Deciphering the Italian Landscape: A Geographical Analysis
Related Articles: Deciphering the Italian Landscape: A Geographical Analysis
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Deciphering the Italian Landscape: A Geographical Analysis. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Deciphering the Italian Landscape: A Geographical Analysis
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/map-of-italy--150365156-59393b0d3df78c537b0d8aa6.jpg)
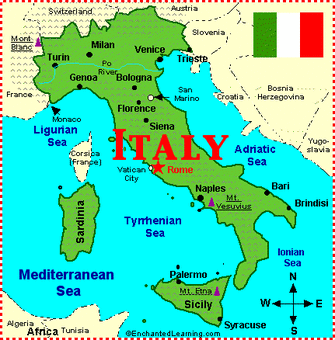
Italy’s geographical position and diverse topography have profoundly shaped its history, culture, and economy. A detailed examination of the Italian peninsula reveals a complex interplay of mountains, plains, and coastlines, contributing to regional variations in climate, agriculture, and population distribution. Understanding this spatial arrangement is crucial for comprehending the nation’s development and challenges.
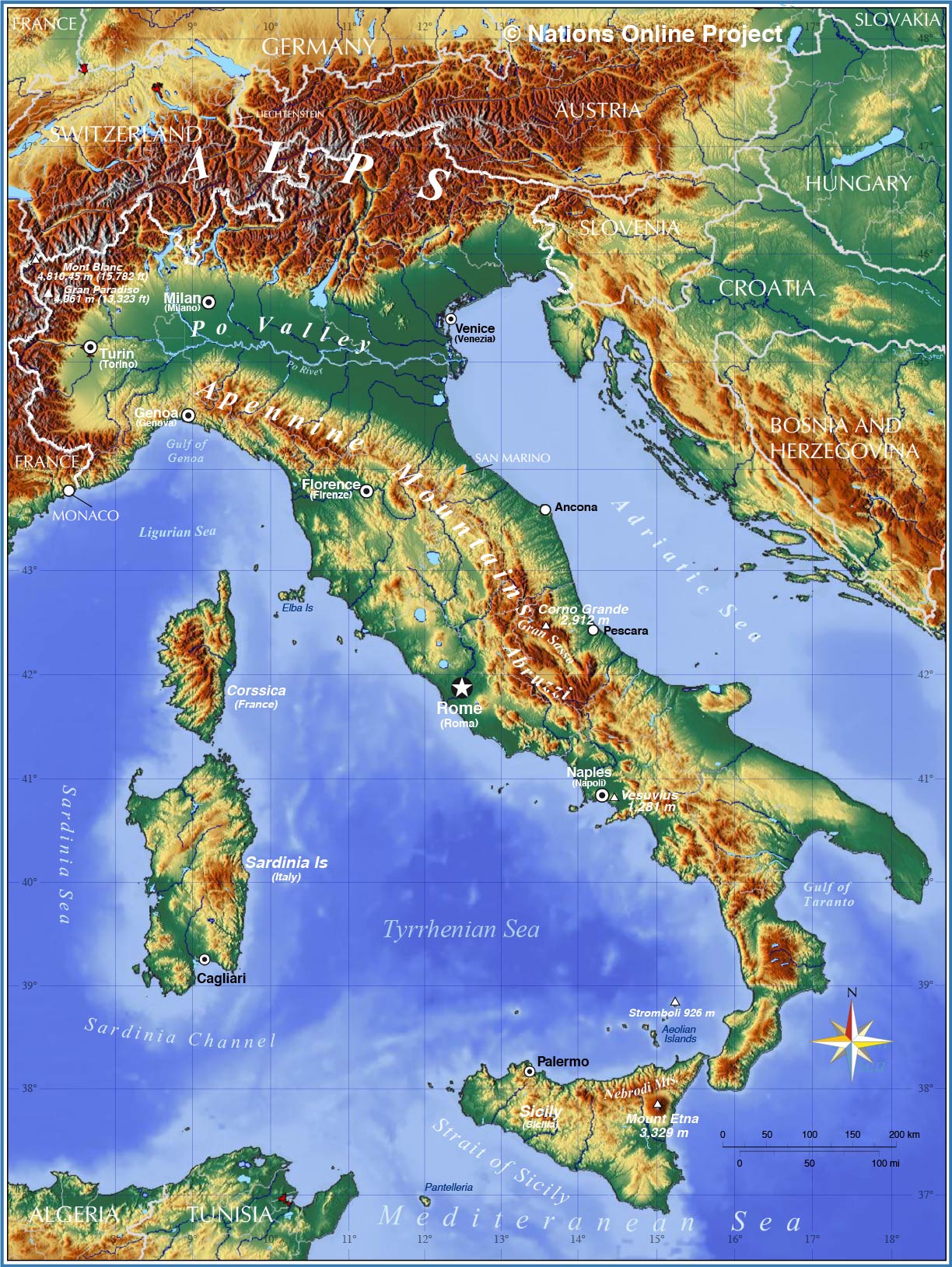
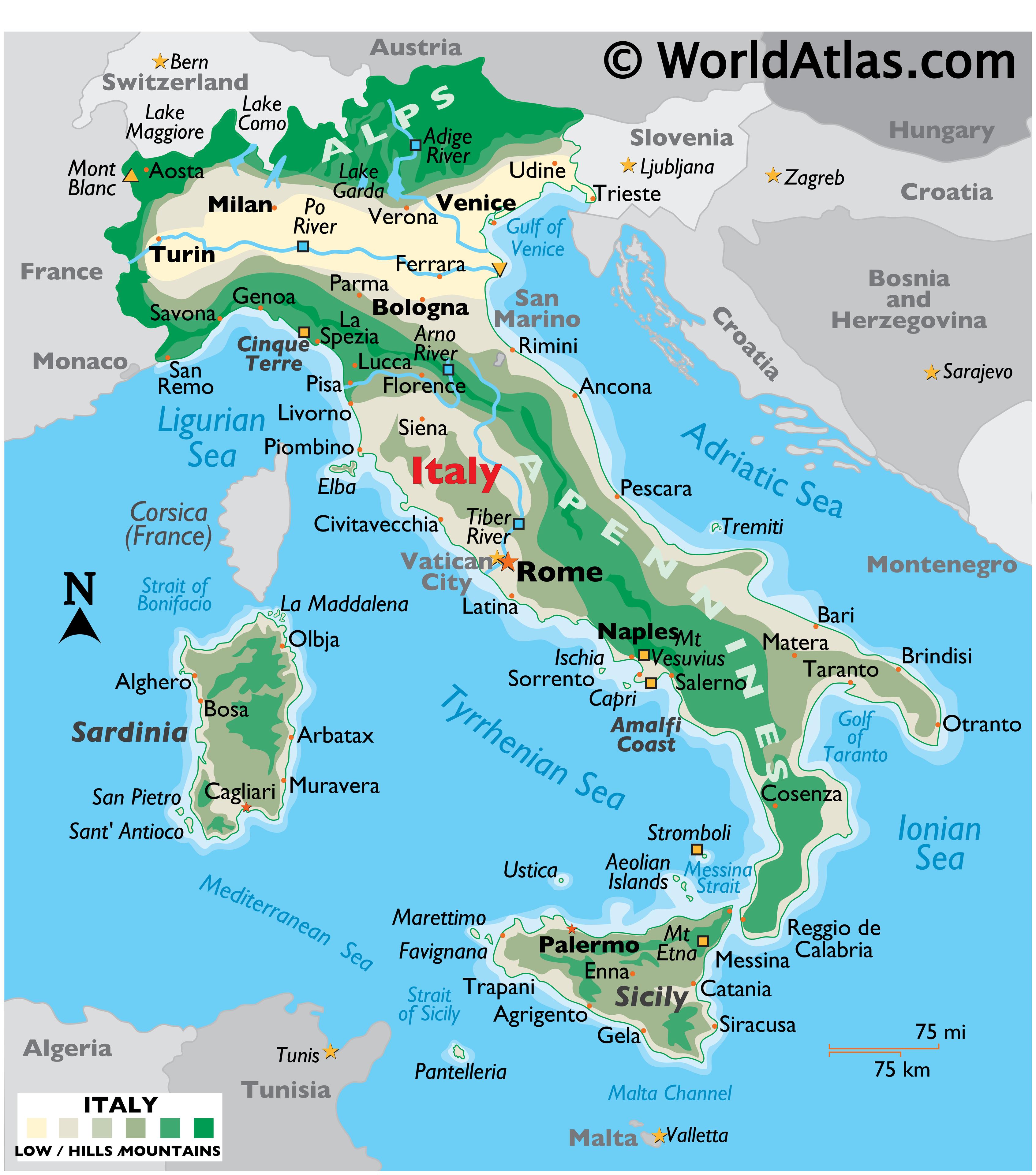
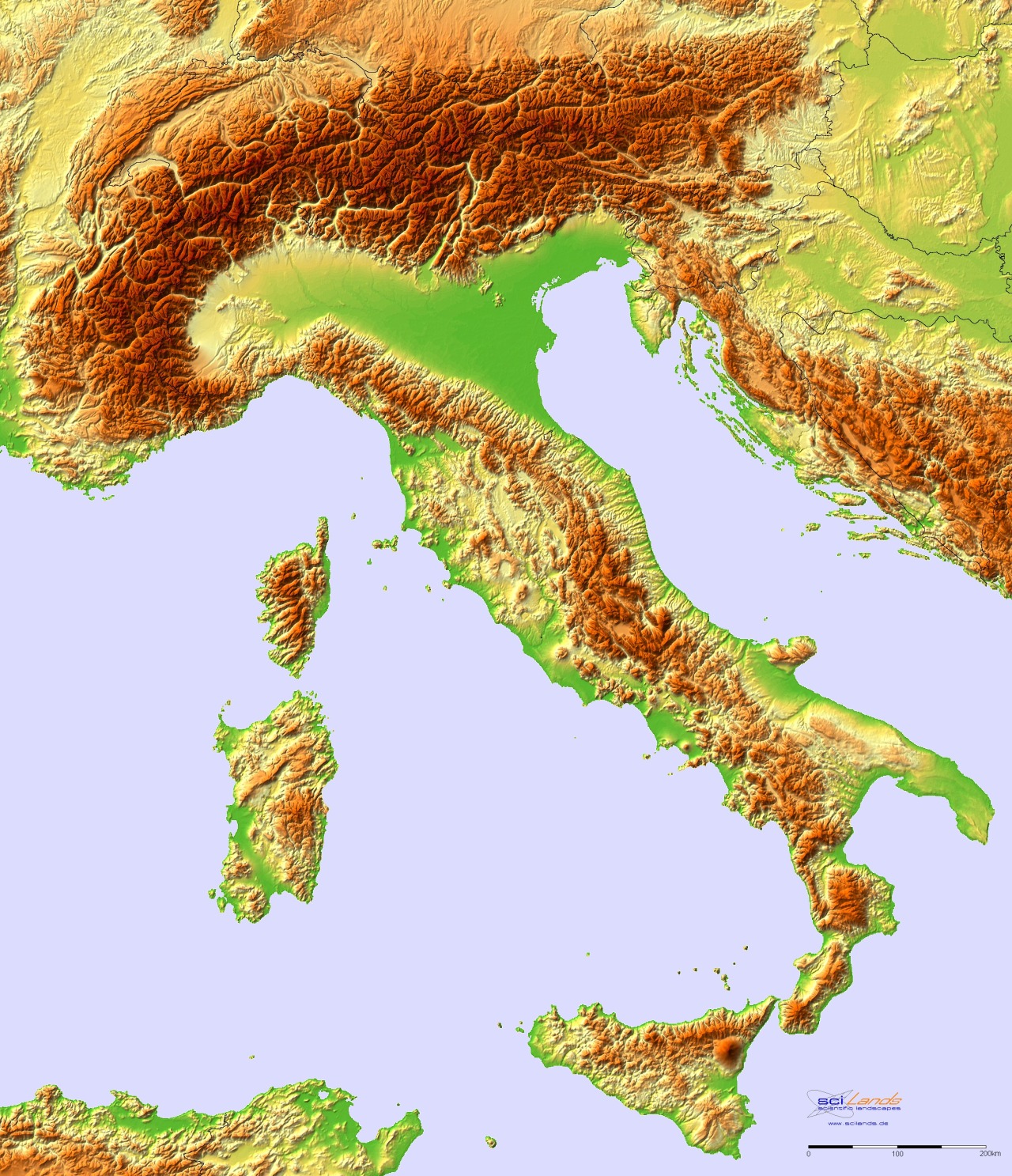
The boot-shaped peninsula dominates the country’s geography, extending southward into the Mediterranean Sea. The Apennine Mountains, a significant mountain range, form the backbone of the peninsula, running from the Alps in the north to the toe of the boot in the south. These mountains are not a single, continuous range, but rather a series of parallel ridges and valleys, creating diverse microclimates and isolating communities. Their rugged terrain has historically limited east-west communication and transportation, fostering regional identities and distinct cultural traditions.
