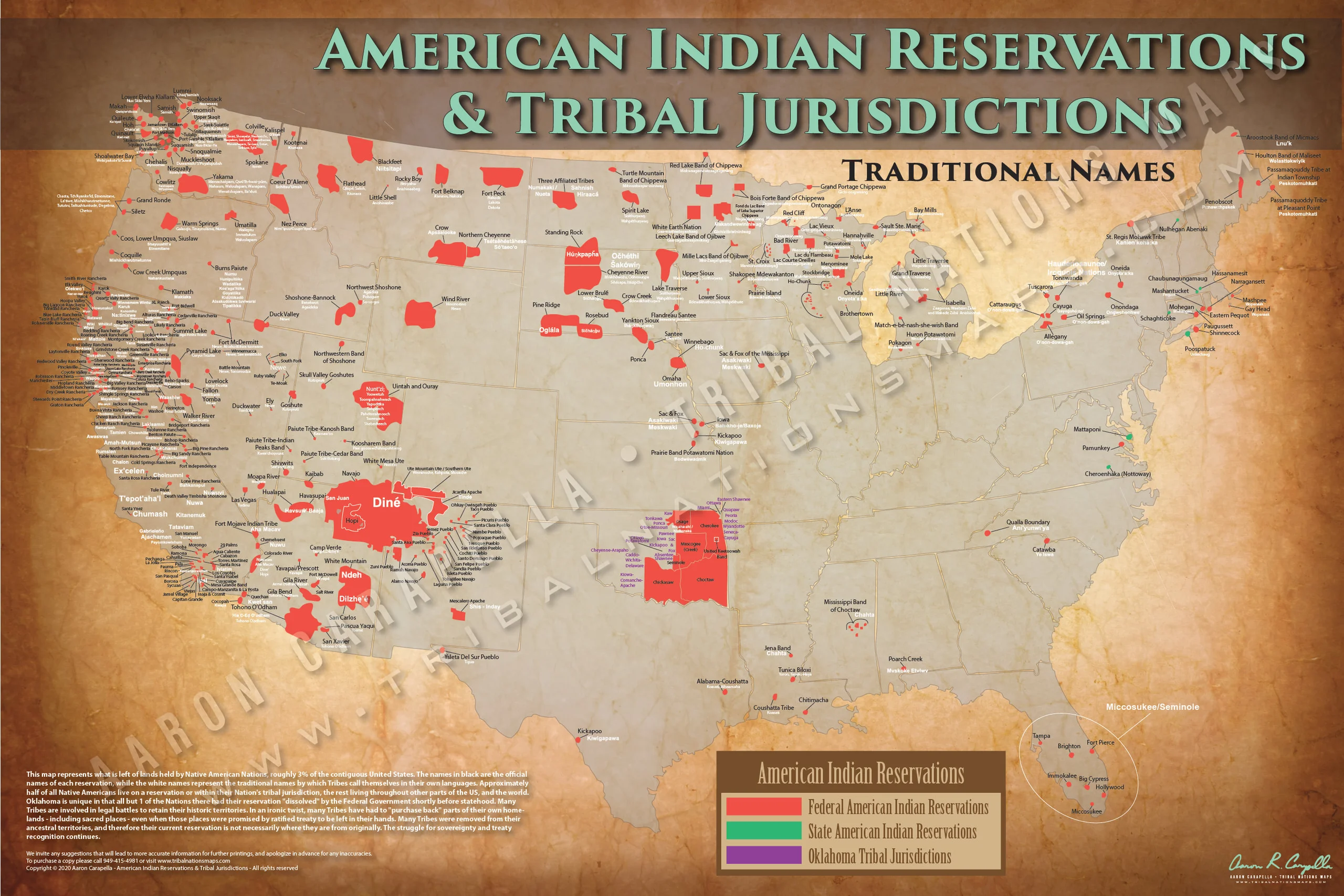
The United States contains a complex network of federally recognized American Indian reservations. These lands, held in trust by the federal government, represent a significant portion of the nation’s landmass and hold immense cultural, historical, and economic significance. Analyzing their geographic distribution reveals crucial information about the history of Indigenous peoples in the US, current socio-economic conditions within these communities, and the ongoing challenges faced in governance and resource management.
Geographic Dispersion and Historical Context:
The current configuration of reservations is a direct consequence of historical treaties, forced removals, and government policies implemented throughout the 19th and 20th centuries. These policies, often characterized by assimilationist goals, resulted in the displacement of Indigenous populations from their ancestral territories and their confinement to designated areas. Consequently, reservations are not uniformly distributed. Concentrations exist in the Southwest, Great Plains, and parts of the Northwest, reflecting the historical patterns of displacement and settlement. However, many reservations are geographically isolated, lacking adequate access to essential services and economic opportunities. This isolation contributes to disparities in education, healthcare, and infrastructure development.
Data Representation and Analysis:
Mapping these reservations provides a visual representation of their geographic extent, allowing for a clearer understanding of their size, location, and proximity to urban centers. This spatial data is crucial for various analyses. For instance, overlaying reservation boundaries with data on poverty rates, access to healthcare, and educational attainment reveals the significant disparities that exist between reservation communities and the broader US population. Similarly, analyzing the proximity of reservations to natural resources, such as forests or mineral deposits, provides insights into the economic potential and challenges associated with resource management on these lands.
Economic Development and Resource Management:
Reservations often possess significant natural resources, but their development is frequently constrained by complex legal frameworks, limited capital, and infrastructural limitations. A clear understanding of the geographic distribution of these resources, in conjunction with knowledge of reservation boundaries, is crucial for developing sustainable economic strategies. Effective resource management requires careful consideration of environmental impacts, tribal sovereignty, and the long-term well-being of the communities involved. Mapping exercises can facilitate this process by identifying areas suitable for development while minimizing negative environmental consequences.
Governance and Tribal Sovereignty:
Each reservation possesses a unique governance structure, reflecting the specific history and traditions of the residing tribe. Understanding the geographic boundaries of these areas is essential for respecting tribal sovereignty and ensuring that federal and state policies do not infringe upon tribal self-determination. Effective intergovernmental relations require a clear understanding of jurisdictional boundaries and a commitment to collaborative decision-making processes that involve tribal leaders and representatives.
Infrastructure and Access to Services:
The geographic isolation of many reservations significantly impacts access to essential services such as healthcare, education, and transportation. Mapping exercises can identify areas with limited access, highlighting the need for targeted infrastructure investments and the development of effective service delivery models. The analysis of distances to healthcare facilities, schools, and transportation hubs can inform policy decisions aimed at improving the quality of life within reservation communities.
Environmental Concerns and Climate Change:
Many reservations are located in ecologically sensitive areas, making them particularly vulnerable to the impacts of climate change. Mapping exercises can identify areas at risk of drought, flooding, or other environmental hazards, providing crucial information for developing adaptation strategies and mitigation plans. The incorporation of climate change projections into spatial analyses can inform long-term planning and resource management decisions.
Frequently Asked Questions:
-
What is the total land area covered by American Indian reservations? The total land area varies depending on the data source and how fragmented lands are counted, but it represents a significant portion of the US landmass. Precise figures require careful consideration of different data sets and methodologies.
-
Are all reservations geographically contiguous? No. Many reservations are fragmented, consisting of non-contiguous parcels of land, a consequence of historical land cessions and policies.
-
How does the geographic distribution of reservations impact access to services? The geographic isolation of many reservations creates significant challenges in accessing healthcare, education, and other essential services, leading to disparities in health outcomes and educational attainment.
-
What role does mapping play in addressing these challenges? Mapping provides a visual representation of the spatial distribution of reservations and their relation to essential services, allowing for a more targeted and effective approach to addressing these challenges.
-
How can mapping support tribal sovereignty? Mapping clearly delineates reservation boundaries, which is crucial for respecting tribal sovereignty and ensuring that governmental policies do not infringe upon tribal self-determination.
Tips for Utilizing Geographic Data on Reservations:
- Consult multiple data sources to ensure accuracy and completeness. Data on reservation boundaries can vary between sources.
- Use Geographic Information Systems (GIS) software to analyze spatial data and create maps.
- Consider overlaying reservation boundaries with other data layers, such as demographic information, infrastructure data, and environmental data, to conduct comprehensive analyses.
- Engage with tribal communities to ensure that data collection and analysis are conducted in a respectful and culturally sensitive manner.