The northern region of Italy is characterized by the Alps, a formidable mountain range shared with several European countries. These towering peaks present significant challenges to transportation and settlement, yet they also offer breathtaking scenery and valuable resources. The Po Valley, located between the Alps and the Apennines, is a fertile alluvial plain, the most extensive in Italy, and a crucial agricultural region. Its flat terrain facilitates agriculture and urban development, making it one of the most densely populated areas of the country.
The coastal regions of Italy are highly varied. The Adriatic coast, on the east, is generally straighter and less indented than the western Tyrrhenian and Ligurian coasts. The Tyrrhenian coast, bordering the Tyrrhenian Sea, is characterized by numerous bays, inlets, and volcanic features. The island of Sicily, separated from the mainland by the Strait of Messina, is a large and geographically diverse region, itself containing volcanic mountains like Mount Etna. Similarly, Sardinia, another significant island, possesses a rugged, mountainous interior and extensive coastlines. These islands contribute significantly to Italy’s maritime heritage and economic activities, including fishing and tourism.
The presence of active and dormant volcanoes significantly impacts Italy’s landscape. Mount Vesuvius, near Naples, is a famously active volcano, while Mount Etna, on Sicily, is Europe’s largest active volcano. Volcanic activity has shaped the landforms, soil composition, and even the cultural landscape of these regions, leaving a legacy of both beauty and potential hazard. The fertile volcanic soils contribute to productive agriculture, while the risk of eruptions necessitates ongoing monitoring and preparedness.
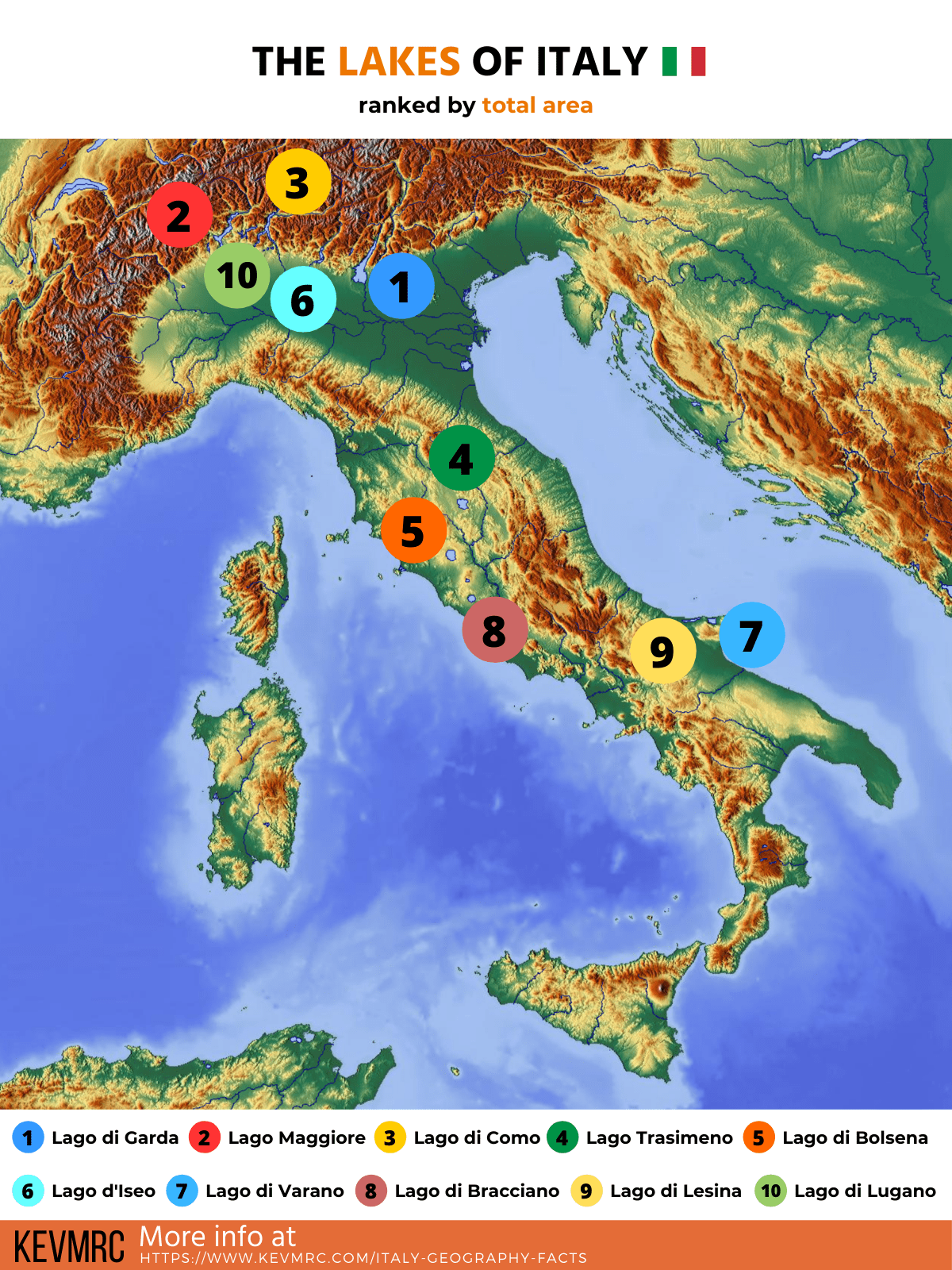
Hydrology plays a significant role in shaping the Italian landscape. The Po River, originating in the Alps, is the longest river in Italy, traversing the Po Valley before emptying into the Adriatic Sea. Numerous smaller rivers flow down the Apennines, often characterized by seasonal variations in flow. Lakes are also a prominent feature, with Lake Garda, Lake Maggiore, and Lake Como being among the largest and most well-known. These water bodies influence local climates, provide recreational opportunities, and serve as sources of hydroelectric power.
The geographical diversity of Italy has had a profound impact on its economic development. The fertile plains of the Po Valley are ideal for agriculture, producing significant quantities of grains, fruits, and vegetables. The mountainous regions have traditionally supported pastoral activities, while the coastal areas have thrived on fishing and maritime trade. Tourism, driven by the country’s diverse landscapes and rich cultural heritage, is a major contributor to the Italian economy.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What are the major mountain ranges in Italy? The Apennine Mountains and the Alps are the principal mountain ranges.
-
What is the most extensive plain in Italy? The Po Valley is the largest and most fertile plain.
-
Which are Italy’s major islands? Sicily and Sardinia are the two largest islands.
-
What is the significance of Italy’s volcanic activity? Volcanic activity has shaped the landscape, soil fertility, and poses both risks and opportunities.
-
How does Italy’s geography influence its economy? The diverse geography supports a variety of economic activities, including agriculture, tourism, and fishing.
Tips for Understanding Italy’s Geography
- Utilize detailed topographic maps to visualize the elevation changes and mountain ranges.
- Study the river systems to understand water resource distribution and potential flood risks.
- Analyze climate maps to understand regional variations in temperature and precipitation.
- Explore satellite imagery to observe the diverse landscapes and urban development patterns.
- Consider the historical context, recognizing how geography has influenced settlements and cultural development.
Conclusion
The geographical map of Italy reveals a dynamic and complex landscape. The interplay of mountains, plains, and coastlines, alongside volcanic activity and diverse hydrographic features, has created a rich tapestry of environments. This geographical diversity has shaped the country’s history, culture, economy, and continues to present both opportunities and challenges for its future development. A thorough understanding of this spatial arrangement is essential for comprehending Italy’s unique character and its place within the broader European context. Further research into specific regions and aspects of Italian geography will reveal even greater detail and nuance.
/the-geography-of-italy-4020744-CS-5c3df74a46e0fb00018a8a3a.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/val-di-funes--vilnoss--592601669-593937b53df78c537b0d6316.jpg)

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Deciphering the Italian Landscape: A Geographical Analysis. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!