- Employ participatory mapping techniques to involve tribal members in the process, leveraging their local knowledge and expertise.
Conclusion:
Understanding the geographic distribution of American Indian reservations is crucial for addressing the complex challenges faced by these communities. The use of geographic data and mapping techniques provides valuable insights into historical patterns, current socio-economic conditions, and the ongoing need for effective resource management, infrastructure development, and policies that respect tribal sovereignty. Continued investment in data collection, analysis, and the development of collaborative partnerships between federal, state, and tribal governments is essential for promoting the well-being and self-determination of American Indian communities.
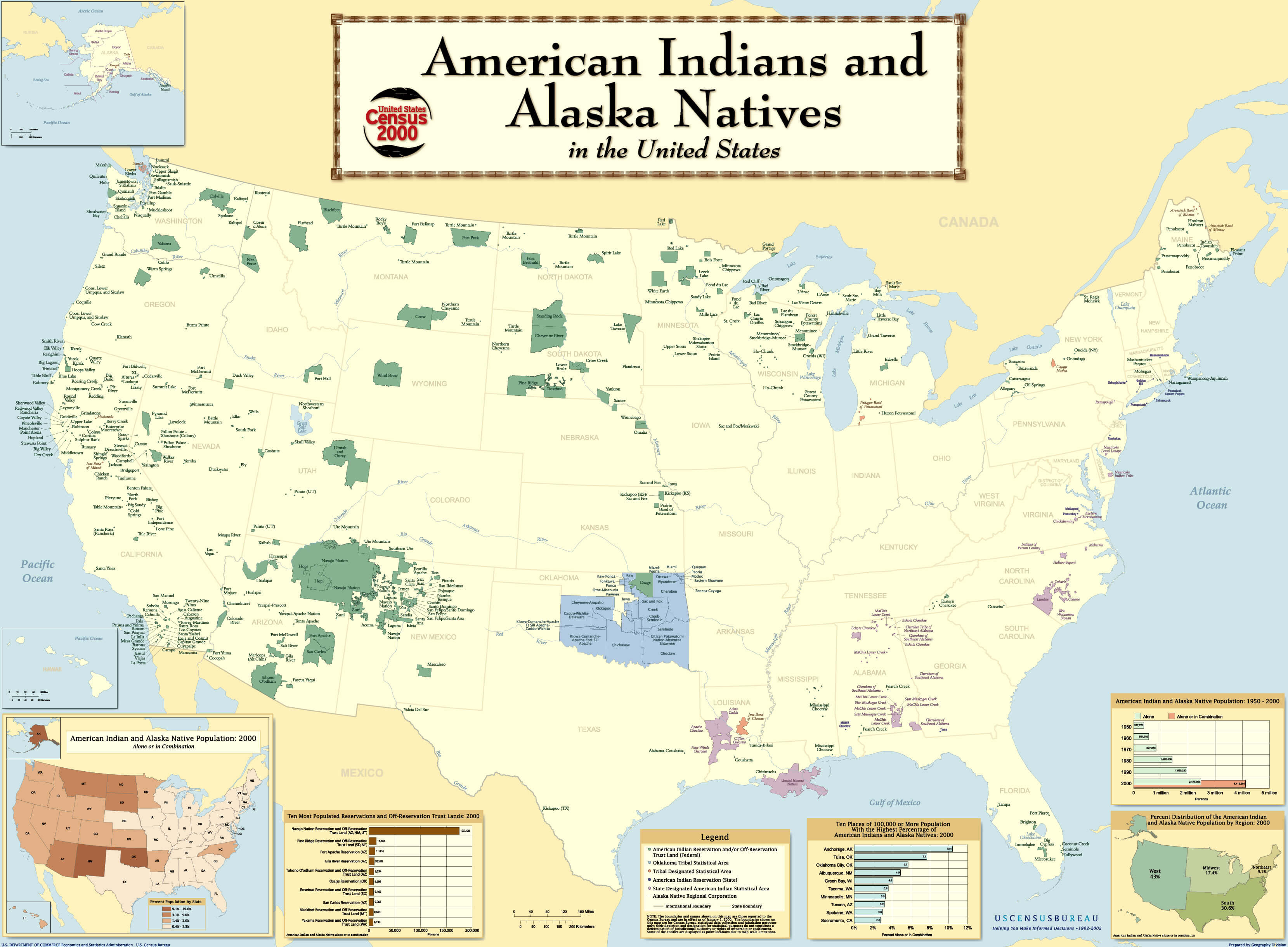






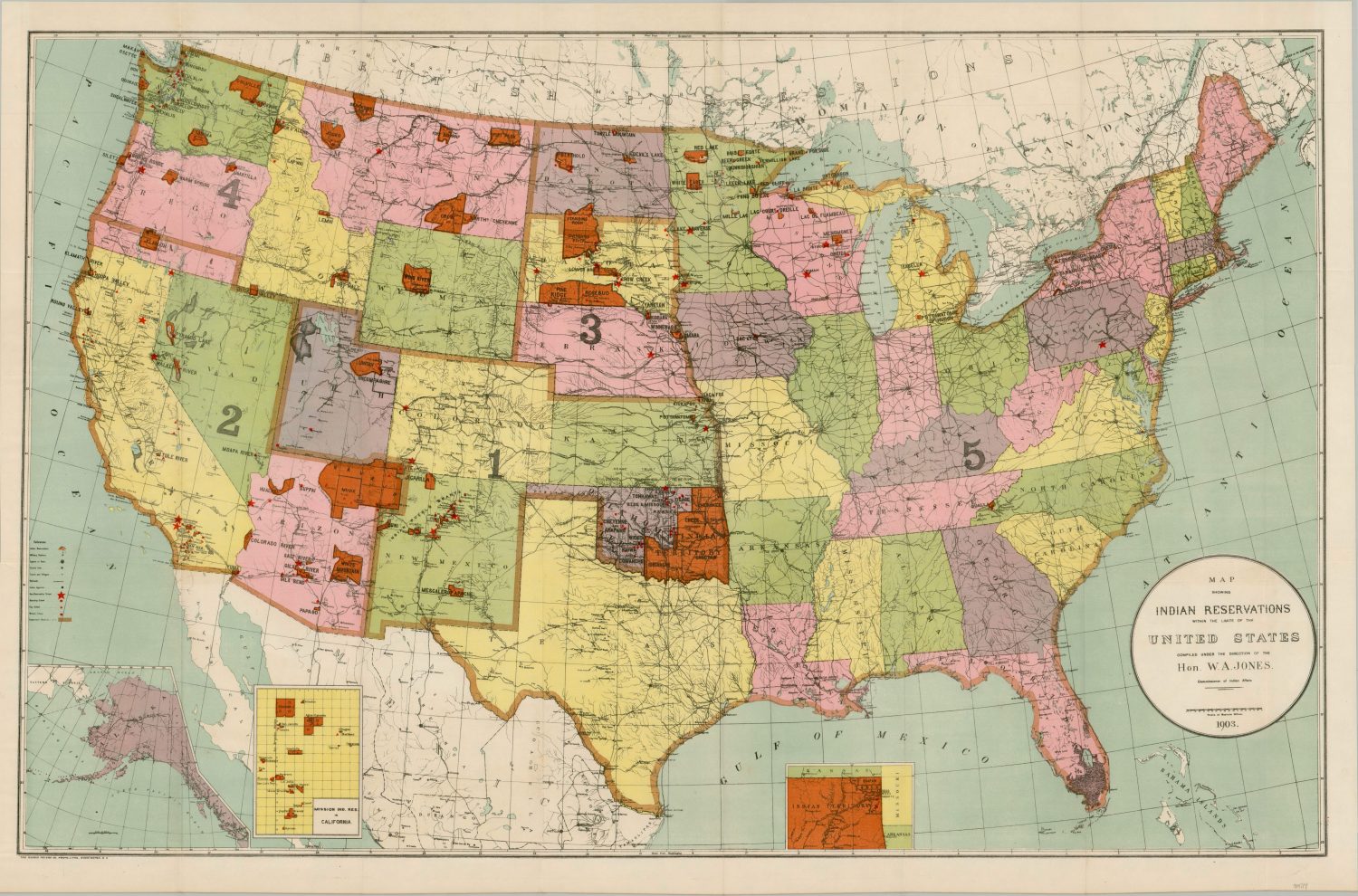
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Geographic Distribution of American Indian Reservations. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!